Hello, aspiring ethical Hackers. This blogpost is a complete guide to Nikto vulnerability scanner. Nikto is a free command line web vulnerability scanner that scans web servers and detects over 6700 potentially dangerous files/CGIs, outdated server software, other vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. Nikto can also detect the installed software on the target web server. We will be running Nikto on Kali Linux as it is installed by default in Kali Linux. So let’s start.
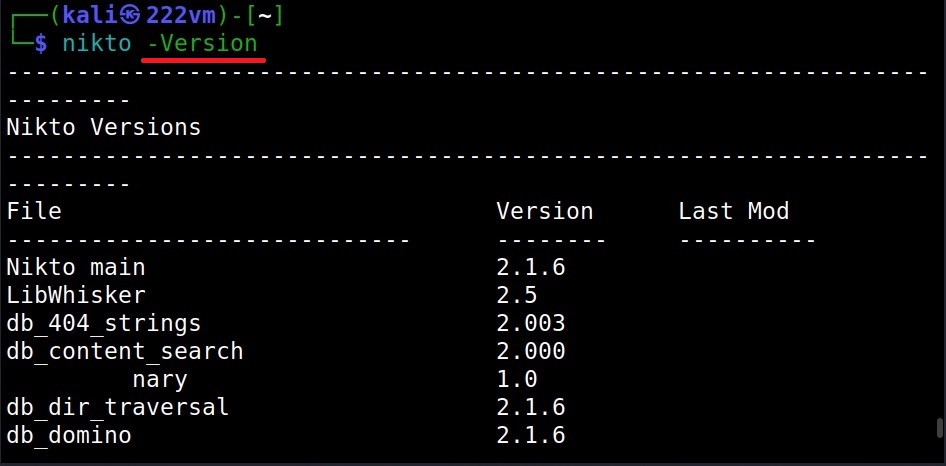
Let’s start with a version check (-Version)
The “version” option of Nikto checks for the version of the software, plugins and database versions.
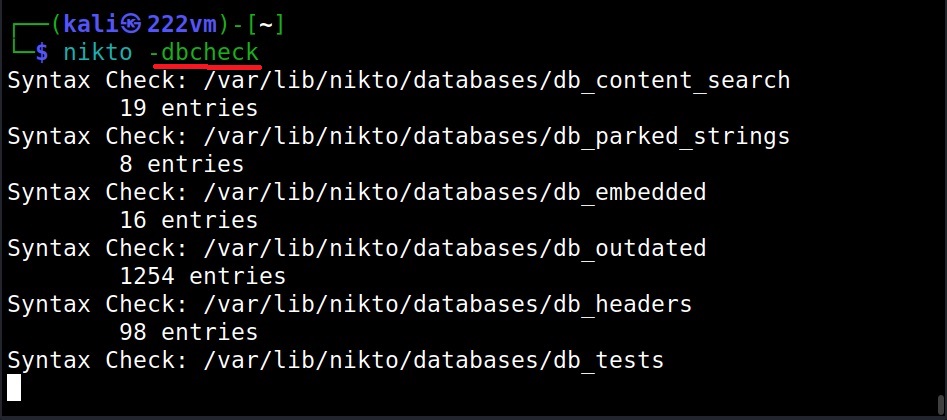
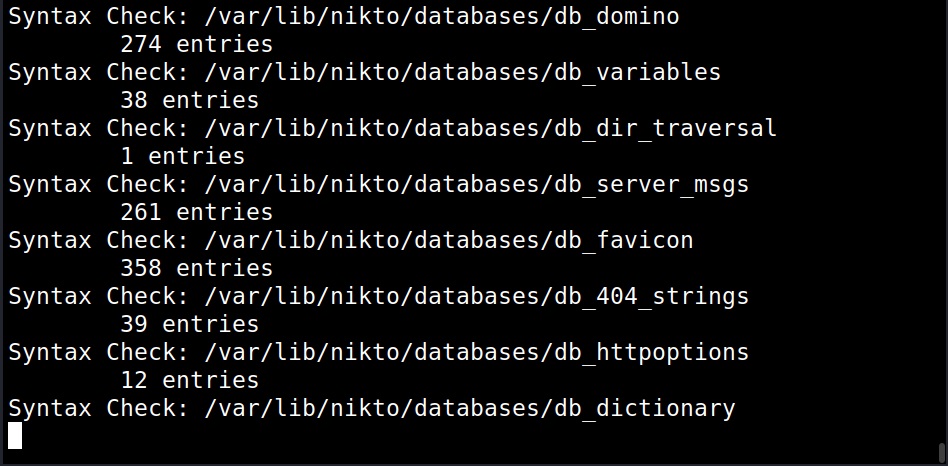
Checking Database (-dbcheck)
It’s always a good thing to check for any errors in the scan database before scanning. The “-dbcheck” option of Nikto checks the scan databases for any errors.
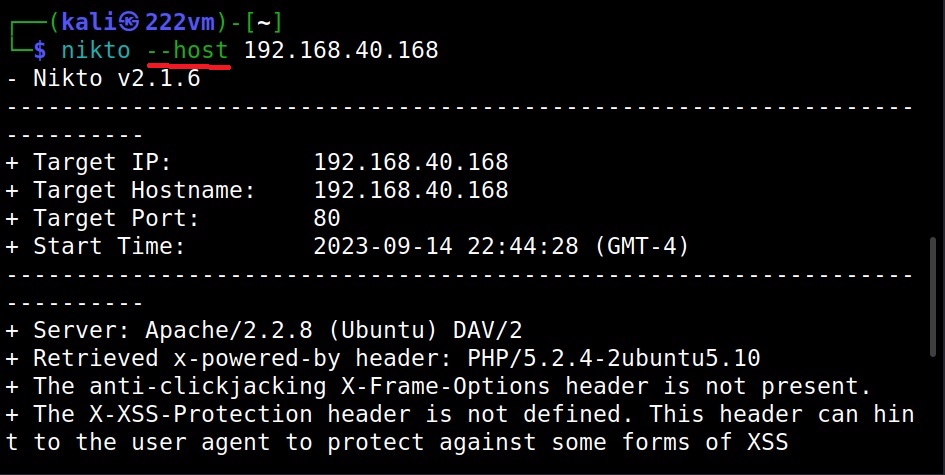
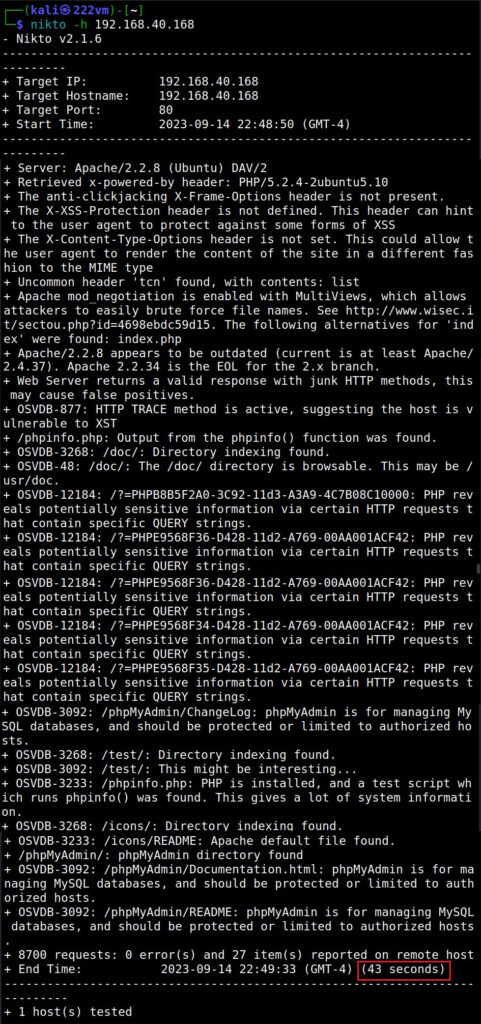
The Host option (–host) (-h)
To scan a target using Nikto, first we need to specify a target. To set the target, we need to use the “host” option. This is shown below.
The target can be IP address of the webserver or URL of the website. This scan took 45 seconds to finish.
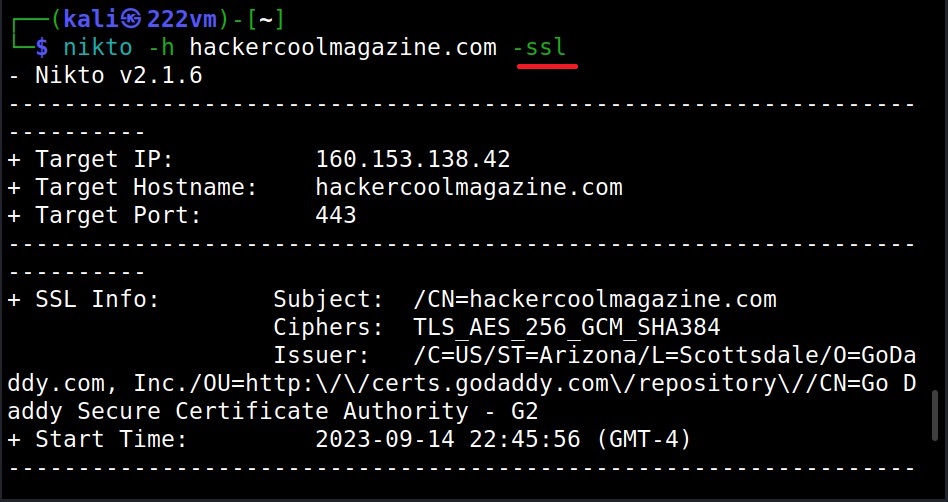
The Host option (–ssl)
To scan a website with HTTPS enabled with nikto, we can use the “SSL” option.
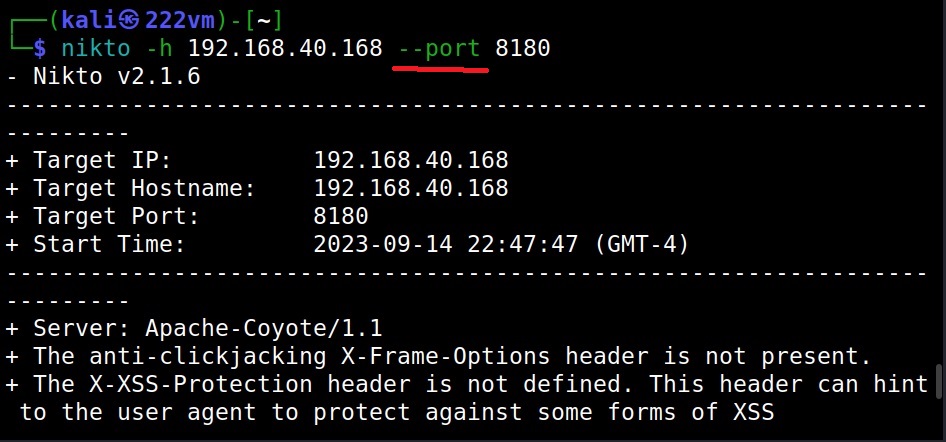
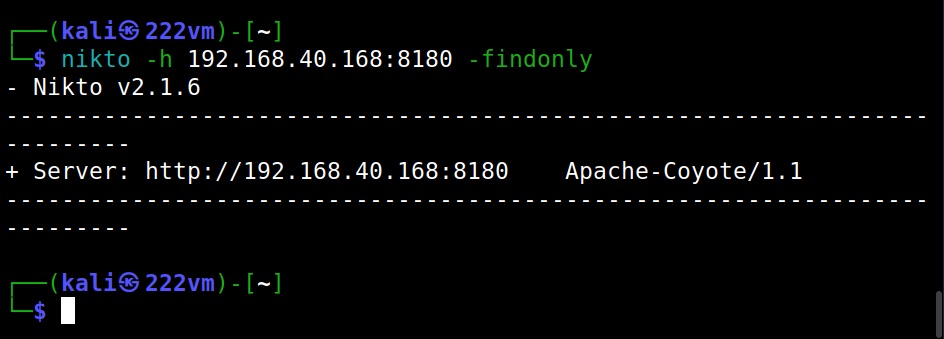
The Port option (–port)
By default, Nikto scans the default HTTP and HTTPS ports when specified. However, if the target web server is running on a custom port you can set Nikto to scan a different port by using the “port” option.
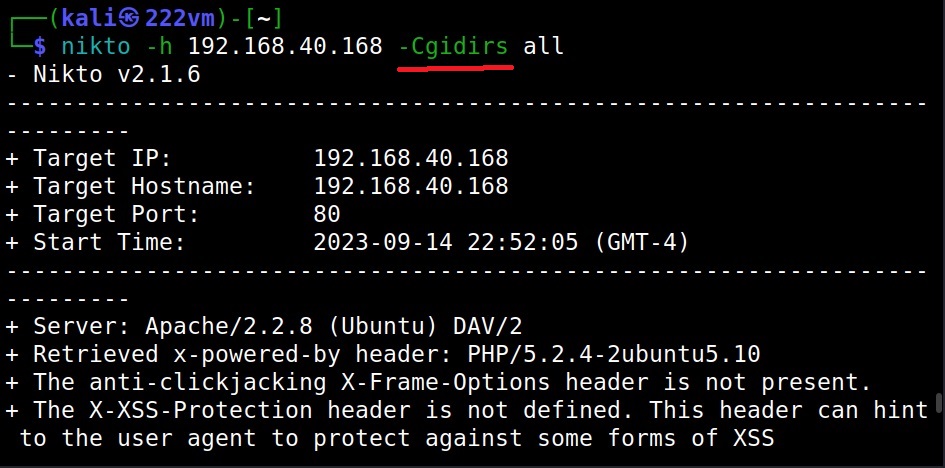
Scanning for CGI directories (–Cgidirs)
To scan for the presence of all CGI directories on the target webserver, the “cgidirs” option can be used.
You can specify a specific CGI directory to search or you can use “all” value to scan for all CGI directories on the target.
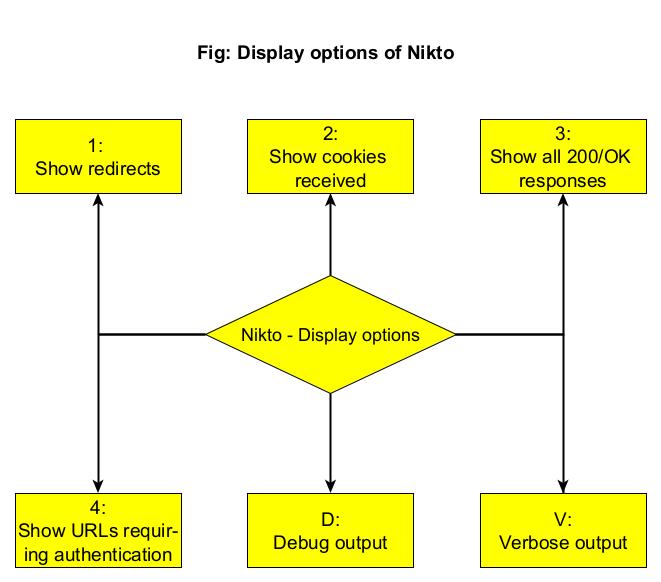
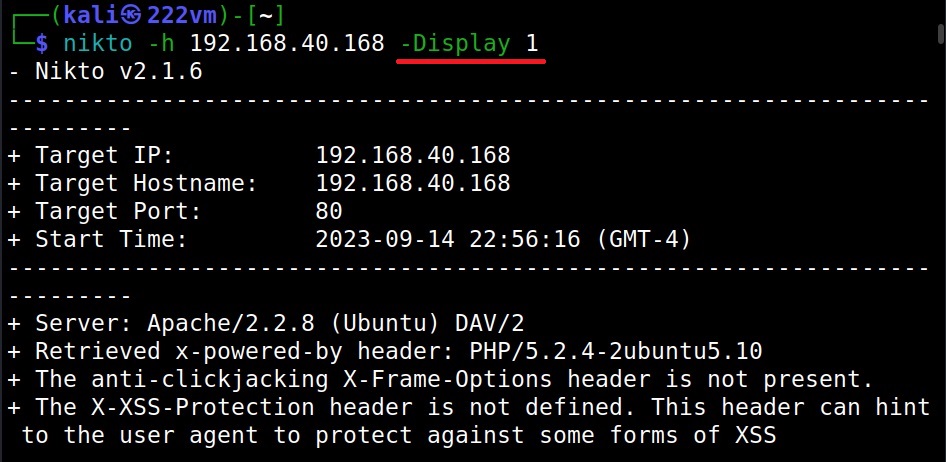
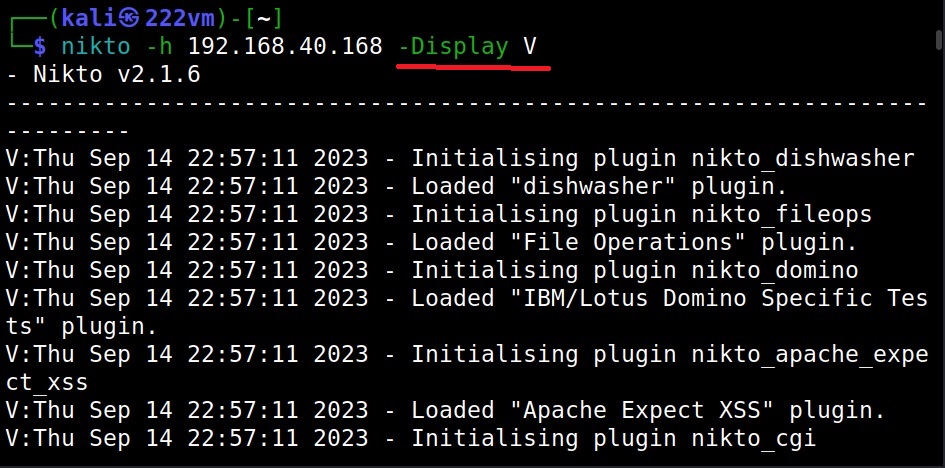
What output you want Nikto to show? (–Display)
To control the type and amount of output Nikto shows after finishing the scan, we can use the “Display” option. Here are the values that can be set for the Display option.
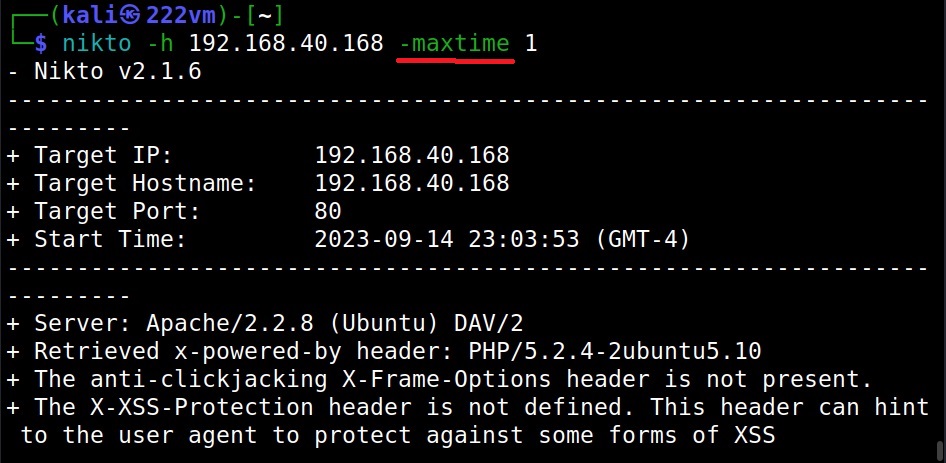
How much time you want Nikto to spend on a scan? (–maxtime)
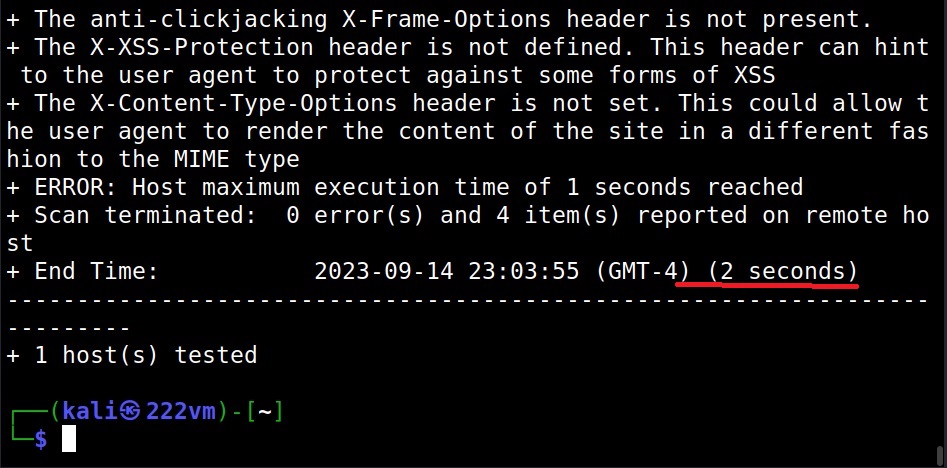
Using the “maxtime” option, we can specify the maximum time to spend for scanning a target. This time can be specified in seconds.
As you can see, the scan ended in 2 seconds while earlier the same scan took 45 seconds.
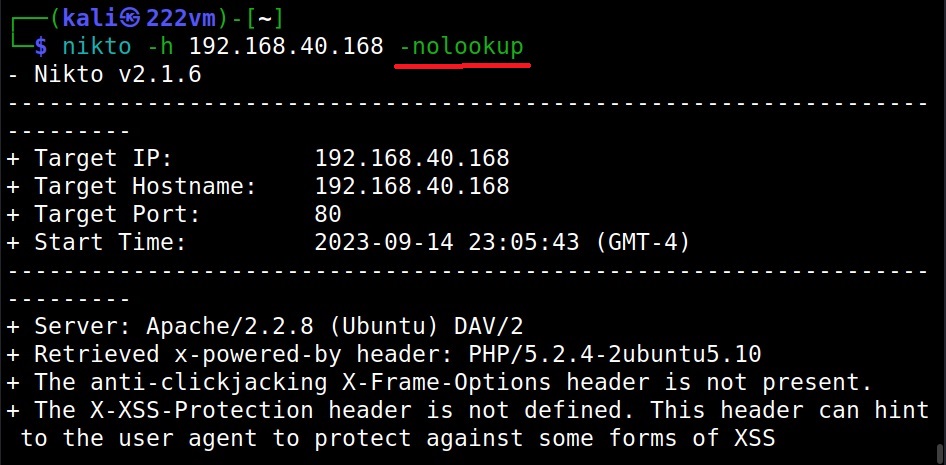
Don’t look for names (-nolookup)
The “nolookup” option specifies Nikto to not query for names when an IP address is specified.
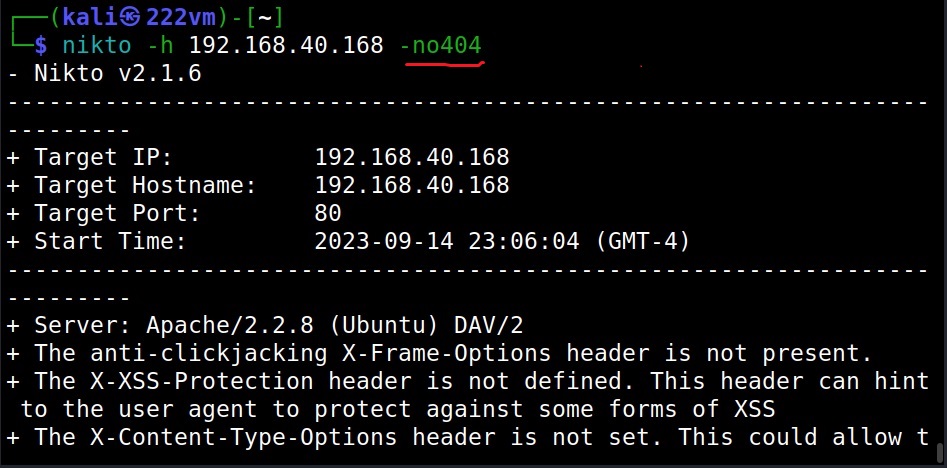
Don’t look for pages that are not there (–no404)
The “no404” option specifies Nikto to disable “file not found” checking. This will reduce the total number of requests made to the target.
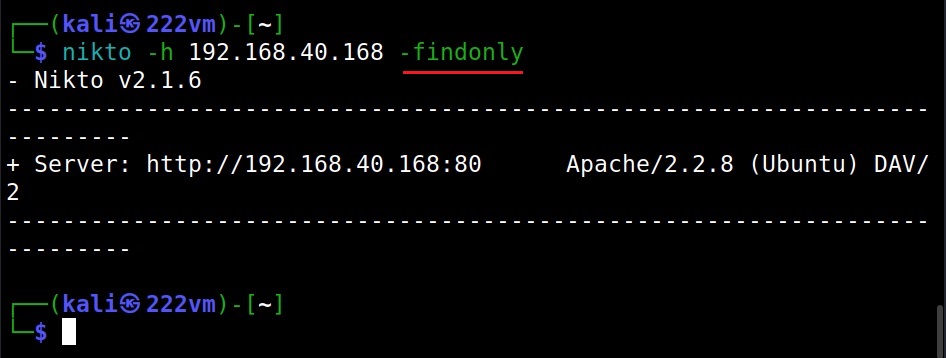
Just discover the ports (–findonly)
If you want to just find the HTTP(S) ports of a target without performing any security scan, you can use the “–findonly” option. Specifying this option allows Nikto to connect to HTTPS or HTTP ports and report the server header.
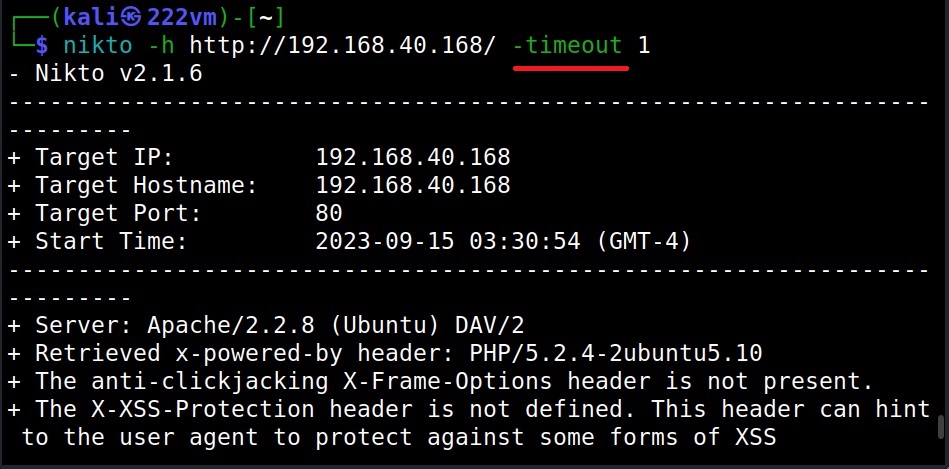
The Timeout option (–timeout)
The “–timeout” option specifies time to wait before timing out a request. The default timeout of Nikto is 10 seconds.
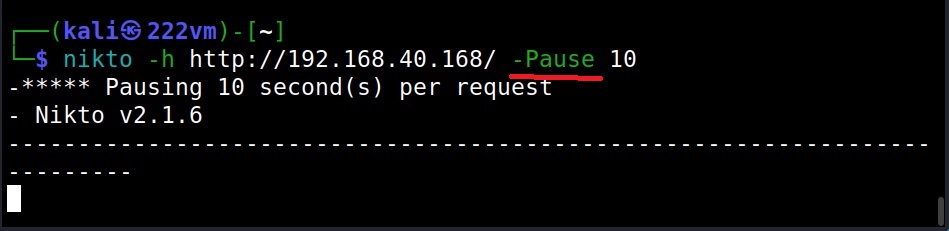
The Pause option (–Pause)
By using “–Pause” option of Nikto, we can specify delay between each test Nikto performs.
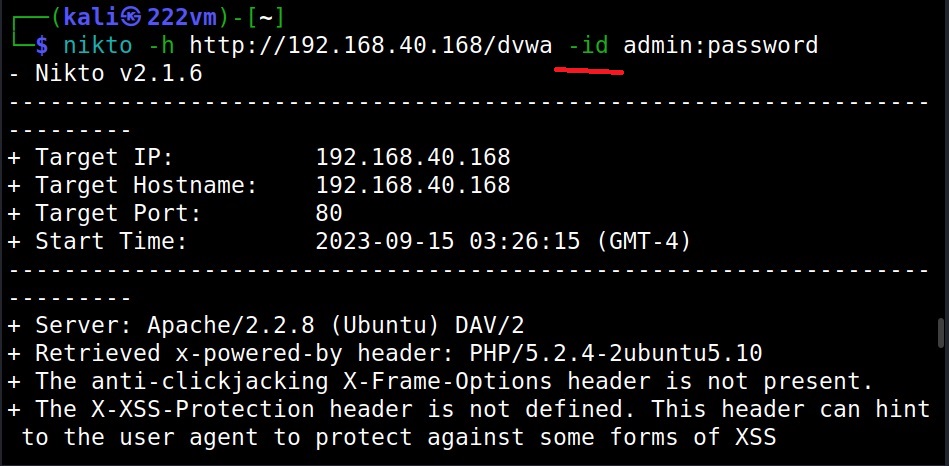
What if we have to authenticate? (–id)
With the “-id” option you can use Nikto to perform basic authentication to the target.
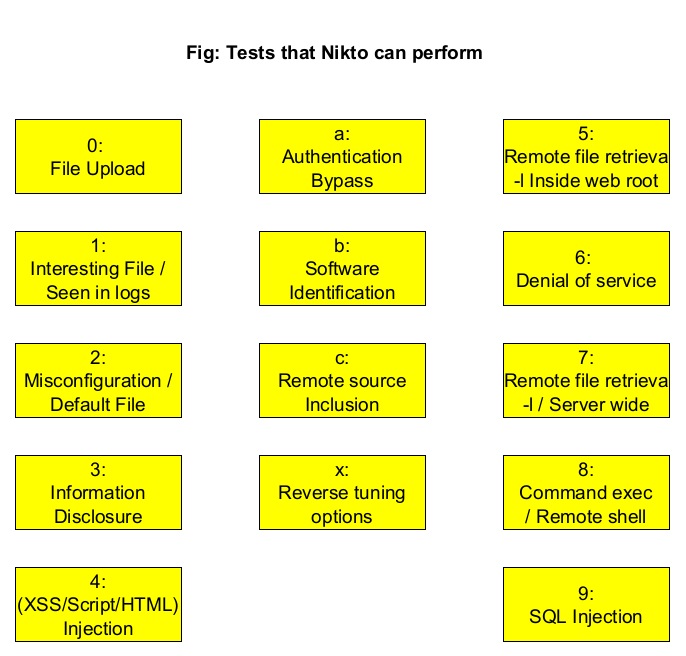
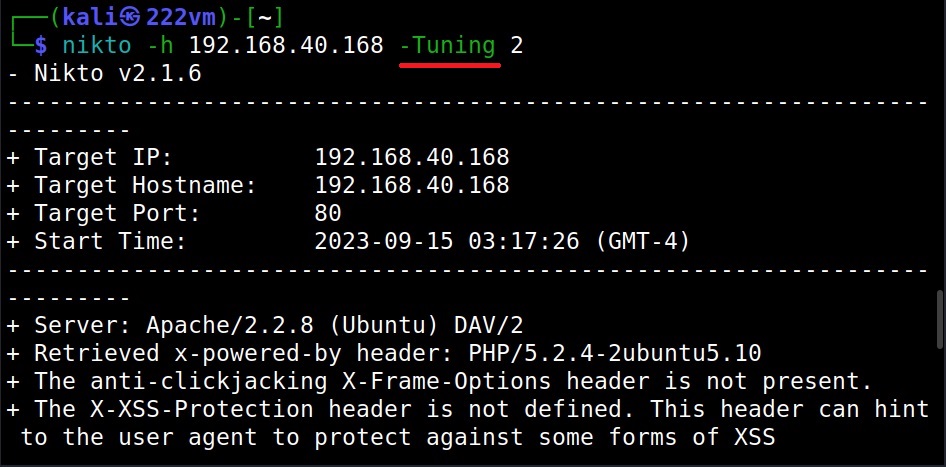
The tuning option (–tuning)
With the “-Tuning” option, we can control the test that Nikto will use against a target. It can take the following values.
For example, this is how we test for misconfigured files on the target.
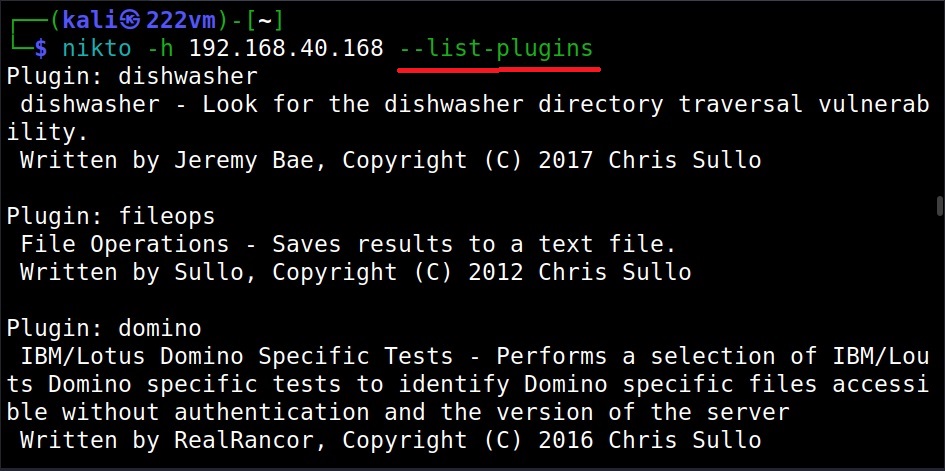
See all Nikto plugins (–list-plugins)
Nikto has lot of plugins that can be used against various targets. To view all these plugins, we can use the “–list-plugins” option.
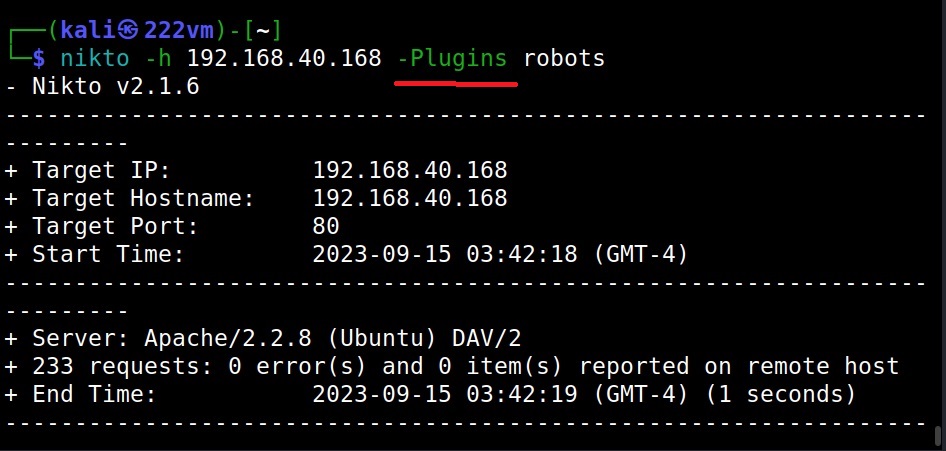
Use a particular plugin (–Plugins)
To use a particular plugin, we can use the “Plugins” option. For example, let’s use the robots plugin as shown below.
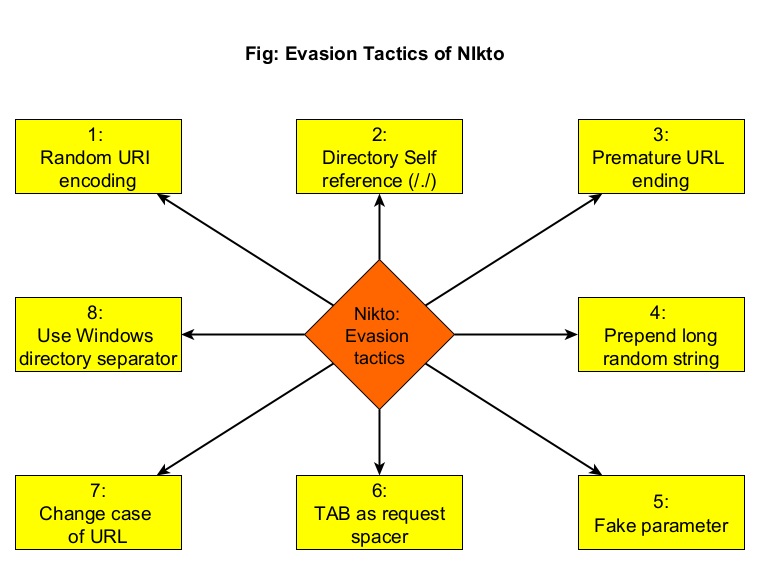
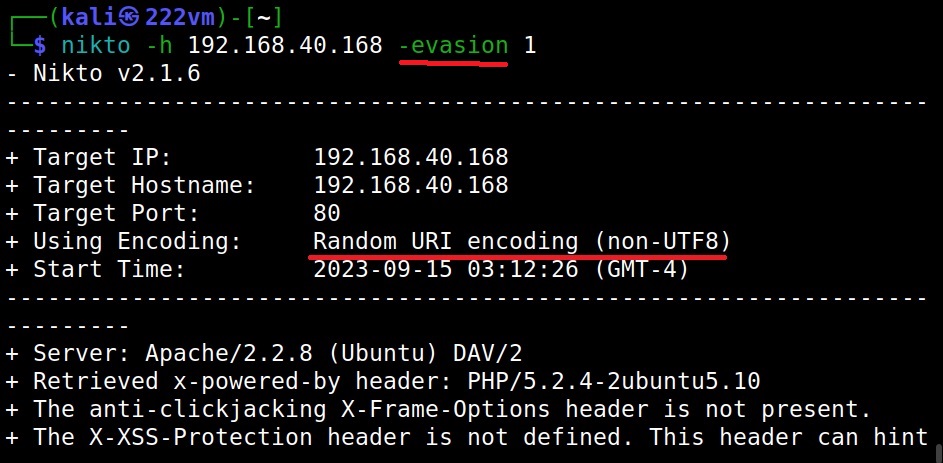
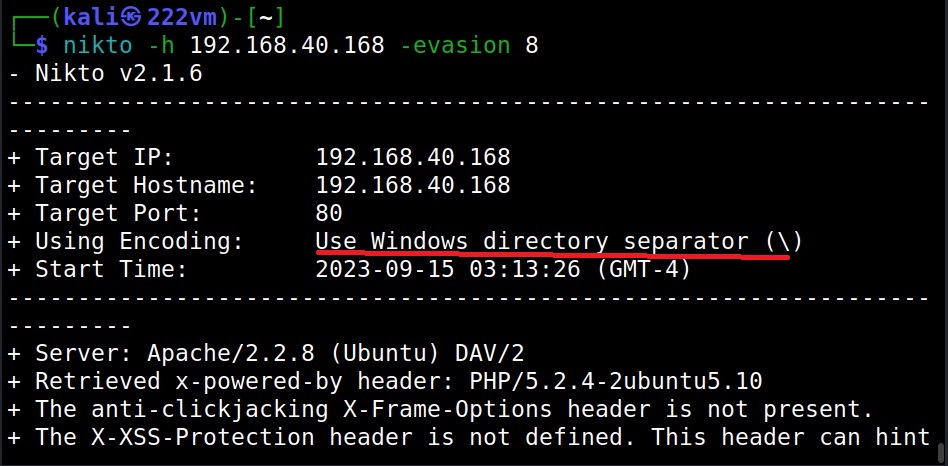
Can Nikto evade detection? (–evasion)
While scanning, Nikto can use various techniques to evade Intrusion Detection System (IDS). The evasion techniques of Nikto are given below.
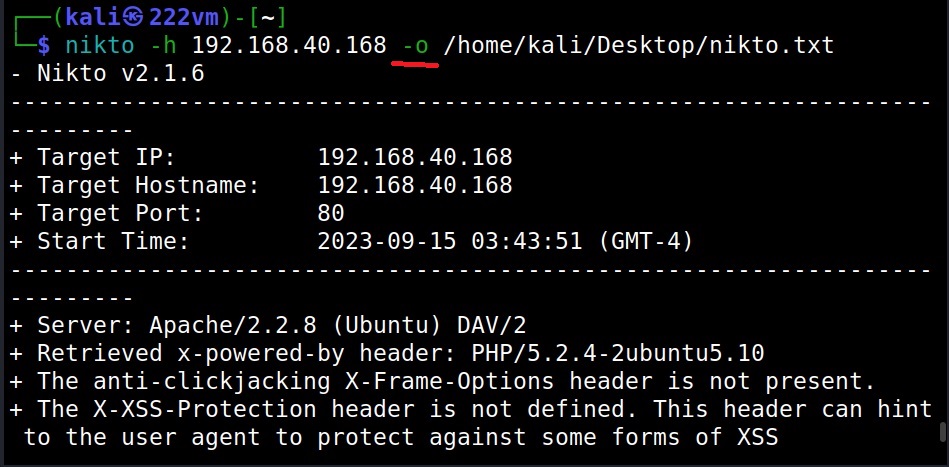
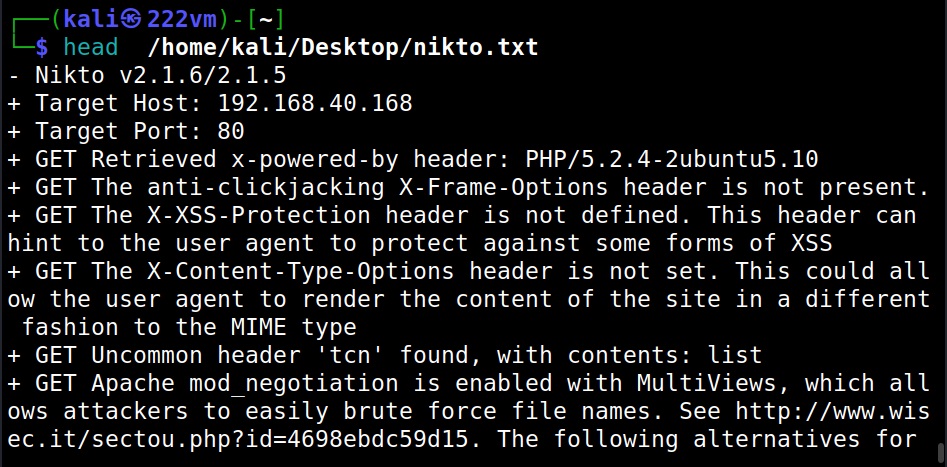
Saving output (-o)
Nikto can save the output of the scan in a file with the “output(-o)” as shown below.
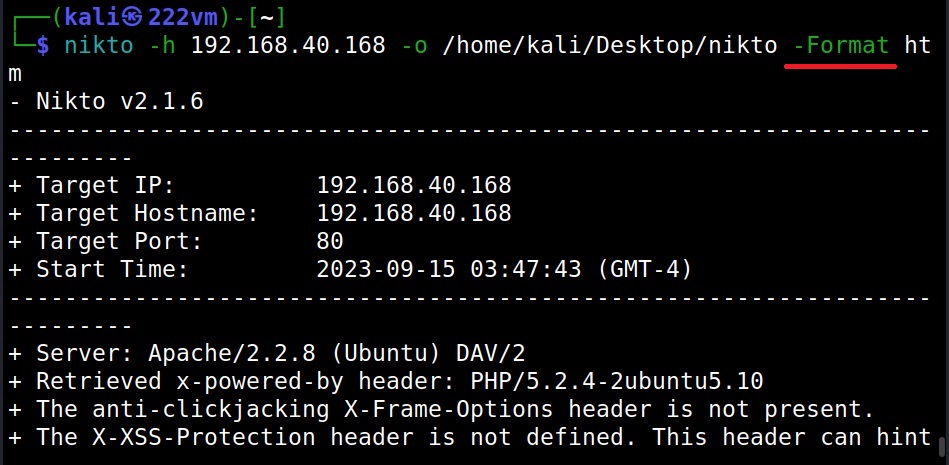
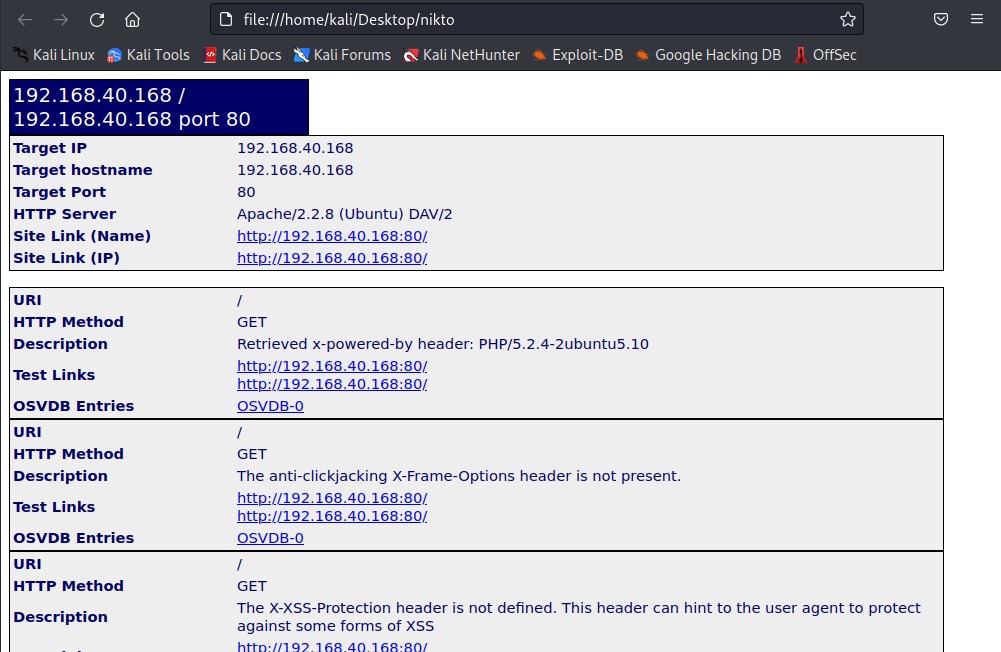
Formats in which you can save output (-Format)
You can save in different formats you like using the “-Format” option. Valid formats are csv, htm, txt and xml.
That is the complete guide for Nikto vulnerability scanner. If you have any questions bring them in the comments section.