Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about threat intelligence. In this article, you will learn about digital forensics. It plays an important role not only in investigating cyber attacks but also in solving crimes that have digital elements attached to it. This digital evidence is admissible in court proceedings. In Information security, unlike penetration testing, forensics comes after the cyber attack has already occurred.
What is digital forensics?
Digital forensics, a branch of forensic science is a process that includes identification collection, acquisition, analysis and reporting of any information or evidence from digital devices that were used as part of a crime or victims of cyber attacks.
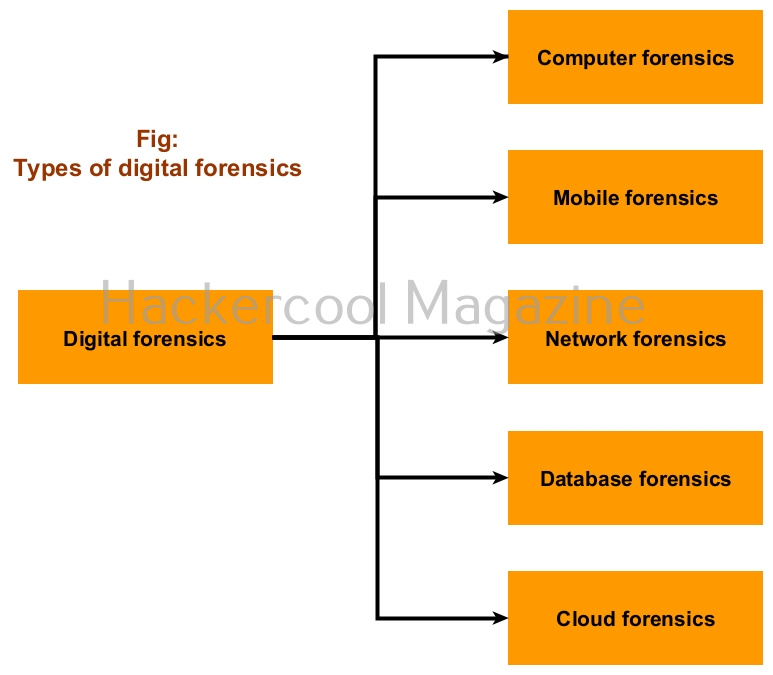
Types of digital forensics
Digital forensics has different branches. They are,
1. Computer forensics:
Also known as cyber forensics, this branch deals with collecting digital evidence from computers.
2. Mobile forensics:
As you might have guessed by now, this branch deals with collection of digital evidence from mobile devices like smart phones, tablets etc.
3. Network forensics:
This branch deals with collection and analysis of digital evidence from network traffic.
4. Database forensics:
This branch deals with analyzing databases for digital evidence.
5. Cloud forensics:
This branch deals with collecting and analyzing digital evidence from the cloud.
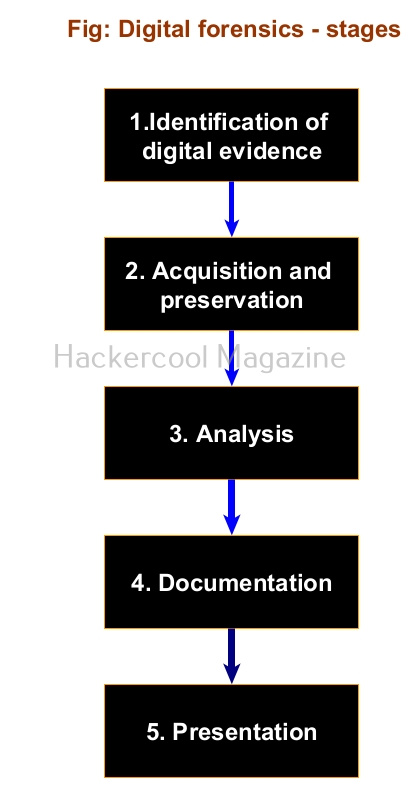
Stages of digital forensics
Digital forensics has five stages. They are,
1. Identification of digital evidence:
The first stage is identifying where the digital evidence may be present after a cyber attack or cyber incident.
2. Acquisition and preservation:
After identifying where digital evidence may be present, the next step is to collect this evidence and more importantly preserve it from being contaminated. If the evidence gets contaminated, it will not be admissible in court.
3. Analysis:
In this stage, the collected and carefully preserved digital evidence is analyzed to reconstruct the events of the cyber attack or cyber crime.
4. Documentation:
After all the evidence related to the cyber crime or cyber attack has been analyzed, the next step is documenting all the evidence in a clean manner to be presented in a court.
5. Presentation:
The last stage is presenting all the documented evidence in court or to the affected and all other stakeholders for conviction and to help courts in decision making.
Next, learn how to respond in case of a cyber incident with incident response.