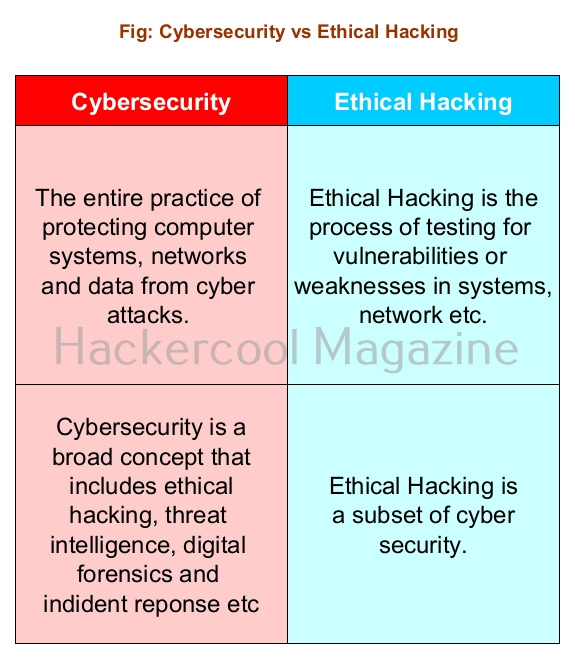
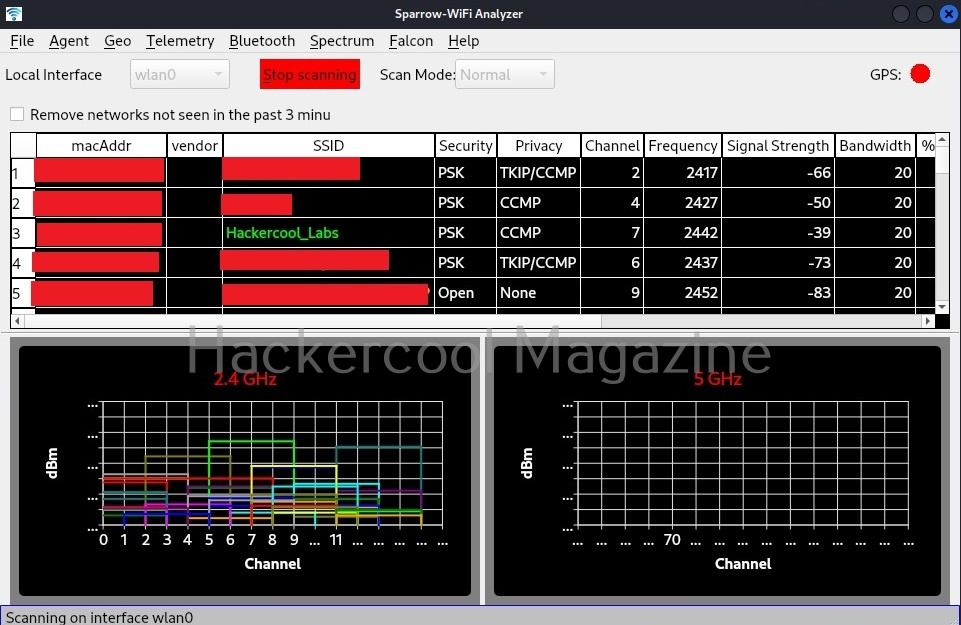
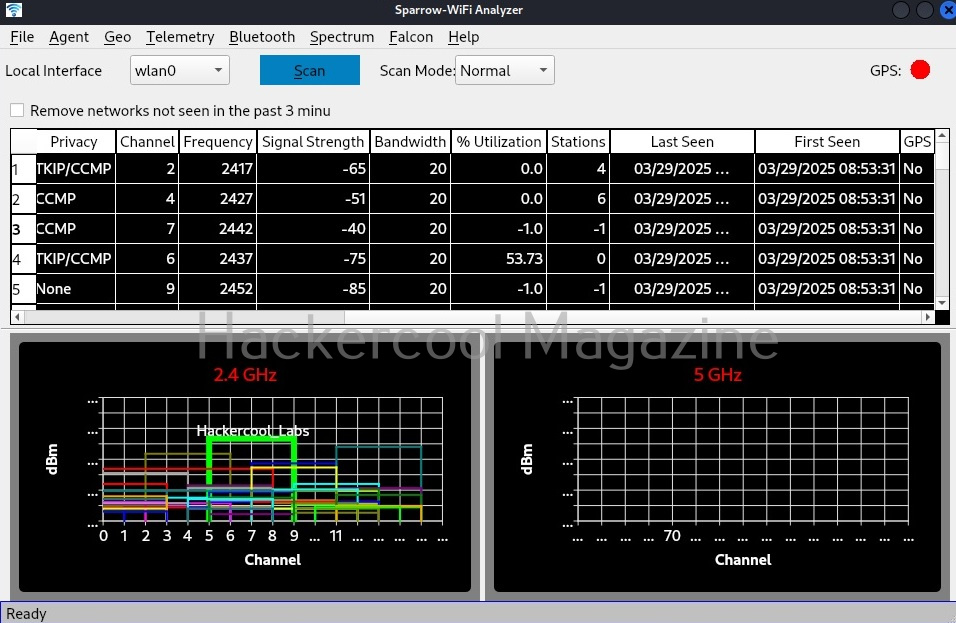
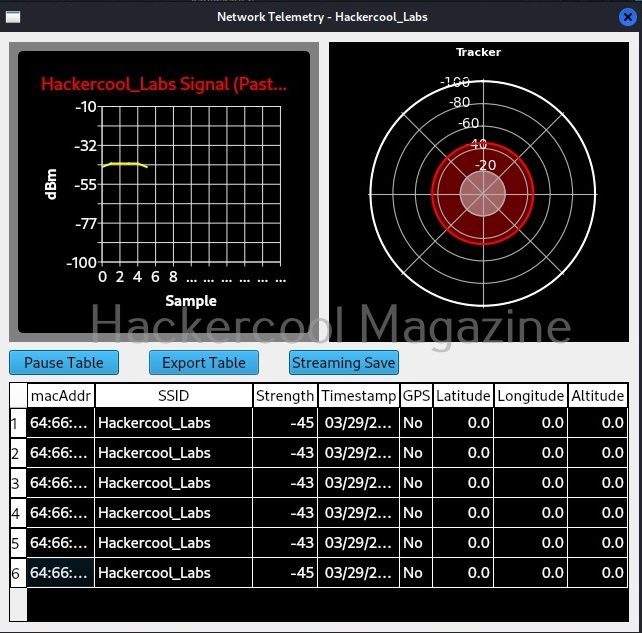
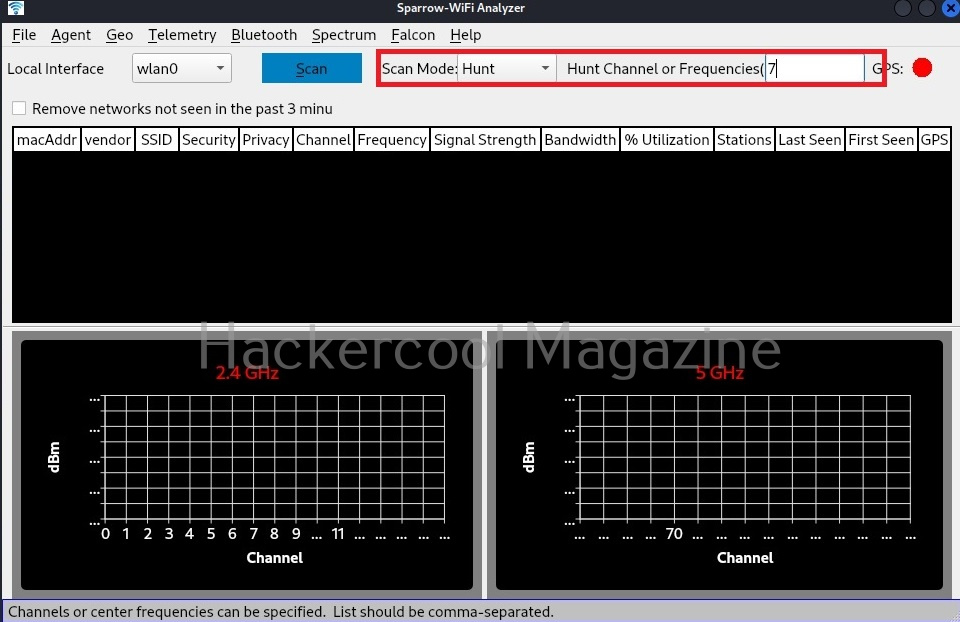
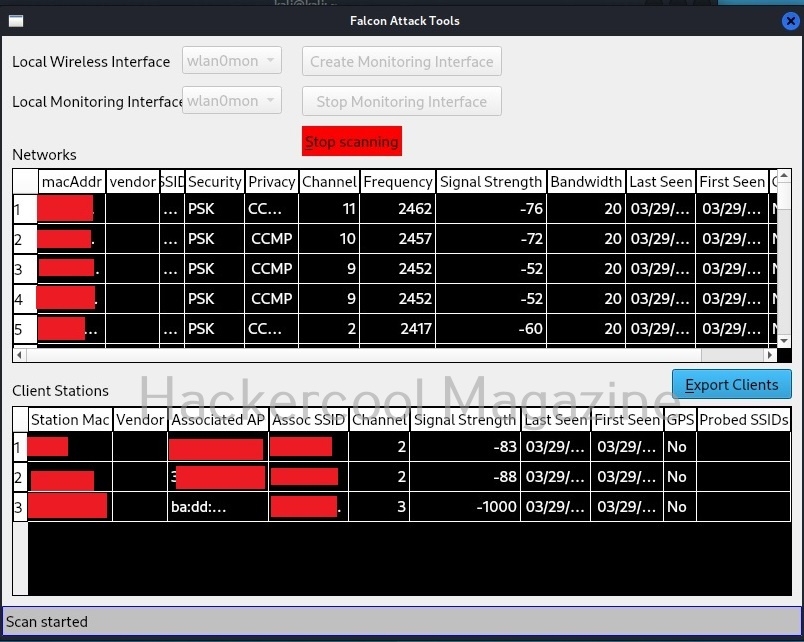
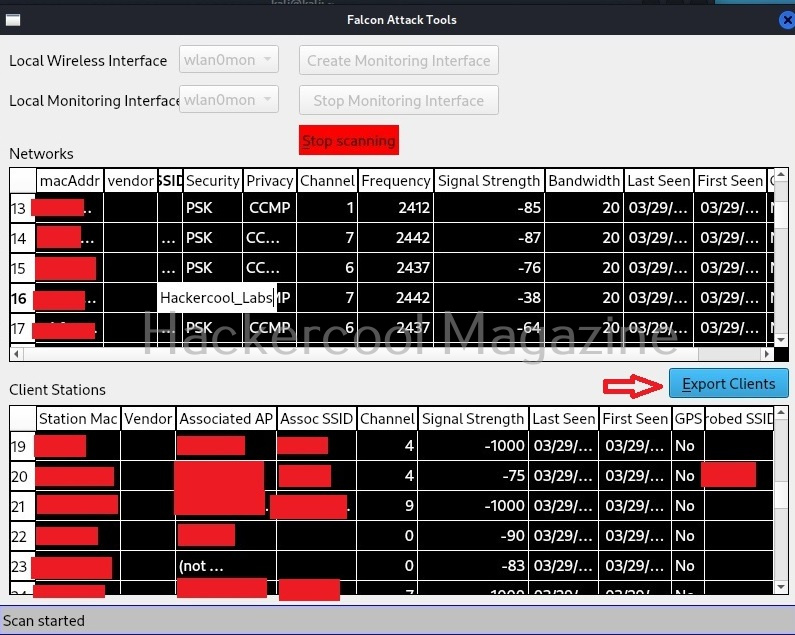
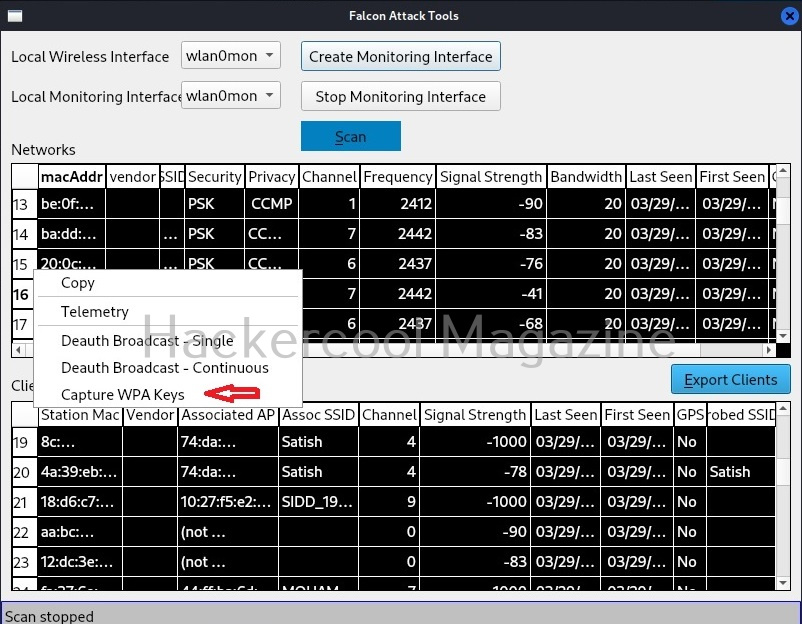
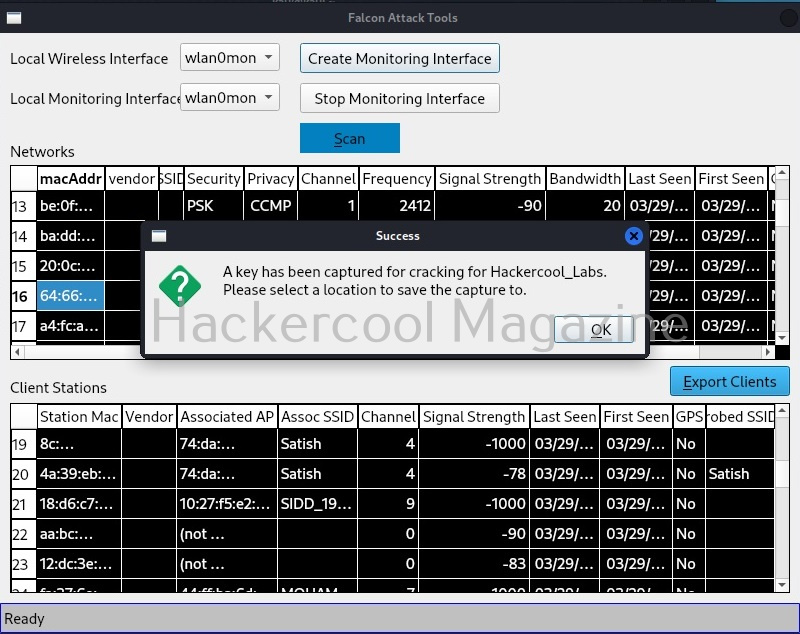
Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about about cybersecurity. In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about threat intelligence. Threat intelligence (TI) plays a very important role in enhancing cybersecurity. But first, let’s start with what actually is a threat.
What is a threat?
A threat is any action or event that can disrupt the organization’s activities. For example, these actions can be deleting the user accounts of employees of the organization, making their services unavailable to their customers etc.
What is threat intelligence?
TI is the collection, processing and analysis of data using various tools and techniques to gather meaningful information about existing and even emerging threats that can affect the security of the organization.
Why is Threat Intelligence important?
TI plays a proactive role in improving the security of the organization by understanding about emerging threats. It helps us to identify, prepare and prevent cyber attacks by providing information about the attacker, their motive and capabilities. A thorough understanding about the vulnerabilities, attacker motives and techniques allows us to prevent and mitigate cyberattacks.
Types of threat intelligence
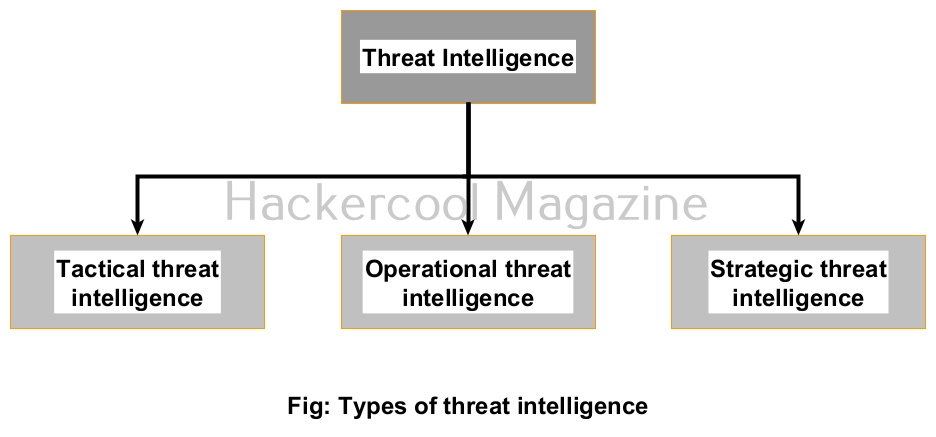
There are three types of intelligence for threats. They are,
- Tactical TI
- Operation TI
- Strategic TI
Let’s learn about each of them in detail.
1. Tactical threat intelligence (TTI):
As you can guess by its name, this type of intelligence identifies information like Indicators Of Compromise (IOC), other information such as IP addresses of listeners and Command & Control (C&C) servers, email subject lines etc.
This information is useful to Security Operation Center’s (SOC’s) to predict and detect future attacks correctly. It is also helpful in incident response, threat hunting and malware analysis.
2. Operational threat intelligence (OTI):
This type of intelligence focusses on understanding target adversary’s strengths and capabilities, their attack infrastructure, TTPs, etc. This information helps us to identify threat actors and APTs that are more likely to attack a particular organization. Obviously, it is more broader in scope than tactical intelligence. After gathering this intel, cybersecurity professionals of an organization can then determine security controls and mitigations to prevent that attacks.
3. Strategic threat intelligence (STI):
This type of intelligence focuses on understanding high level trends like global threat landscapes and the position of an organization inside that threat landscapes. It is less technical and more theoretical and mainly for executive level security professionals like CISO, CIO, CTO etc.
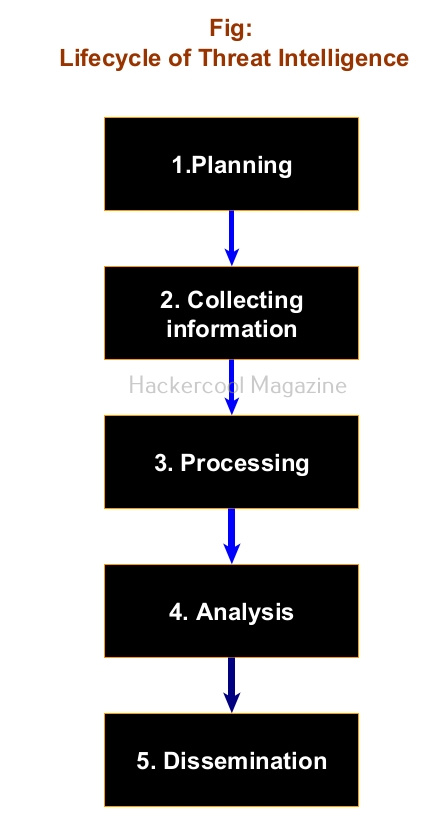
Threat intelligence Life cycle
The TI lifecycle is a continuous process and consists of five stages. They are,
1. Planning:
Before any organization even starts collecting data for TI, it should have a proper threat intelligence plan. This plan should include information about what intel an organization needs to collect to protect its sensitive resources.
2. Collection:
After preparing a TI plan, the next step is to collect new threat data. The data can be collected from systems in local network using tools like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), EDR, XDR, ASM etc and also from sources like underground hacker forums, dark web, open source and commercial threat intelligence feeds and InfoSec community.
3. Processing:
Next, all the collected data is aggregated, standardized and corrected to make analysis of the data easier. Note that all the threat data collected doesn’t have the information we want. There may be false positives ,errors and even irrelevant data.
4. Analysis:
It is at this stage that the raw threat data becomes actual threat intelligence. Here the insights needed to meet TI requirements are extracted and then the next steps are planned.
5. Dissemination:
The threat intel team shows all the insights and recommendations to appropriate stakeholders to plan the next course of action.