Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about ethical hacking. In this article, you will learn what is cybersecurity. Cybersecurity and ethical hacking can be confusing to people. That’s because they are closely related but yet they are different. But don’t worry by the end of this article, you will understand clearly the difference between them.
What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the name give to the complete process of protecting computer systems, network and data from cyber attacks and malware.
Importance of cybersecurity
Now, that you have understood what cybersecurity is, let me explain to you it’s importance. As the world moves more towards digitization, humans increasingly depend on technology and internet. With the difficulty of performing a hacking attack becoming simple day-by-day and threat actors and cybercriminals increasingly evolving their tactics, the role of cybersecurity has become all too important not only for organizations but also individuals.
Principles of Cybersecurity
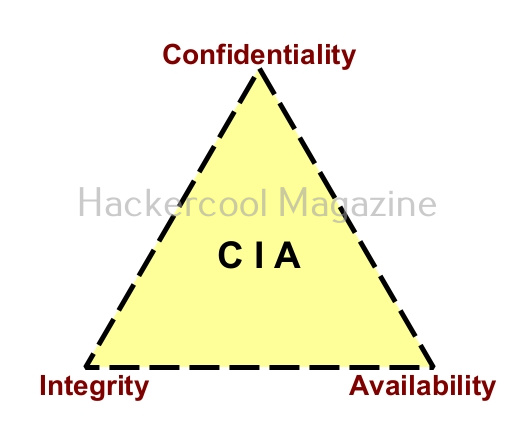
There are three core principles for cybersecurity. Popularly known as CIA triangle, they are Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. Let’s learn about each of them in detail.
1.Confidentiality:
Confidentiality ensures that all the sensitive information is safe from unauthorized access.
2. Integrity:
Integrity ensures that the sensitive information is safe from destruction without proper authorization.
3. Availability:
Availability ensures that the information is available to authorized users whenever they need them.
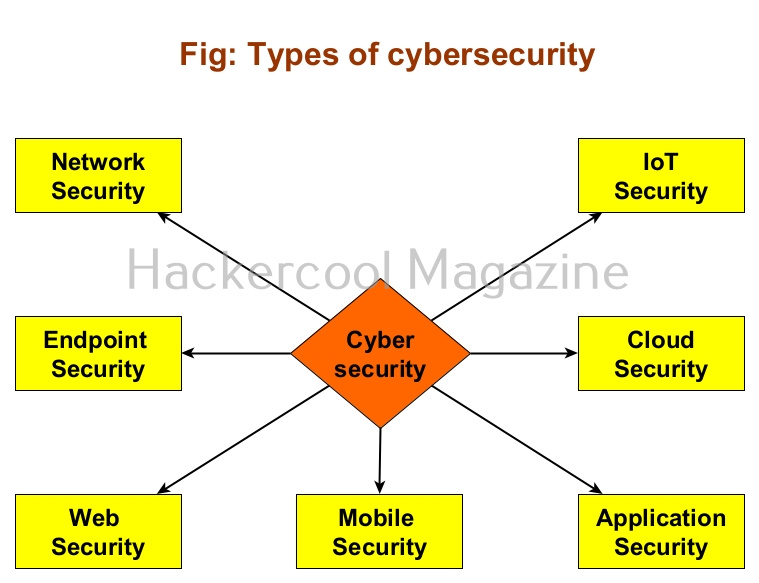
Types of Cybersecurity
Although cybersecurity is a single word, it is a combination of different branches. Let’s learn about each of them in detail.
1.Network security:
Network security refers to protection of the network infrastructure both software and hardware, communication infrastructure, communication protocols etc. This includes all the devices in a network, communication between them and even between them and external assets.
2.Endpoint security:
Endpoint security deals with security of the endpoint devices in the network. These include Desktops, Laptops and other devices that act as access point to an organization’s network.
3. Web security:
This refers to protection of websites, web applications and the infrastructure coming with it.
4. Mobile security:
Mobile security is concerned with security of the mobile devices like mobiles and tablets which are increasingly being used in organizations.
5. Application security
Application security deals with protection of all the applications used in organization.
6. Cloud security:
Cloud security refers to protecting of data, applications and services hosted in private and public cloud environment.
7. IoT Security:
IOT security refers to protection of Internet Of Things (IOT) devices and networks from cyber attack and data breaches.
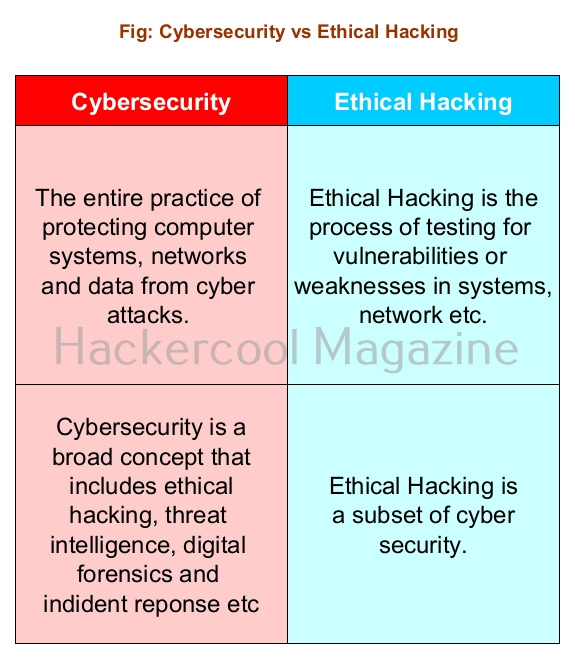
Cybersecurity vs Ethical hacking
By now you should have clearly understood what cyber security is. Let’s see what is the difference between cybersecurity and ethical hacking. Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing is a method used to identify security vulnerabilities in a network, software, applications etc by simulating hacking attacks. This is done to assess the security of an organization. Ethical hacking is part of cybersecurity.