Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt about malware and virus. In this blogpost, you will about Antivirus. But what is an Antivirus.
What is an Antivirus?
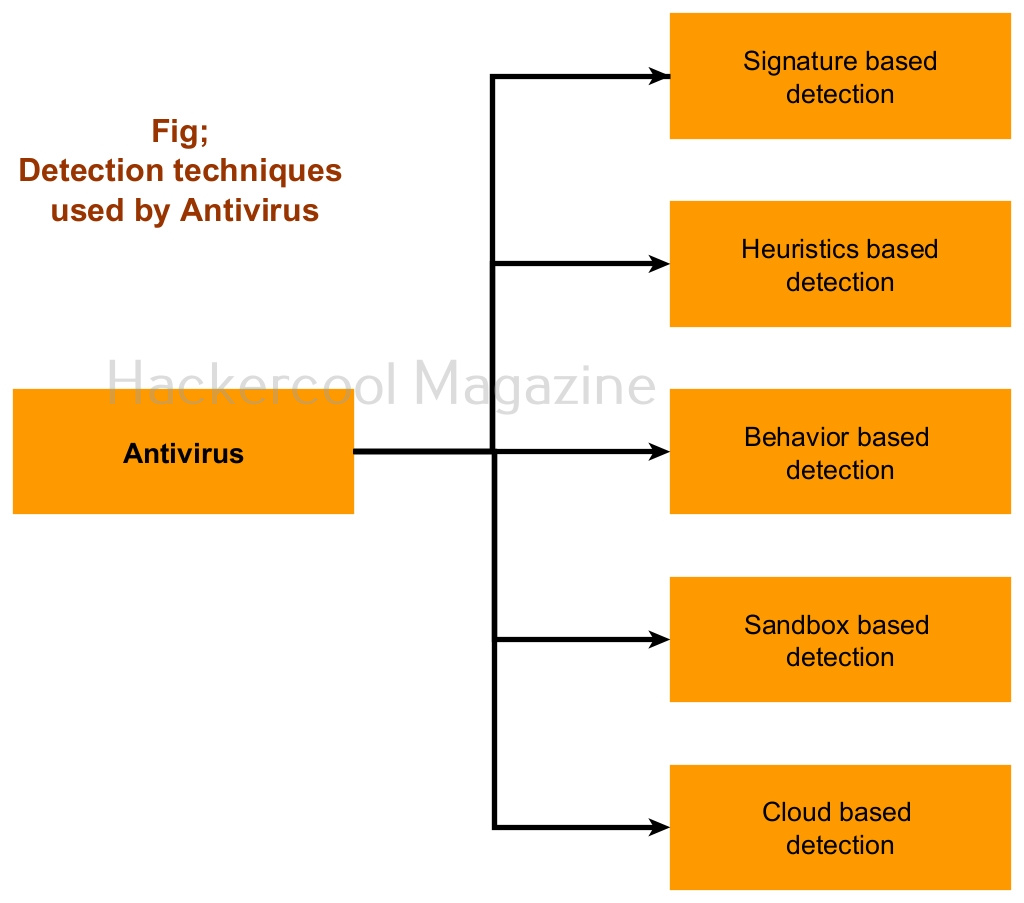
Antivirus, also called as Anti-malware is the software specifically created to detect and stop malware and virus from performing their malicious actions on the computer or mobile. To identify and prevent malware, it uses many techniques. They are,
1. Signature based detection
2. Heuristic based detection
3. Behavior based detection
4. Sandbox based detection
5. Cloud based detection
1. Signature based detection:
This type of AV detects malware by comparing its code with known malware samples. This samples the Anti Malware uses for comparison are known as signatures. These signatures are regularly updated (in most cases, daily) by the anti malware in order to stay one step ahead of malware. This is the reason why antimalware needs regular updates.
2. Heuristics based detection:
The problem with signature based detection is that it can only detect known malware or malware that is around more. To overcome this problem, many of the antivirus nowadays detect malware using heuristic analysis. In this type of analysis, the Antivirus tries to identify malware by examining the code in a virus and analyzing the structure of malware.
By doing this, the antivirus actually tries to simulate running the code and see what it actually does. If it finds any malicious intention in the code like the malware replicating itself or trying to rewrite itself, it classifies the code program as malware. As already mentioned, this is used by almost all modern antimalware.
3. Behavior based detection:
In behavioral detection, the antivirus detects suspicious activity in the operating system. If the AV notices that any new program is trying to modify or make changes to system like altering files or running a code to communicate with external systems, then it flags the program as virus and blocks it. So instead of scanning the code of -the malware, it just scans for any suspicious activity.
4. Sandbox based detection:
In Sandbox detection, the Antivirus classifies a program as malware after executing the program in a contained environment separated from the operating system. This contained environment is known as sandbox. If the program performs any suspicious or malicious activity in the sandbox, the antivirus classifies the program as malware. This method of detection takes a heavy toll on the system resources.
These are the ways in which antivirus can detect malware or payloads we create in penetration testing. There are a few other concepts you need to understand about antivirus.
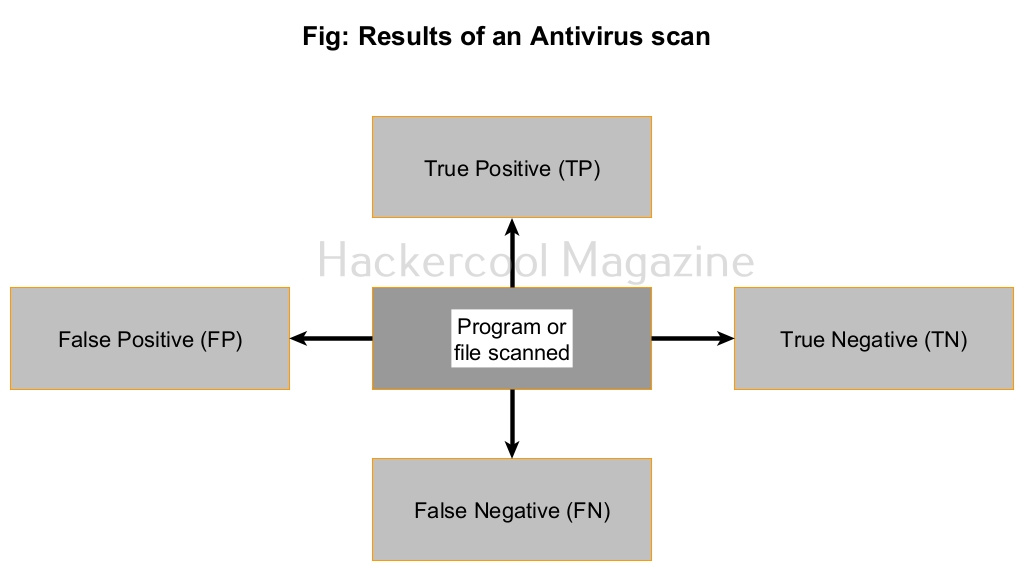
Results of an Antivirus scan
As soon as a new program or file touches the hard disk, the AV scans the file using one or all the methods explained above and concludes. An AV can conclude to any of the four results given below after scanning a file.
- True Positive (TP)
- True Negative (TN)
- False Positive (FP)
- False Negative (FN)
1. True Positive (TP):
When antivirus detects a truly malicious file as malicious, it is called True Positive.
2. True Negative (TN):
When an antivirus doesn’t classify a genuine and harmless file as malicious, it is called as True Negative.
3. False Positive (FP):
When a genuine file is flagged as malicious by the antivirus, it is known as False Positive. False positive is not a problem but becomes a frustration and can also create some problems. For example, in May 2007, Symantec flagged essential operating system files as malicious and deleted them due to faulty virus signatures. This left thousands of PC’s unable to boot. Similarly, in October 2011, Microsoft Security Essentials, mistakenly flagged Google Chrome browser as Zbot banking trojan and removed it.
4. False Negative (FN):
However frustrating and problematic can be a false positive result, the most dangerous result of an Antivirus is False negative. This occurs when an Antivirus fails to identify a malicious program as malicious and flags it as harmless. Black Hat Hacker groups always try to achieve this False negative result while creating their payloads. It is when they get this result in AV’s it is called FUD payload.
Follow Us