Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. In our previous blogpost, you learn what is steganography, its significance and types of steganography to cybersecurity. In this blogpost you will learn in detail about image steganography. But first, let’s see its significance in cybersecurity.
In April 2024, a hacker group being tracked as TA558 has widely used image steganography to deliver malware such as Agent Tesla, FormBook, Remcos RAT, LokiBOT, GuLoader, Snake keylogger and Xworm etc. The malware code embedded in the images contained VBS, PowerShell.
Now that you have understood the importance of image steganography, its time to learn about various images steganography techniques. In cybersecurity, It is a very good thing to learn about various image steganography techniques used to hide data in an image.
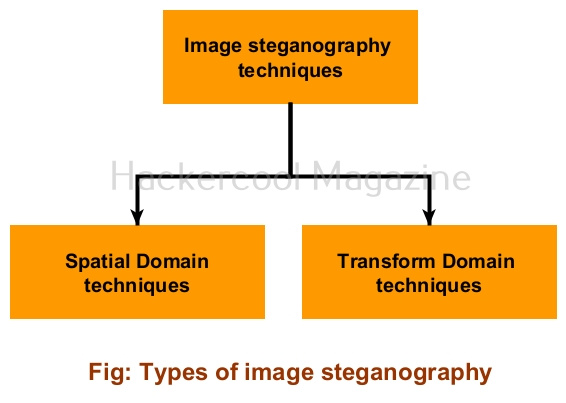
Types of image steganography
Image steganography techniques can be primarily divided into Spatial Domain techniques and Transform Domain techniques.
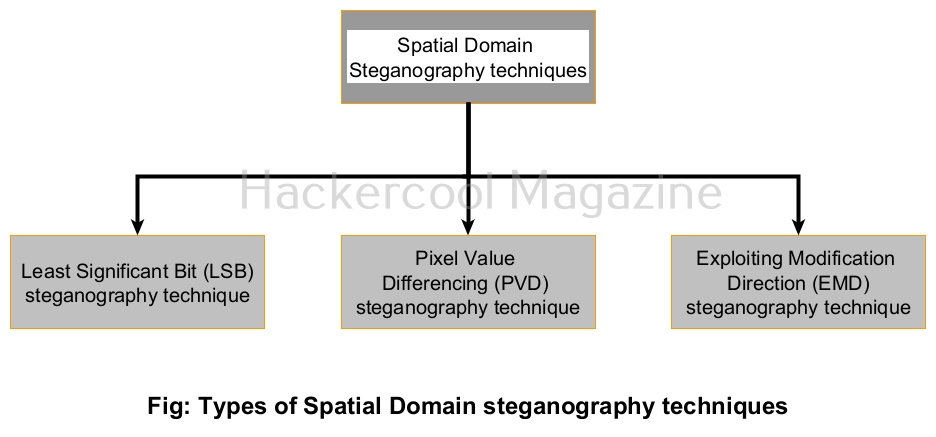
Spatial Domain techniques
Let’s study about various Spatial Domain steganography techniques first.
1. Least Significant Bit (LSB) steganography technique:
In this type of steganographic technique, the secret data is stored in pixels of an image. This is done by replacing the least significant bit of the image.
2. Pixel Value Differencing (PVD) steganography technique:
Pixel Value Differencing (PVD) is a steganography techniques in which secret data is embedded into images using the differences in pixel Value between adjacent pixels.
3. Exploiting Modification Direction (EMD) steganography technique:
In this type of steganographic technique, the secret data is embedded into a group of pixels of an image.
Transform Domain techniques
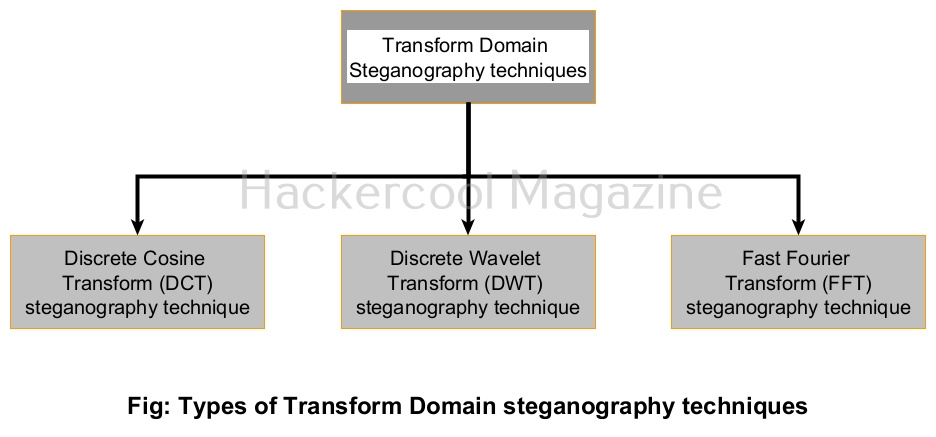
Now let’s learn about various Transform Domain image steganography techniques. In Transform Domain image steganography techniques, secret data is hidden in the transform domain coefficient of an image.
1. Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) steganography technique:
In this steganographic technique, 8*8 blocks of an image are transformed into 64 DCT coefficients. Then, the LSB of each DCT coefficient is replaced with a bit of secret data.
2. Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) steganography technique:
In this steganographic technique, secret data is hidden by modifying the wavelet coefficient of the image.
3. Fast Fourier Transform (FWT) steganography technique:
In this steganography technique, the secret data is expressed as a Fourier series and then coefficients are added to the images.