Hello aspiring Ethical Hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn in detail and clearly about Privilege escalation. Privilege escalation is an act of gaining elevated access to resources that are normally restricted to an application or user. To understand privilege escalation better, you need to first understand about privileges. Since hacking mostly deals with exploiting of operating systems, let me explain you about how privileges in a operating system are assigned.
Since Operating Systems (OS) are meant for user interaction and perform some specific functions you should have noticed that different users are assigned different privileges on a system.
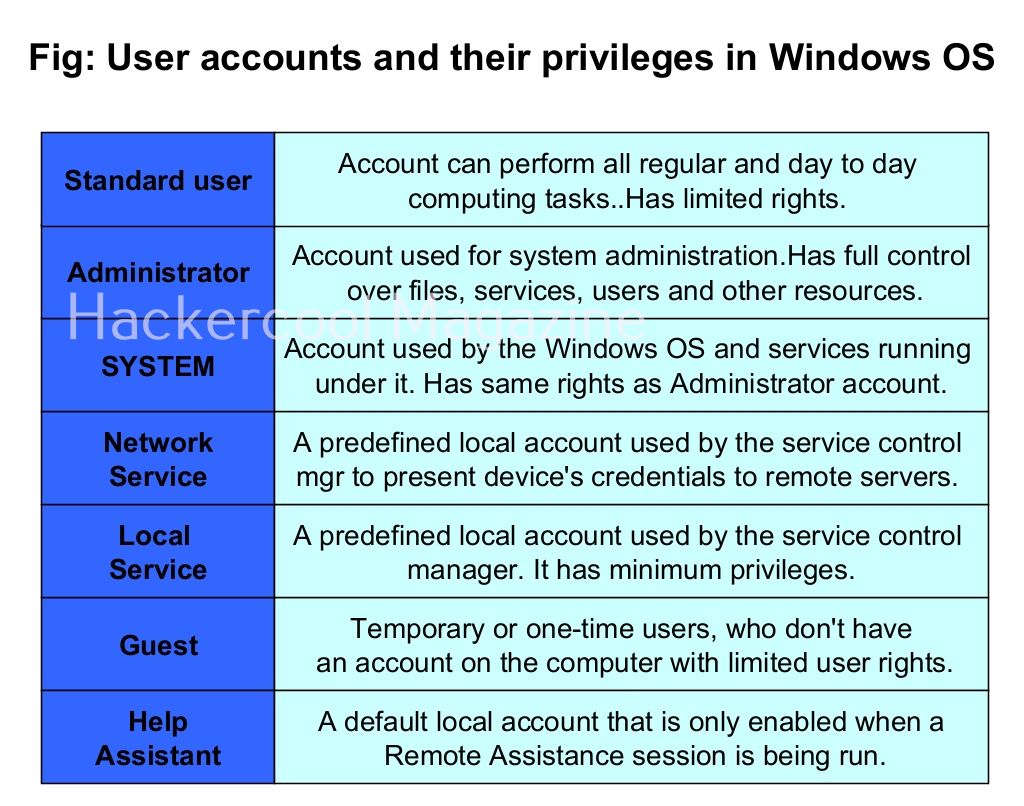
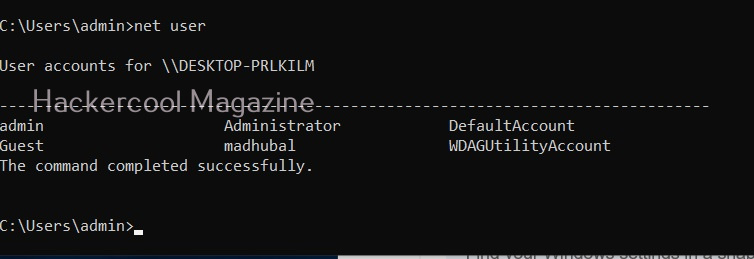
Let’s see the example of the Windows operating system. Windows OS has generally 7 types of accounts. When I am talking about accounts, I am talking about local user accounts instead of remote or online accounts. A local user account is defined locally on a device (computer) and are assigned rights and permissions on that particular device only. The types of Windows user accounts are given below.
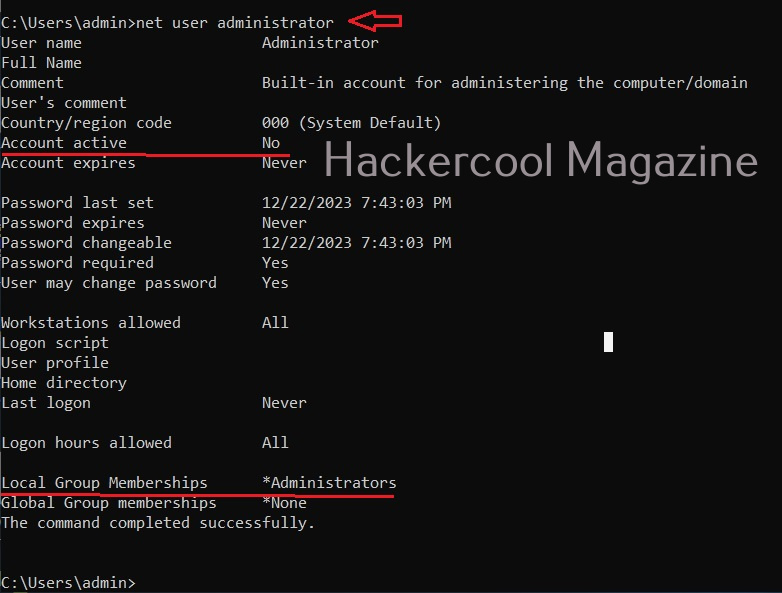
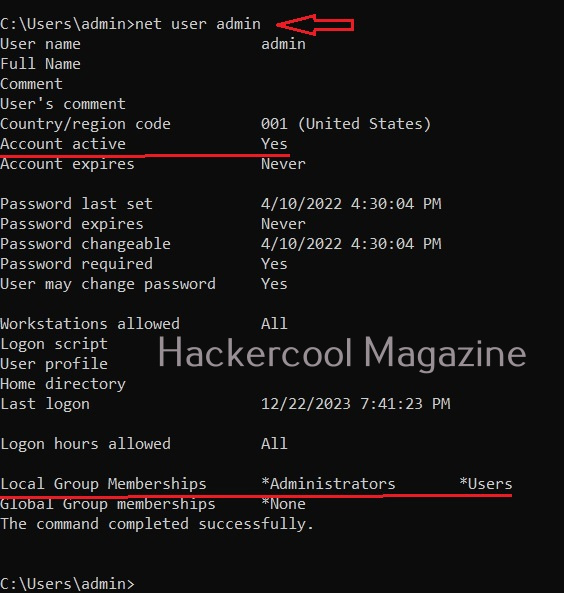
When you do a fresh installation of Windows (Windows 7 to 11), the first user account that is created during setup is the Administrator account, As the name suggests, the Administrator account is a default local user account (account created during Windows installation) used for system administration. This account has full control of the files, directories, services and other resources on the local device. As you might have experienced by now, an administrator account can create, delete and assign permissions to other users.
This default Administrator account can neither be deleted or locked but it can be disabled or renamed. Windows setup disables the built-in administrator account after installation of Windows and creates another local account that is a member of the administrators group.
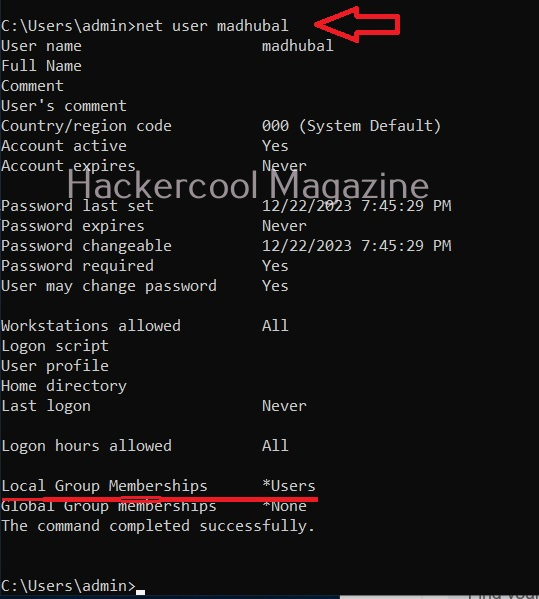
The newly created user belonging to the Administrator group has same powers as the default administrator account. Since this is too risky if some malicious user gains access to the system as Administrator user, Windows provides option to create an account called standard account. Most organization provide their workers a standard account. A standard account on Windows can run almost all application on a Windows system and perform all other day-to-day computing tasks.
However, to perform some tasks like installing programs or applications, making changes to the registry etc and other operations that require elevated privileges, the standard user is asked for credentials of Administrator of the system through the user Account control. Simply put, you cannot make any major changes to the operating system with standard account.
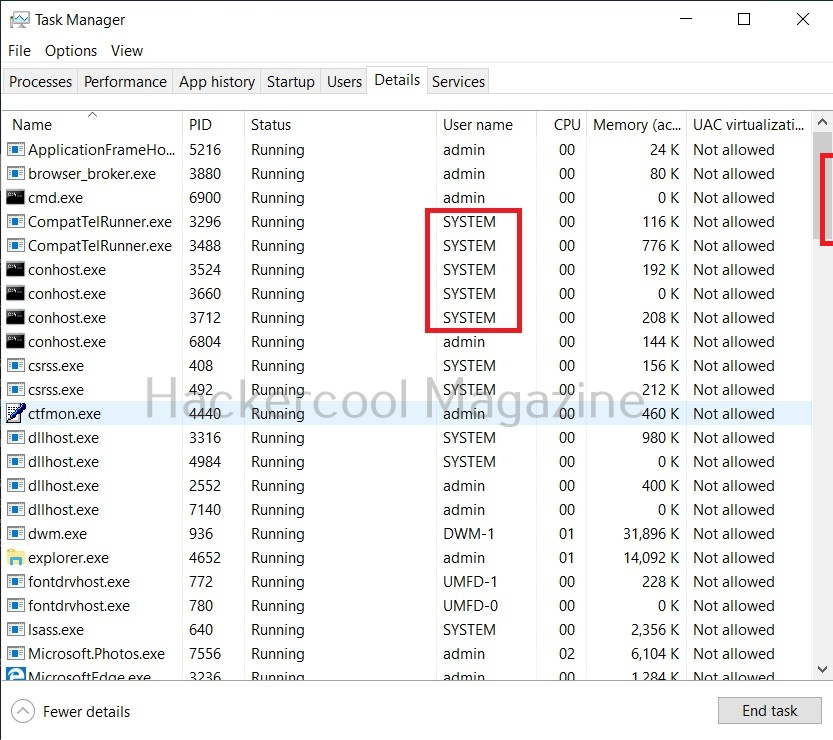
Apart from these two accounts, Windows has some default local user accounts that are automatically created while operating system is installed. They first one you need to learn about is the “SYSTEM” account. This account is used by the operating system and its services running under Windows. This account doesn’t show up in user manager which means you cannot login with this account.
It belongs to Windows and used by all Windows processes. You can view the processes running with this “SYSTEM” privileges from details tab of the Window Task Manager.
The ms08_067 vulnerability affected a process svchost.exe that runs with SYSTEM privileges. So, once you exploit it, you automatically get SYSTEM privileges. It can be exploited remotely and grant SYSTEM PRIVILEGS to attackers. No wonder it is considered very CRITICAL.
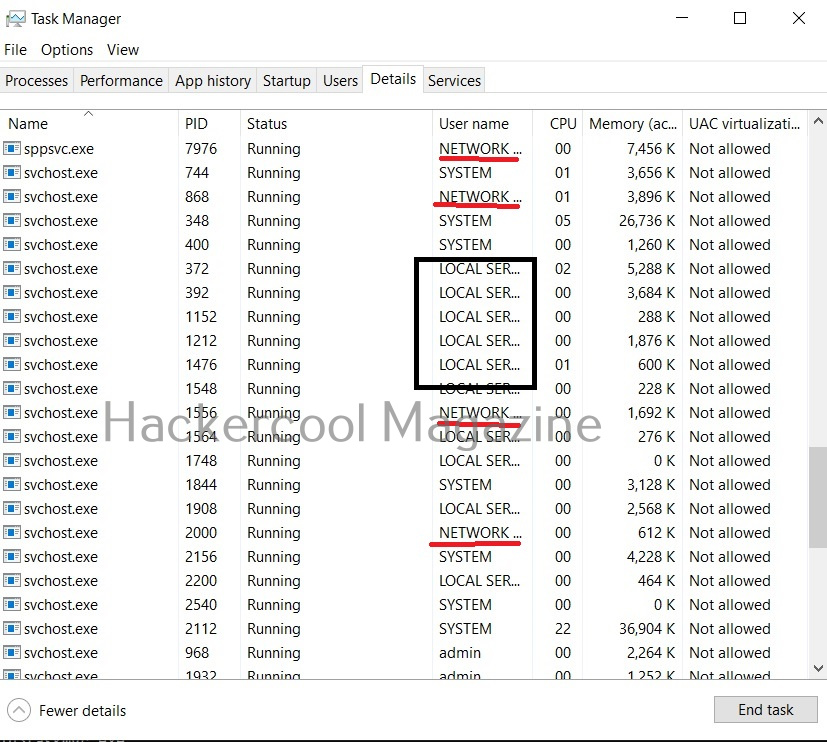
Another local default user account is the “Network service” account. This account is used by the service control manager (SCM). It is used to present the computer credentials while it is communicating with remote servers. Similarly, Windows has an account called “Local Service” which is also used by the service control manager. It has minimum privileges on the local computer.
Linux systems too have different types of user accounts. They are 1) Super user account 2) Regular account 3) System account 4) Service accounts.
On Linux, the Super User account is the most powerful account and is the default administrator of the Linux system. This account is popularly known as root account. The root account has unlimited control on the Linux system and you can literally do anything you want with this account.
The root user in Linux has (#) symbol on their terminal. All other users who are later added are together known as regular accounts. Regular accounts are similar to “standard account” on Windows and to perform administrative actions on the OS, they need to use sudo or su command. Apart from these two accounts, Linux has “system account” and “service account” that are created during the installation of the OS and are by OS processes just like “SYSTEM account on Windows. However, these accounts don’t run with superuser privileges. Service accounts are created whenever a service is installed on the system.
Since you are now accustomed with privileges and user accounts with different privileges, you can now understand privilege escalation.
What is privilege escalation?
Privilege escalation is an act or process of gaining access to privileges of the other user account using any means or techniques. Normally privileges of user account with higher privileges are targeted by hackers.
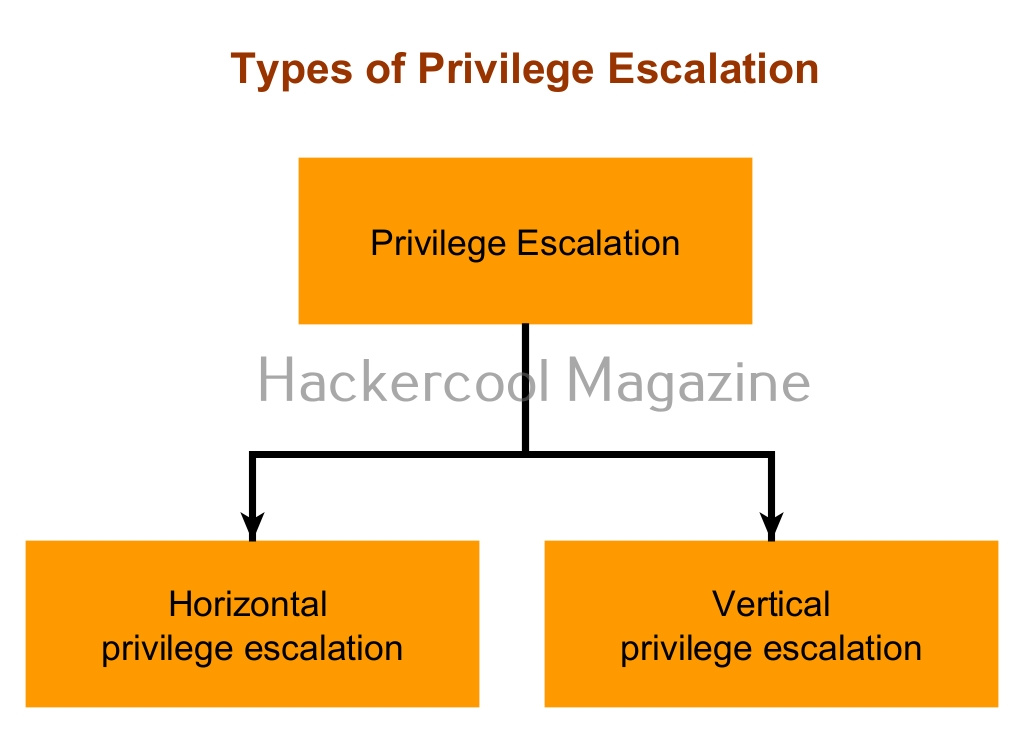
Privilege escalation is of two types: They are,
- Horizontal privilege escalation.
- Vertical privilege escalation.
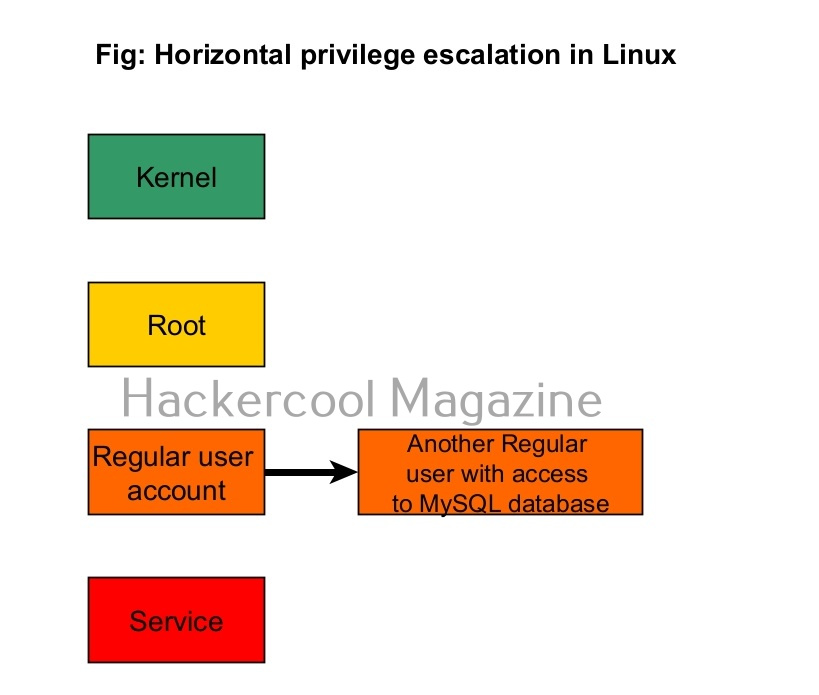
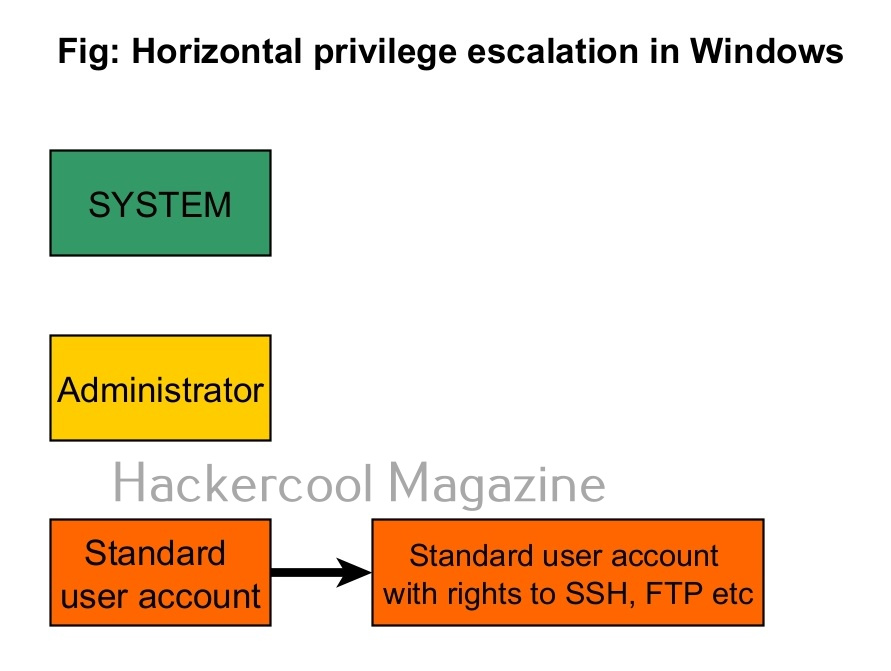
1. Horizontal Privilege Escalation:
In horizontal privilege escalation, an attacker gaining access to the privileges of another user with same rights as him but with access to some other resources. For example, imagine on a Linux system, you gained access as a regular user (user_1). On the same system, there is another regular user (user_2) with same rights as him but with access to the MySQL databases. Elevating privileges to this user (user_2) can give you access to MySQL database.
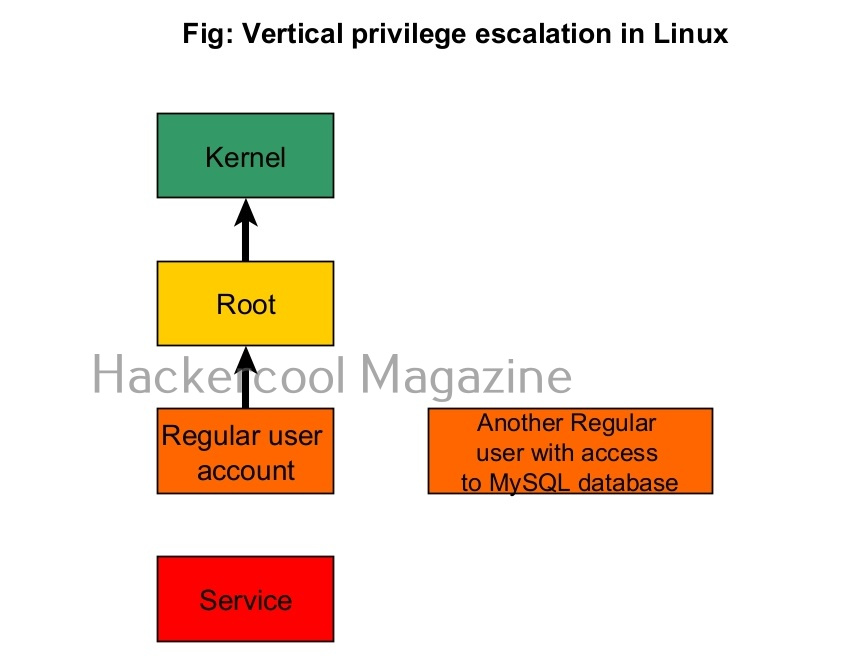
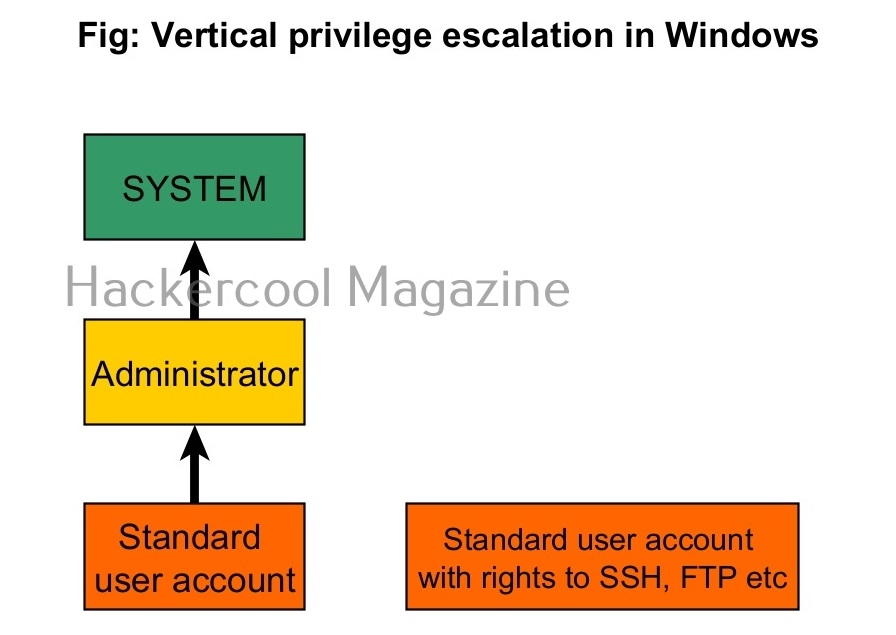
2. Vertical Privilege escalation:
In cyber security or hacking, when anyone says “privilege escalation”, they are talking about this type of privilege escalation most of the time. In vertical privilege escalation, an attacker with low privileges tries to gain access to higher privileges.
Techniques used for Privilege escalation
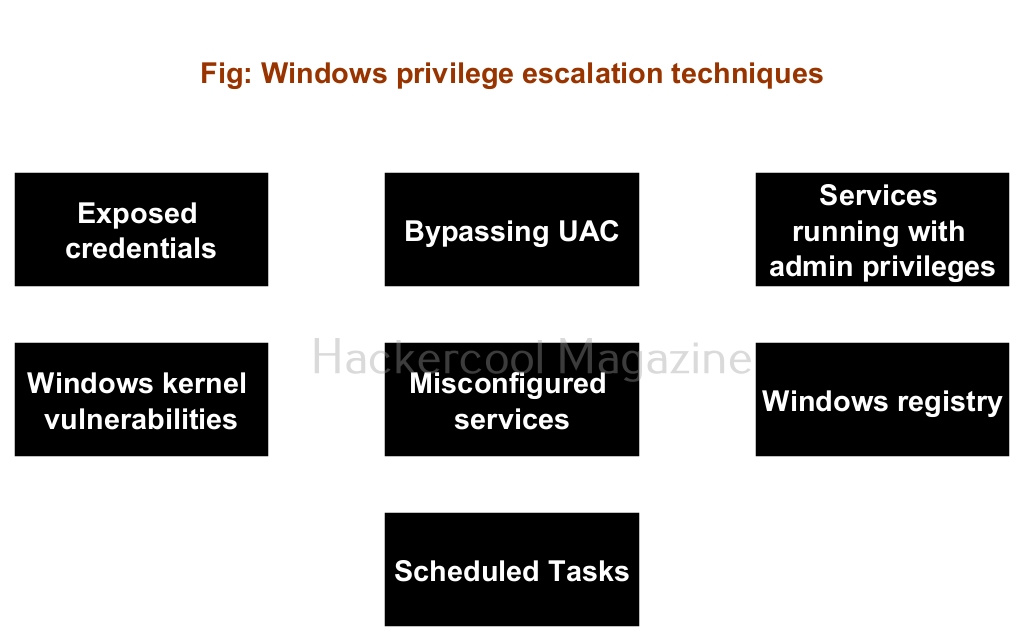
Attackers use various techniques to elevate privileges. Some of the most general techniques are given below.
1. Social Engineering:
In Social Engineering, attackers somehow convince high privileges users to give access their credentials. These techniques include phishing, spear phishing attacks etc. For example, let’s say the attackers gained access to the email of the user with low privileges. From this email, he/she can send an email to the user with high privileges and somehow convince him/her to give any credentials.
In the first week top of September 2023, Okta, a company providing Identity services warned its users of social engineering attacks to obtain super administrator privileges on the organizations using Okta’s services. In these attacks, attackers performed social engineering attacks against IT service desk personnel by calling them and convincing them to reset multi-factor authentication (MFA’s) of high privileged users. Then attackers (allegedly APT Muddled Libra) abused these high privileged super admin accounts to impersonate users of the compromised organizations.
2. Password cracking:
Sometimes attackers crack the passwords of high privileged users to be used in privilege escalation.
3. Exploiting vulnerabilities:
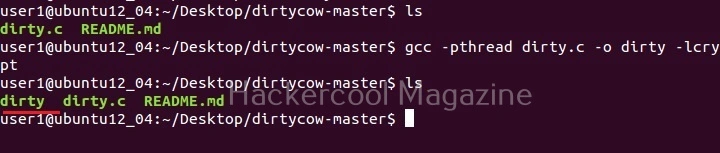
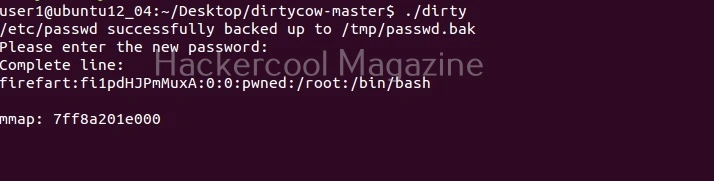
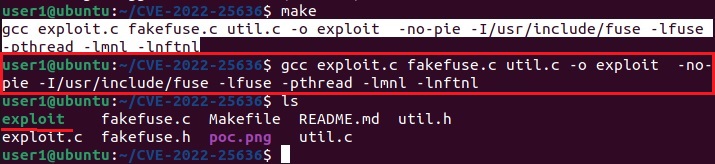
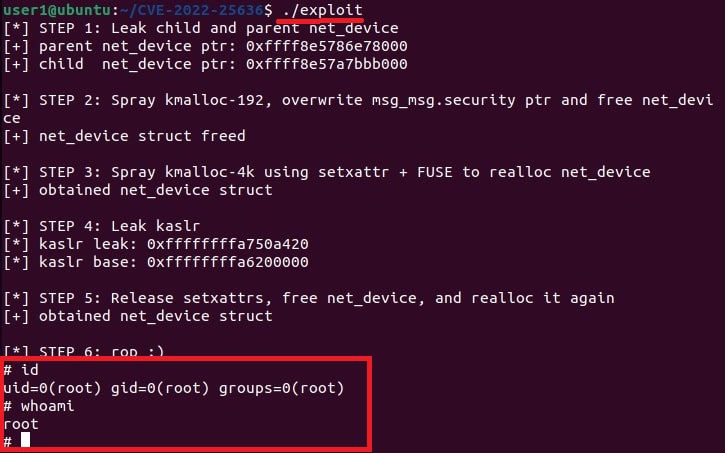
This is one of the popular methods of escalating privileges. In this technique, attackers exploit vulnerability in software installed on the target system to elevate privileges. For example, PrintNightmare, Zerologon, Fodhelper etc in Windows and Dirtypipe, DirtyCow, PWNKIT, Netfilter, Heartbleed and Looney Tunables.
4. Misconfigurations:
In this type of attack, attackers use any misconfiguration on the target system for privilege escalation. These misconfigurations can include weak passwords, setting empty string as password, unsecured network service, open ports and exposed services etc. Examples are exploiting cronjobs and exploiting SetUID bits etc.
Many APT’s and Threat Actors exploit the recently (before patches are applied) released local privilege escalation vulnerabilities to elevate their privileges.