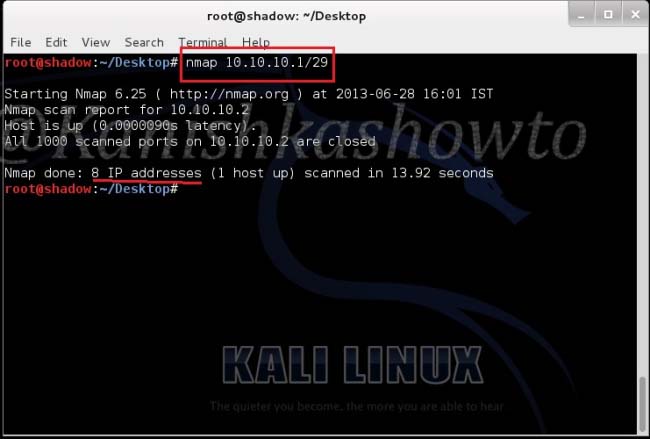
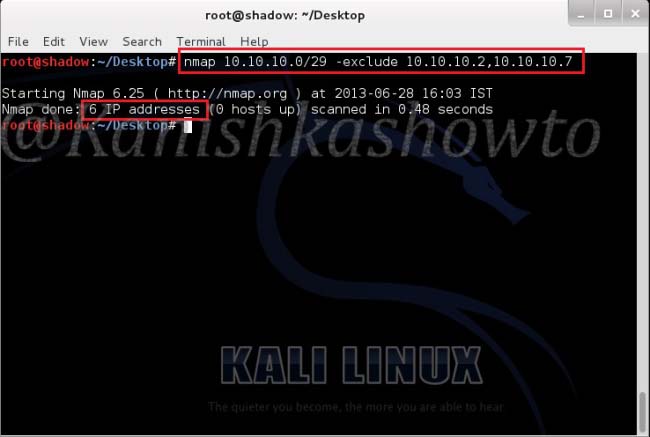
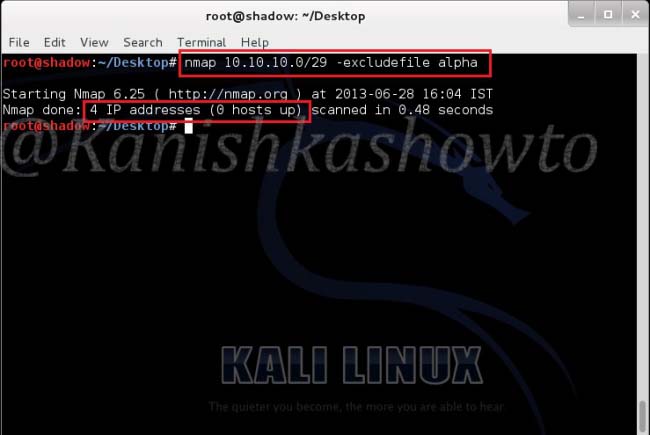
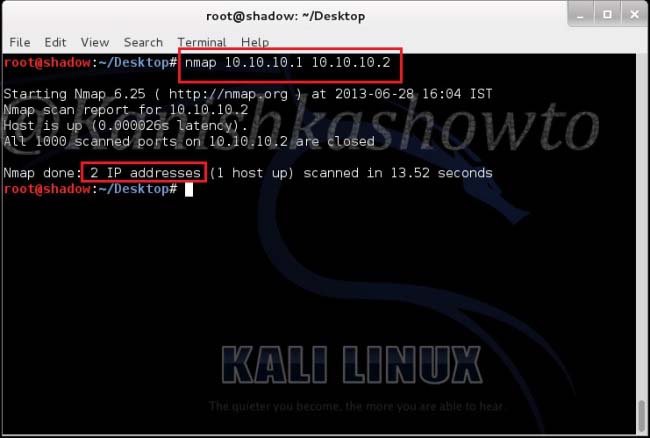
Good evening Friends. Today we will see how to install Veil Evasion in Kali Linux. Although this howto is made on Kali Linux Sana, it is same for all the versions of Kali. For the novices, Veil-Evasion is a tool to generate payload executables that bypass common antivirus solutions. First of all download and save the zip file of veil evasion as shown below from here.
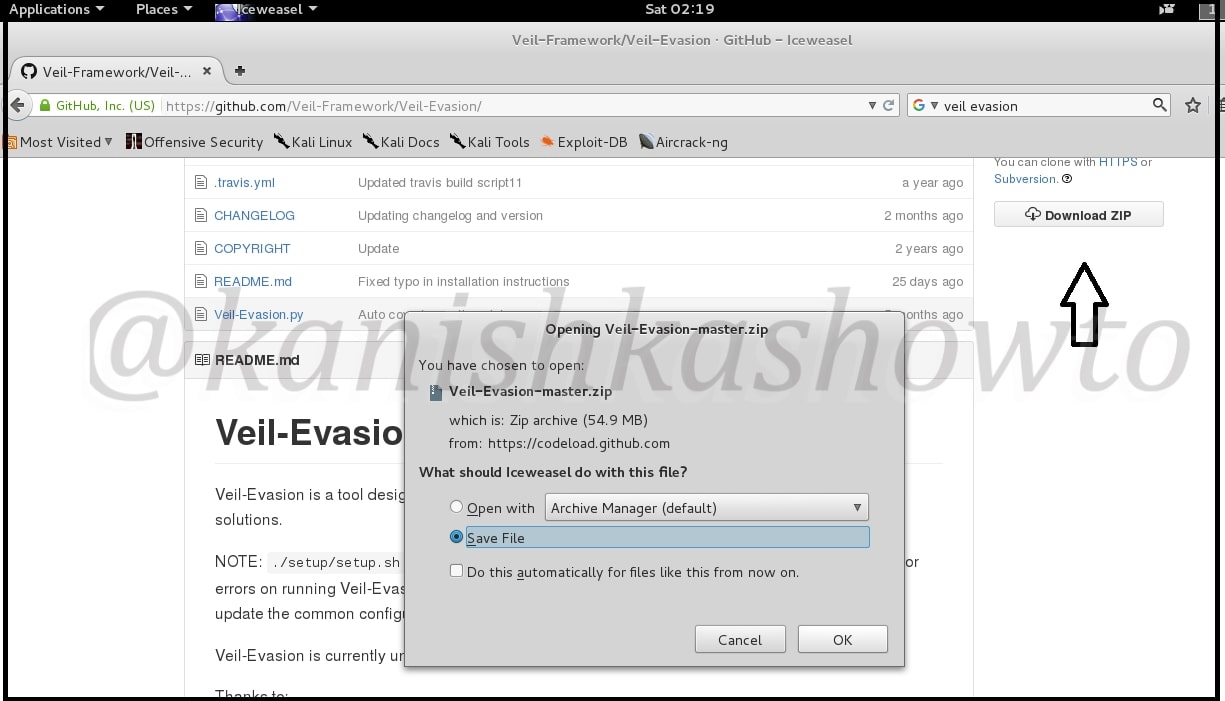
Next, Open terminal and go to the directory where the zip has been downloaded. Commonly it is root or Downloads. Mine is in root. Next unzip the contents of the zip file by using command unzip “Veil-Evasion-master.zip” as shown below.
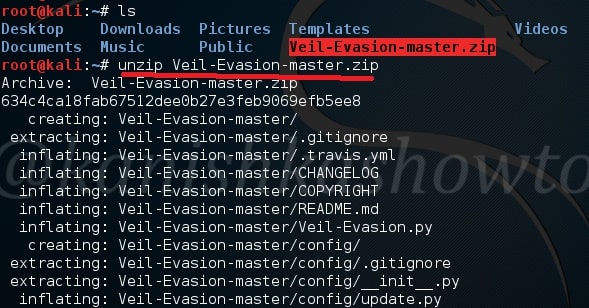
When unzipping is finished, type “ls” command once again. You will see a new directory “Veil-Evasion-master”. Change into that directory as shown below and type “ls” to see the contents of that directory.
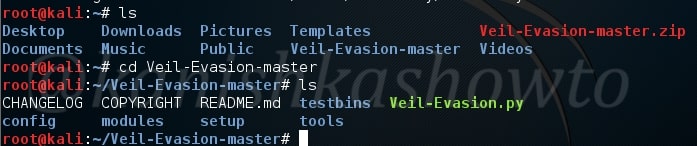
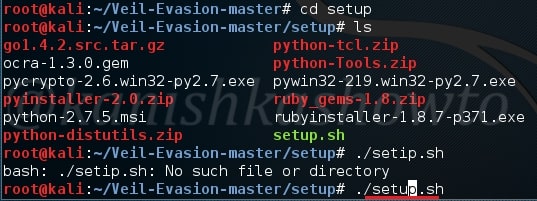
There will be a dircetory named “setup”. Change into that directory. You will see a file named “setup.sh”. Execute that file using command “./setup.sh“
It will prompt you a question whether you want to continue with the installation or not. Type “y”.
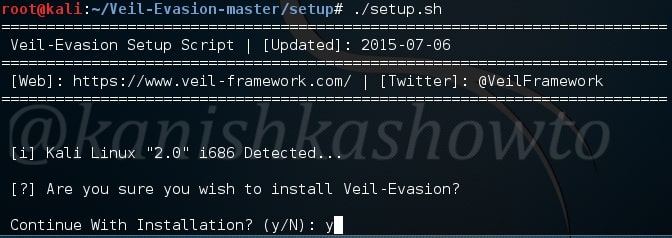
The installation will start. It will ask you whether to install Wine. Click on “Install”.
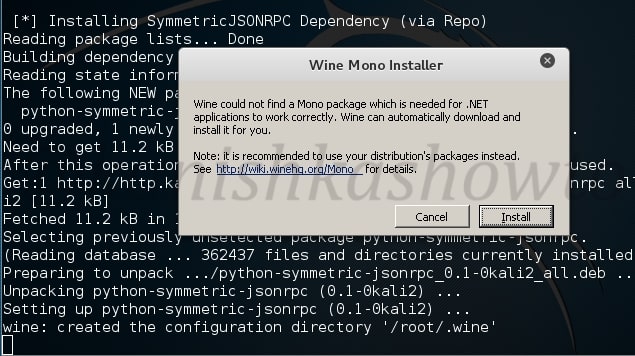
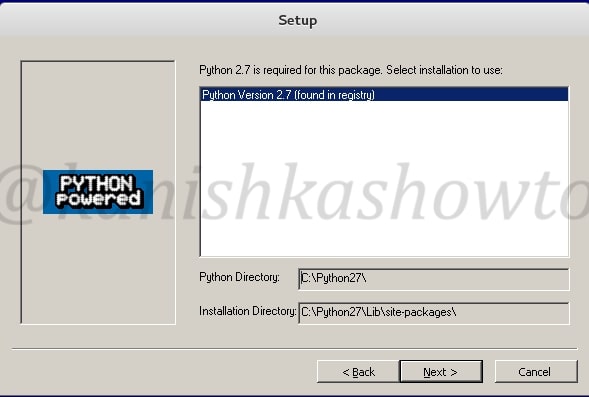
Next it will install Python. Click on “Next”.
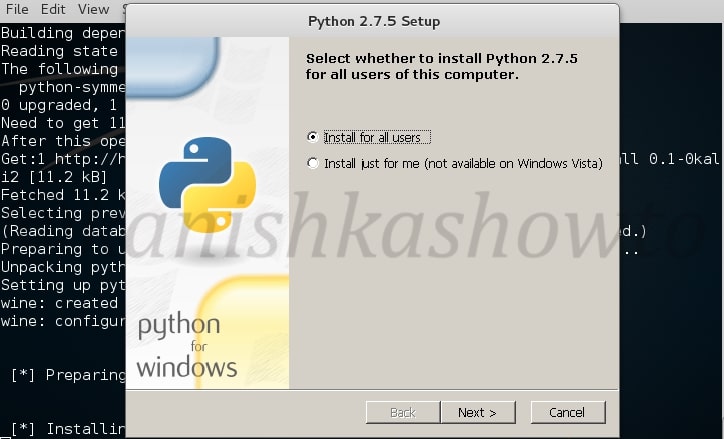
Click on “Next”.
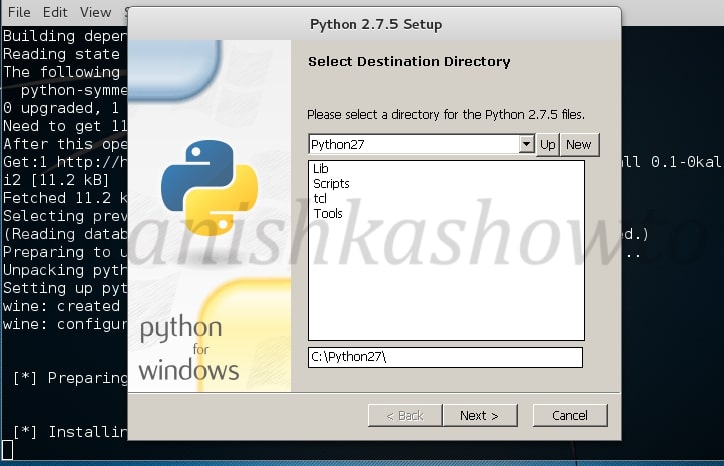
If it asks you to overwrite existing files of any Python, select “yes”.
Click on “Next” for the below window.
Finsih the installation by clicking on “finish”.
Next, the system will ask you to install pywin32. Pywin32 is a set of extension modules that provides access to many of the Windows API functions. Click on “Next”.
Click on “Next”.
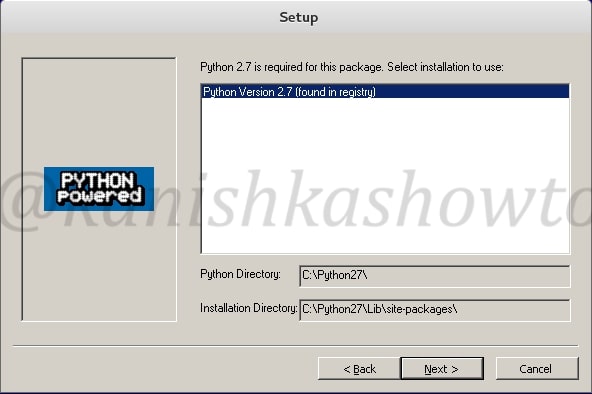
Click on “Next”.
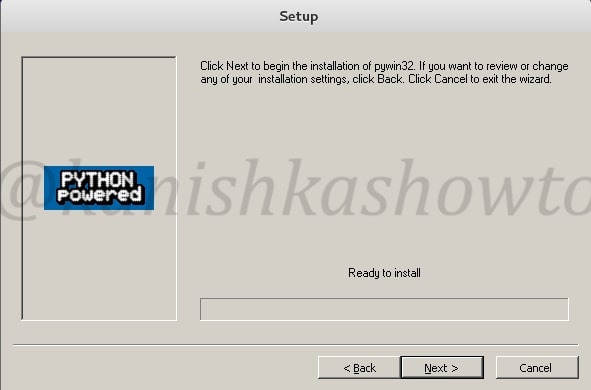
Click on “Finish” the script.
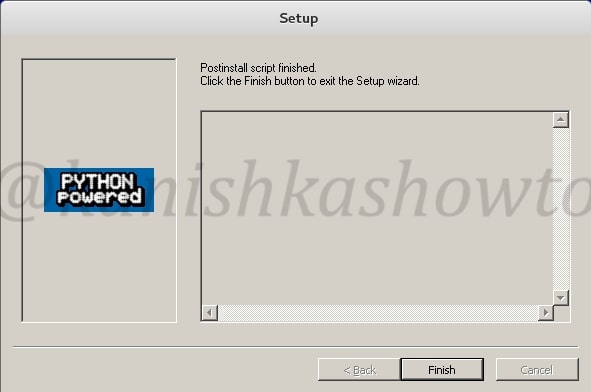
Next it will install pycrypto. Click on “Next”.
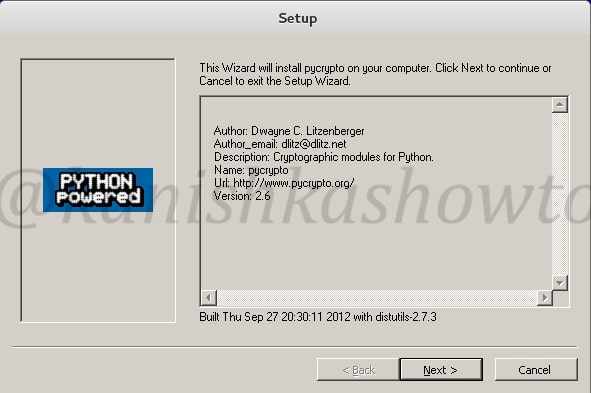
Click On “Next”.
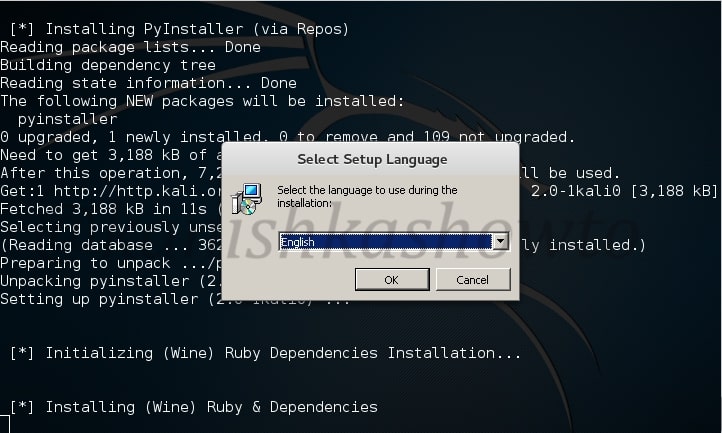
Select language as “English” and click on “OK”.
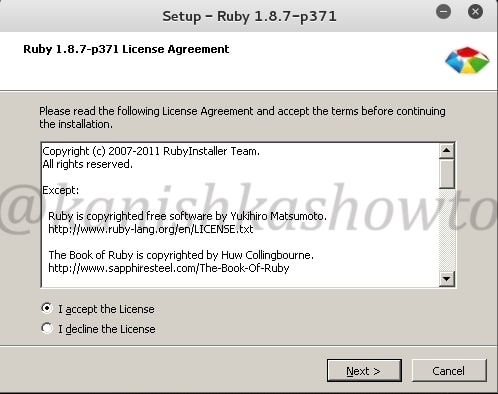
Next it prompt you to install Ruby. Accept the license and click on “Next”.
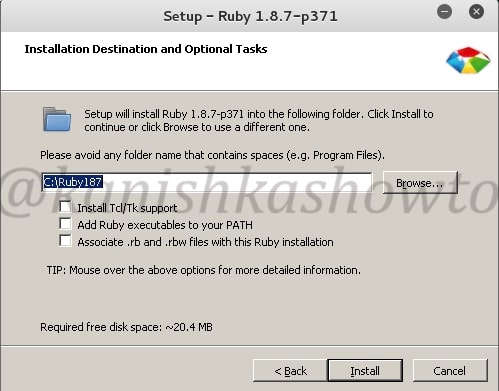
Click on Install.
Click on Finish to to finish the installation of Ruby.
You will see the below screen as the installation finishes.
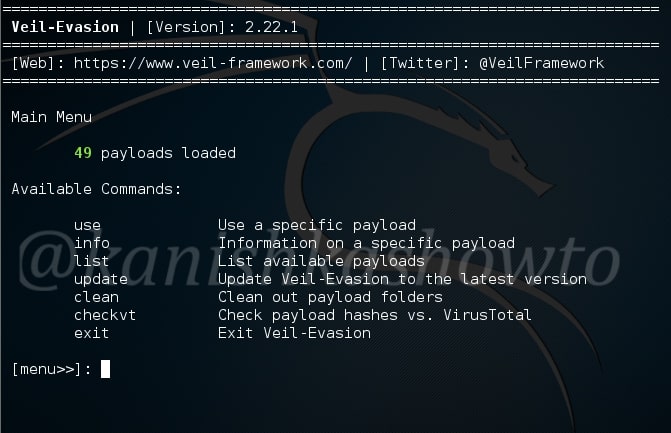
Now let us see if our installation has been successful by starting the program. Go to the “Veil-Evasion-master” directory in which there is a python script called “Veil-Evasion.py”. Execute this script by typing command “./Veil-Evasion.py”.
This is how Veil-Evasion looks when started.