Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. In this blogpost, you will learn about Network Scanning. Network Scanning is the second stage in a Penetration Test and is the first step where an Ethical Hacker directly interacts with the target network.
What is Network Scanning?
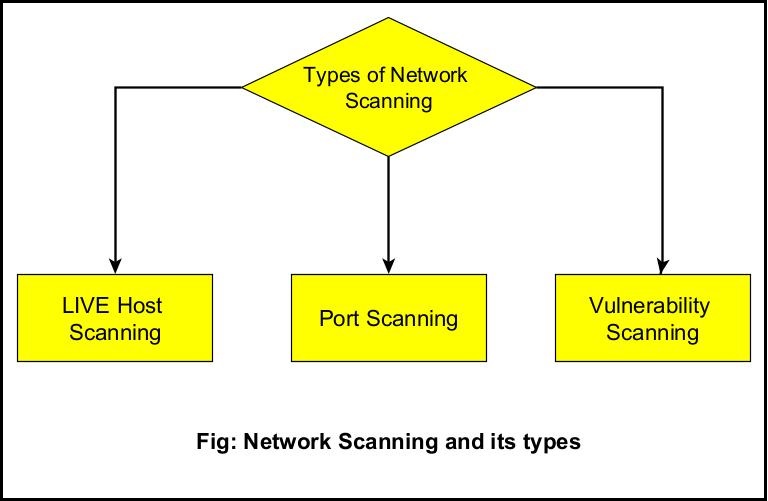
Network scanning is the technique in which the target network is scanned for LIVE systems (Active Systems), open ports and vulnerabilities. Network Scanning is of three types.
They are,
- LIVE Host Scanning or Host Scanning.
- Port Scanning.
- Vulnerability Scanning.
LIVE Host Scanning
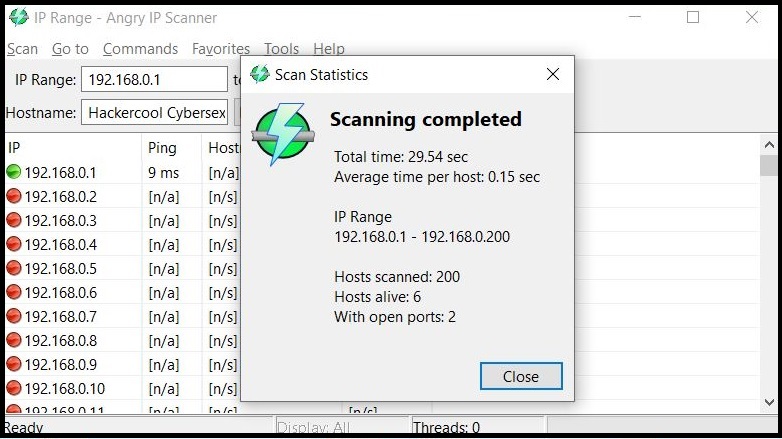
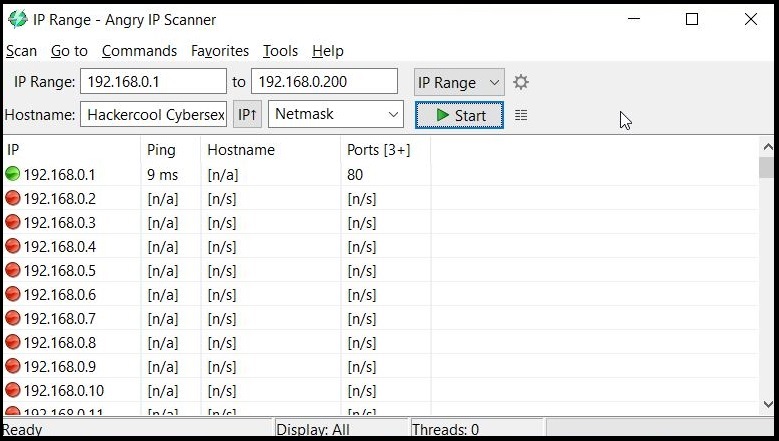
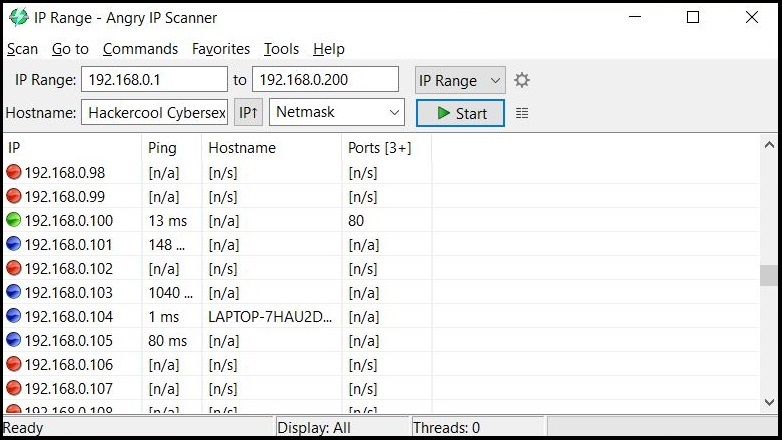
In LIVE Host Scanning, a range of IP addresses (obtained earlier from Network Footprinting) are scanned for LIVE systems or active systems (systems that are turned on) as a system that is shut down is safe from hacking. Network Scanning can be done manually but when we have to scan an entire range of IP addresses, it is best to use a network scanner.
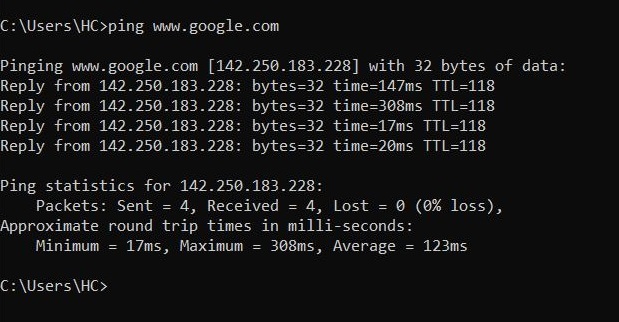
How do network scanners detect if a system is LIVE or not? Although, they use a variety of methods to scan for LIVE systems, one of the most common method any network scanner uses is Ping.
Ping is a network diagnostic tool that helps users determine if a destination system is active or not. Ping works by sending a “echo request” to the target destination IP. If the destination system is LIVE, it will send a “echo reply” message. Ping is available in both Windows and Linux systems. It works by using ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol).
In LIVE Host Scanning, a range of IP addresses (obtained earlier from Network Footprinting) are scanned for LIVE systems or active systems (systems that are turned on) as a system that is shut down is safe from hacking.
Network Scanning can be done manually but when we have to scan an entire range of IP addresses, it is best to use a network scanner.
How do network scanners detect if a system is LIVE or not? Although, they use a variety of methods to scan for LIVE systems, one of the most common method any network scanner uses is Ping.
Ping is a network diagnostic tool that helps users determine if a destination system is active or not. Ping works by sending a “echo request” to the target destination IP. If the destination system is LIVE, it will send a “echo reply” message. Ping is available in both Windows and Linux systems. It works by using ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
Apart from Ping, Network scanners also use ARP scanning to determine if a system is LIVE or not.
2. Port Scanning
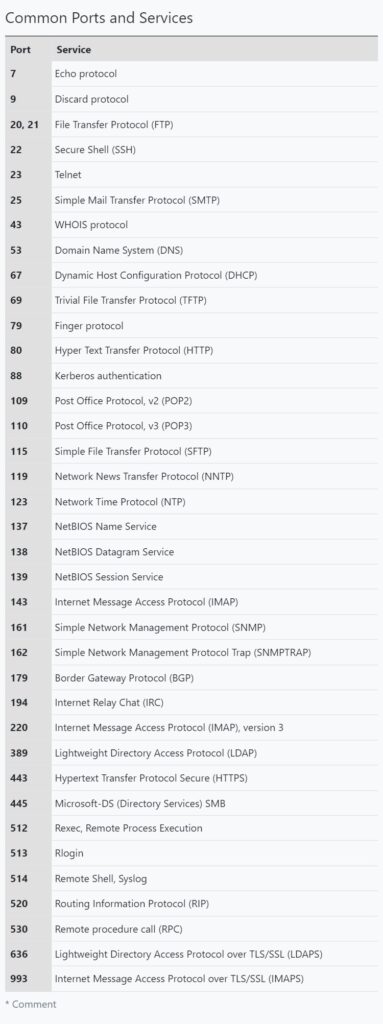
A port is a virtual point where all network connection start and end. Ports are software based virtual addresses where all network connections start and end. Each service is given one separate port and it is managed by the computer’s Operating System. Given below are some important port numbers and services associated with them.
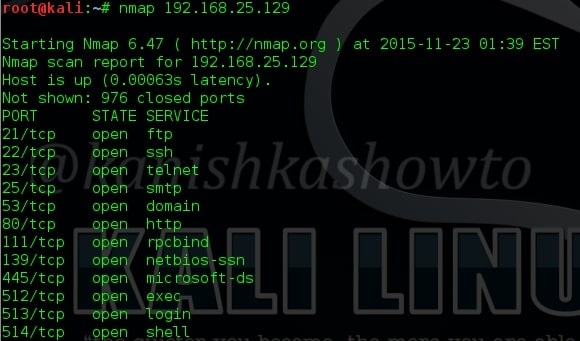
Just like Host scanners, Port scanners are used to perform port scanning. NMAP is the most popular and versatile port scanner. But how does port scanning work. A port scanning sends a TCP or UDP network packet to a specific port to enquire about its status. Learn about Port scan results here. Attackers use various techniques of port scanning before coming to a conclusion about a particular port of interest. Learn about various port scanning techniques here.
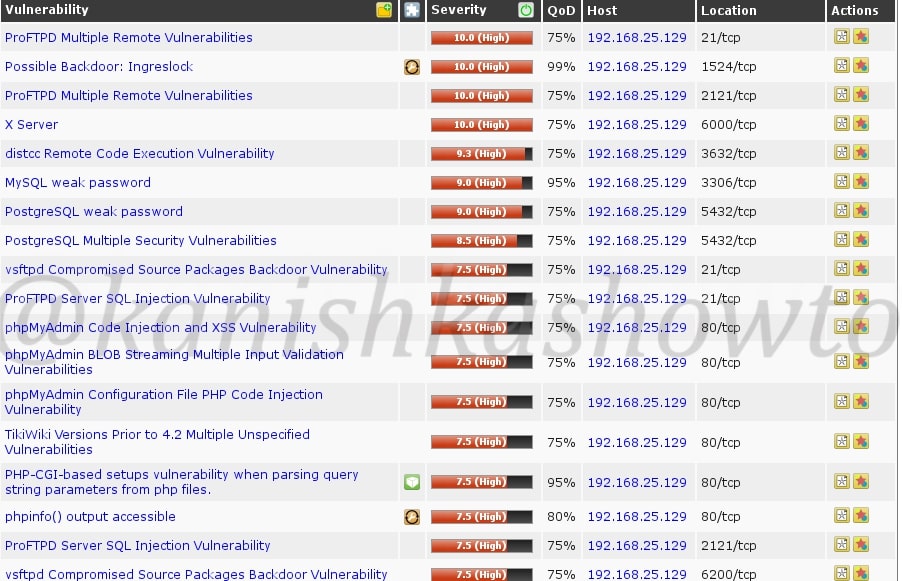
3. Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning identifies vulnerabilities in network, applications and services. A Vulnerability scanner use a database to compare details about version of software running on target system to detect and identify vulnerabilities. This database used by vulnerability scanner has common programming bugs, default credentials, default configurations, common username & passwords etc.
Follow Us