Hello, aspiring Ethical Hackers. In our previous blogpost, you have learnt what is footprinting and various methods to perform footprinting. One such type of Footprinting is Email Footprinting or Email analysis.
What is Email Footprinting?
Email analysis is gathering information from emails. This can be done in two ways. Email Tracing and Email Tracking.
Email Tracking: Email tracking is done when we send an email to a target and then track them.
Email Tracing: Email racing is performed on an email that we receive from our target.
This article deals with Email tracing.
What information does Email Footprinting reveal?
Email Footprinting can reveal information like
- Email address of the sender.
- Name of the sender.
- IP address of the sender
- Posts active sender
- Geo location
- Mail server
- Mail server authentication system being used etc. and much more information that can be useful in a pen test.
How to perform Email Footprintig?
Email Footprinting can be performed either manually or using tools or other online sources. For this blogpost, let’s focus on manual analysis as automated tools can be used by script kiddies too. To perform email footprinting, we need to view the header of the received email. How to view the header of any email? Let’s see an example of a mail received on Gmail. Go to your Inbox and open a mail.
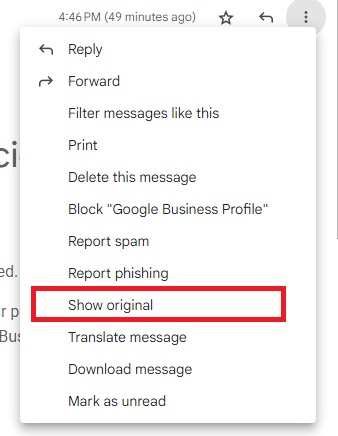
Go to the vertical dots (move button) at the top right of the email and click on it.
Click on “show original”.
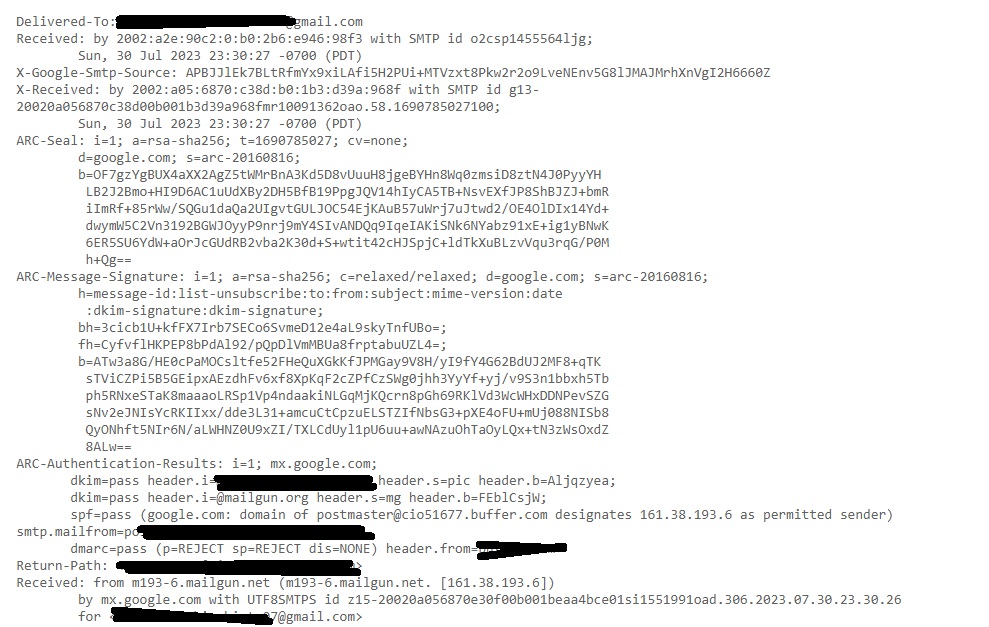
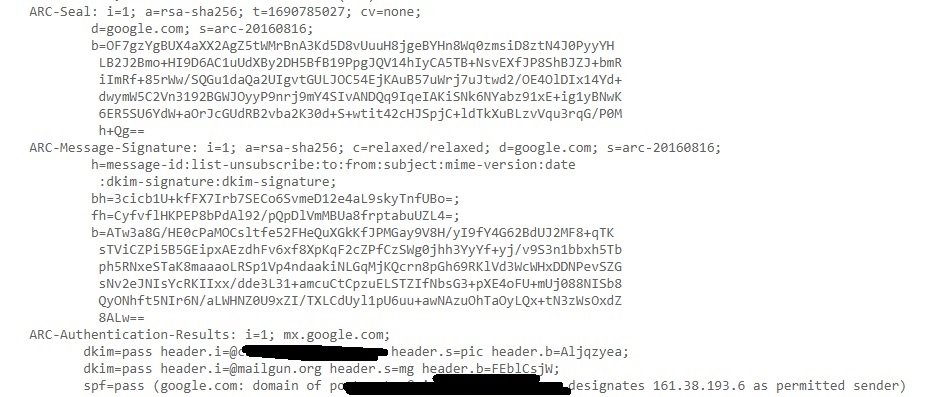
This should show you the entire Email headers of the mail.
Let’s learn about each header.
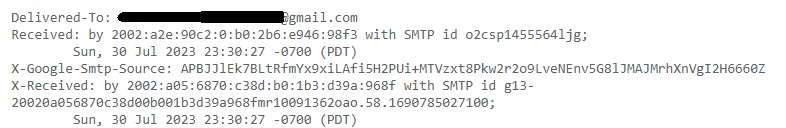
Delivered To: Email address to whom the mail has been delivered.
Received: This header indicates all the SMTP servers through which this email has passed through before reaching to your Inbox. This contains server’s IP address, SMTPID etc.
X-Google-SMTP-source: shows the transferring email using a Gmail SMTP server. If this header is present then it means this was transferred by GMAIL SMTP server.
X-Received-BY: This header indicates the last visited SMTP server before reaching your Inbox. It contains Server IP address, SMTP ID of the visited server and Date & time when the email was received by the SMTP server.
ARC-Seal, ARC-Message-Signature, ARC-Authentication-Results: ARC stands for Authenticated Receiver Chain (ARC). This is used to preserve email authentication results and to verify the identity of email intermediaries that forward a manage to its final destination (i.e. your Inbox).
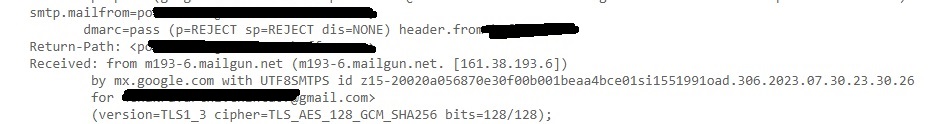
Smtp-mailfrom: You can see the IP address of the sender of the email.
Return-Path: This is the path specified to go when email is bounced or not sent.
Received SPF: SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework. This is used to prevent sender address forgery. It SPF is set to PASS, the Email source is valid, if it is softfail, it is likely the email source is fake and if it is having value Fail, source is invalid.
This is how Email analysis is performed.
Follow Us